Marie Antoinette
| Marie Antoinette | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Portrait by Élisabeth Vigée Le Brun, 1778 | |||||
| Queen consort of France | |||||
| Tenure | 10 May 1774 – 21 September 1792 | ||||
| Born | (1755-11-02)2 November 1755 Hofburg Palace, Vienna, Archduchy of Austria, Holy Roman Empire | ||||
| Died | 16 October 1793(1793-10-16) (aged 37) Place de la Révolution, Paris, French First Republic | ||||
| Burial | 21 January 1815 Basilica of St Denis | ||||
| Spouse | Louis XVI of France (m. 1770; died 1793) | ||||
| Issue |
| ||||
| |||||
| House | Habsburg-Lorraine (by birth) Bourbon (by marriage) | ||||
| Father | Francis I, Holy Roman Emperor | ||||
| Mother | Maria Theresa of Austria | ||||
| Religion | Roman Catholicism | ||||
| Signature | |||||
 Coat of arms of Marie Antoinette of Austria | |||||
Marie Antoinette (/ˌæntwəˈnɛt, ˌɒ̃twə-/;[1]French: [maʁi ɑ̃twanɛt]; born Maria Antonia Josepha Johanna; 2 November 1755 – 16 October 1793) was the last Queen of France before the French Revolution. She was born an Archduchess of Austria and was the penultimate child and youngest daughter of Empress Maria Theresa and Francis I, Holy Roman Emperor. She became Dauphine of France in May 1770 at age 14 upon her marriage to Louis-Auguste, heir apparent to the French throne. On 10 May 1774, her husband ascended the throne as Louis XVI and she assumed the title Queen of France and Navarre, which she held until September 1791, when she became Queen of the French as the French Revolution proceeded, a title that she held until 21 September 1792.
After eight years of marriage, Marie Antoinette gave birth to Marie Thérèse, the first of her four children. A growing percentage of the population came to dislike her, accusing her of being profligate and promiscuous and of harboring sympathies for France's enemies, particularly her native Austria. The Affair of the Diamond Necklace damaged her reputation further. During the Revolution, she became known as Madame Déficit because the country's financial crisis was blamed on her lavish spending and her opposition to the social and financial reforms of Turgot and Necker.
Several events linked to Marie Antoinette during the Revolution, after the government had placed the royal family under house arrest in the Tuileries Palace in October 1789. The June 1791 attempted flight to Varennes and her role in the War of the First Coalition had disastrous effects on French popular opinion. On 10 August 1792, the attack on the Tuileries forced the royal family to take refuge at the Assembly, and they were imprisoned in the Temple Prison on 13 August. On 21 September 1792, the monarchy was abolished. Her trial began on 14 October 1793, and two days later Marie Antoinette was convicted by the Revolutionary Tribunal of high treason and executed by guillotine on the Place de la Révolution.
Contents
1 Early life (1755–70)
2 Dauphine of France (1770–74)
3 Queen of France and Navarre (1774–91)
3.1 Early years (1774–78)
3.2 Motherhood, changes at court, intervention in politics (1778–81)
3.3 Declining popularity (1782–85)
3.4 Prelude to the Revolution: scandals and the failure of reforms (1786–89)
3.4.1 Diamond necklace scandal
3.4.2 Failure of political and financial reforms
4 French Revolution before Varennes (1789–91)
4.1 Mirabeau
4.2 Civil Constitution of the Clergy
5 Flight, arrest at Varennes and return to Paris (21–25 June 1791)
6 Radicalization of the Revolution after Varennes (1791–92)
7 Events leading to the abolition of the monarchy on 10 August 1792
7.1 Louis XVI's trial and execution
8 Marie Antoinette in the Temple
8.1 Conciergerie
9 Trial and execution (14–16 October 1793)
10 Legacy
11 In popular culture
12 Ancestry
13 Children
14 See also
15 References
15.1 Notes
15.2 Bibliography
16 Further reading
17 External links
Early life (1755–70)

Archduchesses Maria Antonia in a pink dress and Maria Carolina in blue (watercolor on ivory by Antonio Pencini, 1764)

Archduchess Maria Antonia (watercolor by Jean-Étienne Liotard, 1762)
Maria Antonia was born on 2 November 1755 at the Hofburg Palace in Vienna, Austria. She was the youngest daughter of Empress Maria Theresa, ruler of the Habsburg Empire, and her husband Francis I, Holy Roman Emperor.[2] Her godparents were Joseph I and Mariana Victoria, King and Queen of Portugal; Archduke Joseph and Archduchess Maria Anna acted as proxies for their newborn sister.[3][4] Shortly after her birth she was placed under the care of the governess of the imperial children, Countess von Brandeis.[5] Maria Antonia was raised together with her sister Maria Carolina, who was three years older, and with whom she had a lifelong close relationship.[6] Maria Antonia had a difficult but ultimately loving relationship with her mother.[7]
Maria Antonia spent her formative years between the Hofburg Palace and Schönbrunn, the imperial summer residence in Vienna,[8] where on 13 October 1762, when she was seven, she met Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, two months her junior and a child prodigy.[9][10][11][12] Despite the private tutoring she received, the results of her schooling were less than satisfactory.[13] At the age of ten she could not write correctly in German or in any language commonly used at court, such as French or Italian,[14] and conversations with her were stilted.[15][16]
Under the teaching of Christoph Willibald Gluck, Maria Antonia developed into a good musician. She learned to play the harp,[13] the harpsichord and the flute. She sang during the family's evening gatherings, as she had a beautiful voice.[17] She also excelled at dancing, had "exquisite" poise, and loved dolls.[18]
Dauphine of France (1770–74)

Marriage of Marie Antoinette with Louis-Auguste celebrated in the Royal Chapel of Versailles by the Archbishop-Duke of Reims on May 16, 1770
Following the Seven Years' War and the Diplomatic Revolution of 1756, Empress Maria Theresa decided to end hostilities with her longtime enemy, King Louis XV of France. Their common desire to destroy the ambitions of Prussia and Great Britain and to secure a definitive peace between their respective countries led them to seal their alliance with a marriage: on 7 February 1770, Louis XV formally requested the hand of Maria Antonia for his eldest surviving grandson and heir, Louis-Auguste, Duke of Berry and Dauphin of France.[19]

Marie Antoinette at the age of thirteen; this miniature portrait was sent to the Dauphin to show him what his future bride looked like (by Joseph Ducreux, 1769)
Maria Antonia formally renounced her rights to Habsburg domains, and on 19 April she was married by proxy to the Dauphin of France at the Augustinian Church in Vienna, with her brother Archduke Ferdinand standing in for the Dauphin.[20][21][22] On 14 May she met her husband at the edge of the forest of Compiègne. Upon her arrival in France, she adopted the French version of her name: Marie Antoinette. A further ceremonial wedding took place on 16 May 1770 in the Palace of Versailles and, after the festivities, the day ended with the ritual bedding.[23][24] The couple's longtime failure to consummate the marriage plagued the reputations of both Louis-Auguste and Marie Antoinette for the next seven years.[25][26]
The initial reaction to the marriage between Marie Antoinette and Louis-Auguste was mixed. On the one hand, the Dauphine was beautiful, personable and well-liked by the common people. Her first official appearance in Paris on 8 June 1773 was a resounding success. On the other hand, those opposed to the alliance with Austria had a difficult relationship with Marie Antoinette, as did others who disliked her for more personal or petty reasons.[27]

Marie Antoinette in hunting attire, one of her mother's favorite portraits of her daughter (by Joseph Krantzinger, 1771)
Madame du Barry proved a troublesome foe to the new dauphine. She was Louis XV's mistress and had considerable political influence over him. In 1770 she was instrumental in ousting Étienne François, duc de Choiseul, who had helped orchestrate the Franco-Austrian alliance and Marie Antoinette's marriage,[28] and in exiling his sister, the duchesse de Gramont, one of Marie Antoinette's ladies-in-waiting. Marie Antoinette was persuaded by her husband's aunts to refuse to acknowledge du Barry, which some saw as a political blunder that jeopardised Austria's interests at the French court. Marie Antoinette's mother and the Austrian ambassador to France, comte de Mercy-Argenteau, who sent the Empress secret reports on Marie Antoinette's behavior, pressured Marie Antoinette to speak to Madame du Barry, which she grudgingly agreed to do on New Year's Day 1772.[29][30] She merely commented to her, "There are a lot of people at Versailles today", but it was enough for Madame du Barry, who was satisfied with this recognition, and the crisis passed.[31] Two days after the death of Louis XV in 1774, Louis XVI exiled du Barry to the Abbaye de Pont-aux-Dames in Meaux, pleasing both his wife and aunts.[32][33][34][35][36] Two and a half years later, at the end of October 1776, Madame du Barry's exile ended and she was allowed to return to her beloved chateau at Louveciennes, but she was never permitted to return to Versailles.[37]

Royal monogram of Marie Antoinette as Queen of France
Early years (1774–78)

Archduke Maximilian Francis of Austria visits Marie Antoinette and Louis XVI on 7 February 1775 at the Château de la Muette (painting by the Austrian portraitist Josef Hauzinger)
Upon the death of Louis XV on 10 May 1774, the Dauphin ascended the throne as King Louis XVI of France and Navarre with Marie Antoinette as his Queen. At the outset, the new queen had limited political influence with her husband, who, with the support of his two most important ministers, Chief Minister Maurepas and Foreign Minister Vergennes, blocked several of her candidates from assuming important positions, including Choiseul.[38][39] The queen did play a decisive role in the disgrace and exile of the most powerful of Louis XV's ministers, the Duke of Aiguillon.[40][41][42]
On 24 May 1774, two weeks after the death of Louis XV, the king gave his wife an estate, the Petit Trianon, and free rein to renovate it; soon rumours circulated that she had plastered the walls with gold and diamonds.[43]

Marie Antoinette dans son salon (by Jean-Baptiste-André Gautier-Dagoty, 1777)
The queen spent heavily on fashion, luxuries and gambling, though the country was facing a grave financial crisis and the population was suffering. Rose Bertin created dresses for her, and hair styles such as poufs, up to three feet (90 cm) high, and the panache (a spray of feather plumes). She and her court also adopted the English fashion of dresses made of indienne (a material banned in France from 1686 until 1759 in order to protect local French woolen and silk industries), percale and muslin.[44][45] By the time of the Flour War of 1775, a series of riots (due to the high price of flour and bread) had damaged her reputation among the general public. Eventually, Marie Antoinette's reputation was no better than that of the favorites of previous kings. Many French people were beginning to blame her for the degrading economic situation, suggesting the country’s inability to pay off its debt was the result of her wasting the crown’s money.[46] In her correspondence, Marie Antoinette's mother, Maria Theresa, expressed concern over her daughter's spending habits, citing the civil unrest it was beginning to cause.[47]
As early as 1774, Marie Antoinette had begun to befriend some of her male admirers, such as the baron de Besenval, the duc de Coigny, and Count Valentin Esterházy,[48][49] and also formed deep friendships with various ladies at court. Most noted was Marie-Louise, princesse de Lamballe, related to the royal family through her marriage into the Penthièvre family. On 19 September 1774 she appointed her superintendent of her household,[50][51] an appointment she soon transferred to her new favourite, the duchesse de Polignac.
In 1774, she took under her patronage her former music teacher, the German opera composer Christoph Willibald Gluck, who remained in France until 1779.[52][53]
Motherhood, changes at court, intervention in politics (1778–81)

Marie Antoinette, Queen of France, en grand habit de cour (by Jean-Baptiste-André Gautier-Dagoty, 1775)
Amidst the atmosphere of a wave of libelles, the Holy Roman Emperor Joseph came to France incognito, using the name Comte de Falkenstein, for a six-week visit during which he toured Paris extensively and was a guest at Versailles. He met his sister and her husband on 18 April 1777 at the château de la Muette, and spoke frankly to his brother-in-law, curious as to why the royal marriage had not been consummated, arriving at the conclusion that no obstacle to the couple's conjugal relations existed save the queen's lack of interest and the king's unwillingness to exert himself.[54] In a letter to his brother Leopold, Joseph described them as "a couple of complete blunderers."[55]
Suggestions that Louis suffered from phimosis, which was relieved by circumcision, have been discredited.[56] Nevertheless, following Joseph's intervention, the marriage was finally consummated in August 1777.[57] Eight months later, in April 1778, it was suspected that the queen was pregnant, which was officially announced on May 16.[58] Marie Antoinette's daughter, Marie-Thérèse Charlotte, Madame Royale, was born at Versailles on 19 December 1778.[7][59][60] The child's paternity was contested in the libelles.[61]
In the middle of the queen's pregnancy two events occurred which had profound impact on her later life: the return of her friend, the Swedish diplomat Count Axel von Fersen to Versailles for two years, and her brother's claim to the throne of Bavaria, contested by the Habsburg monarchy and Prussia.[62] Marie Antoinette pleaded with her husband for the French to intercede on behalf of Austria. The Peace of Teschen, signed on 13 May 1779, ended the brief conflict, with the queen imposing French mediation at her mother's insistence and Austria's gaining a territory of at least 100,000 inhabitants—a strong retreat from the early French position which was hostile towards Austria. This gave the impression, partially justified, that the queen had sided with Austria against France.[63][64]

Marie Antoinette en chemise, portrait of the queen in a "muslin" dress (by Louise Élisabeth Vigée Le Brun, 1783). This controversial portrait was considered by her critics to show improperly informal attire for a queen,[65] whereas a similar portrait in formal dress did not create controversy.
Meanwhile, the queen began to institute changes in court customs. Some of them met with the disapproval of the older generation, such as the abandonment of heavy make-up and the popular wide-hooped panniers[66]. The new fashion called for a simpler feminine look, typified first by the rustic robe à la polonaise style and later by the gaulle, a layered muslin dress Marie Antoinette wore in a 1783 Vigée-Le Brun portrait.[67] In 1780 she began to participate in amateur plays and musicals in a theatre built for her by Richard Mique at the Petit Trianon.[68]
Repayment of the French debt remained a difficult problem, further exacerbated by Vergennes and also by Marie Antoinette's prodding[citation needed] Louis XVI to involve France in Great Britain's war with its North American colonies. The primary motive for the queen's involvement in political affairs in this period may arguably have more to do with court factionalism than any true interest on her part in politics themselves[69], but she played an important role in aiding the American Revolution by securing Austrian and Russian support for France, which resulted in the establishment of a neutral league that stopped Great Britain's attack, and by weighing in decisively for the nomination of Philippe Henri, marquis de Ségur as Minister of War and Charles Eugène Gabriel de La Croix, marquis de Castries as Secretary of the Navy in 1780, who helped George Washington to defeat the British in the American Revolutionary War, which ended in 1783.[70]

The Royal Family of France, 1781. From left to right: The Dukes of Berry and Angoulême with their sister Mademoiselle Sophie, the Countess and Count of Artois, the King and Queen holding the Dauphin with his older sister Madame Royale holding his train, Madame Élisabeth, the Count and Countess of Provence.
In 1783, the queen played a decisive role in the nomination of Charles Alexandre de Calonne, a close friend of the Polignacs, as Controller-General of Finances, and of the baron de Breteuil as the Minister of the Royal Household, making him perhaps the strongest and most conservative minister of the reign.[citation needed] The result of these two nominations was that Marie Antoinette's influence became paramount in government, and the new ministers rejected any major change to the structure of the old regime. More than that, the decree by de Ségur, the minister of war, requiring four quarterings of nobility as a condition for the appointment of officers, blocked the access of commoners to important positions in the armed forces, challenging the concept of equality, one of the main grievances and causes of the French Revolution.[71][72]
Marie Antoinette's second pregnancy ended in a miscarriage early in July 1779, as confirmed by letters between the queen and her mother, although some historians believed that she may have experienced bleeding related to an irregular menstrual cycle, which she mistook for a lost pregnancy.[73] Her third pregnancy was affirmed in March 1781, and on 22 October she gave birth to Louis Joseph Xavier François, Dauphin of France.
Empress Maria Theresa died on 29 November 1780 in Vienna. Marie Antoinette feared that the death of her mother would jeopardise the Franco-Austrian alliance (as well as, ultimately, herself), but her brother, Joseph II, Holy Roman Emperor, wrote to her that he had no intention of breaking the alliance.[74]
A second visit from Joseph II, which took place in July 1781 to reaffirm the Franco-Austrian alliance and also to see his sister, was tainted with rumours that Marie Antoinette was sending money to him from the French treasury .[75][76]
Declining popularity (1782–85)
Despite the general celebration over the birth of the Dauphin, Marie Antoinette's political influence, such as it was, did greatly benefit Austria.[77] During the Kettle War, in which her brother Joseph attempted to open the Scheldt River for naval passage, Marie Antoinette succeeded in obliging Vergennes to pay a huge financial compensation to Austria. Finally, the queen was able to obtain her brother's support against Great Britain in the American Revolution and she neutralized French hostility to his alliance with Russia.[78][79]
In 1782, after the governess of the Enfants de France, the princesse de Guéméné, went bankrupt and resigned, Marie Antoinette appointed her favourite, the duchesse de Polignac, to the position.[80] This decision met with disapproval from the court as the duchess was considered to be of too modest a birth to occupy such an exalted position. On the other hand, both the king and the queen trusted Mme de Polignac completely, gave her a thirteen-room apartment in Versailles and paid her well.[81] The entire Polignac family benefited greatly from royal favour in titles and positions, but its sudden wealth and lavish life style outraged most aristocratic families, who resented the Polignacs' dominance at court, and also fueled the increasing popular disapproval of Marie Antoinette, mostly in Paris.[82] De Mercy wrote to the Empress: "It is almost unexampled that in so short a time, the royal favour should have brought such overwhelming advantages to a family".[83]
In June 1783, Marie Antoinette's new pregnancy was announced, but on the night of 1–2 November, her 28th birthday, she suffered a miscarriage.
Count Axel von Fersen, after his return from America in June 1783, was accepted into the queen's private society. There were and still are claims that the two were romantically involved,[84] but since most of their correspondence has been lost or destroyed, there is no conclusive evidence.[85] In 2016, the Telegraph's Henry Samuel announced that researchers at France’s Research Centre for the Conservation of Collections (CRCC), "using cutting-edge x-ray and different infrared scanners," had deciphered a letter from her that proved the affair.[86]
Around this time, pamphlets describing farcical sexual deviance including the Queen and her friends in the court were growing in popularity around the country. The Portefeuille d’un talon rouge was one of the earliest, including the Queen and a variety of other nobles in a political statement decrying the immoral practices of the court. As time went on, these came to focus more and more on the Queen. They described amorous encounters with a wide range of figures, from the duchesse de Polignac to Louis XV. As these attacks increased, they were connected with the public’s dislike of her association with the rival nation of Austria. It was publicly suggested that her supposed behavior was learned at the court of the rival nation, particularly lesbianism, which was known as the "German vice".[87] Her mother again expressed concern for the safety of her daughter, and she began to use Austria's ambassador to France, comte de Mercy, to provide information on Marie Antoinette's safety and movements.[88]

Le hameau de la reine by the artificial lake in the gardens of the Petit Trianon.
In 1783 the queen was busy with the creation of her "hamlet", a rustic retreat built by her favoured architect, Richard Mique, according to the designs of the painter Hubert Robert.[89] Its creation, however, caused another uproar when its cost became widely known.[90][91] Around this time she accumulated a library of 5000 books. Those on music, often dedicated to her, were the most read, though she also liked to read history.[92][93] She sponsored the arts, in particular music, and also supported some scientific endeavours, encouraging and witnessing the first launch of a Montgolfière, a hot air balloon.[94]
On 27 April 1784, Beaumarchais's play The Marriage of Figaro premiered in Paris. Initially banned by the king due to its negative portrayal of the nobility, the play was finally allowed to be publicly performed because of the queen's support and its overwhelming popularity at court, where secret readings of it had been given by Marie Antoinette. The play was a disaster for the image of the monarchy and aristocracy. It inspired Mozart's Le nozze di Figaro, which premiered in Vienna on 1 May 1786.[95]
On 24 October 1784, putting the baron de Breteuil in charge of its acquisition, Louis XVI bought the Château de Saint-Cloud from the duc d'Orléans in the name of his wife. This was unpopular, particularly with those factions of the nobility who disliked the queen, but also with a growing percentage of the population, who disapproved of a Queen of France independently owning a private residence. The purchase of Saint-Cloud thus damaged the public's image of the queen even further. The château's high price, almost 6 million livres, plus the substantial extra cost of redecorating, ensured that much less money was going towards repaying France's substantial debt.[96][97]
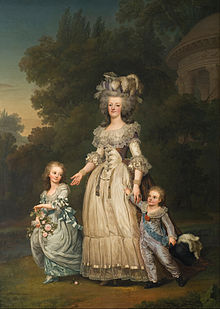
Marie Antoinette with her two eldest children, Marie-Thérèse Charlotte and the Dauphin Louis Joseph, in the gardens of the Petit Trianon (by Adolf Ulrik Wertmüller, 1785)
On 27 March 1785, Marie Antoinette gave birth to a second son, Louis Charles, who bore the title of Duke of Normandy.[98] The fact that the birth occurred exactly nine months after Fersen's return did not escape the attention of many, leading to doubt as to the parentage of the child and to a noticeable decline of the queen's reputation in public opinion.[99] The majority of Marie Antoinette's and Louis XVII's biographers believe that the young prince was the biological son of Louis XVI, including Stefan Zweig and Antonia Fraser, who believe that Fersen and Marie Antoinette were indeed romantically involved.[100][101][102][103][104][105][106][107] Courtiers at Versailles noted in their diaries that the date of the child's conception in fact corresponded perfectly with a period when the king and the queen had spent much time together, but these details were ignored amid attacks on the queen's character.[108] These suspicions of illegitimacy, along with the continued publication of the libelles and never-ending cavalcades of court intrigues, the actions of Joseph II in the Kettle War, the purchase of Saint-Cloud, and the Affair of the Diamond Necklace combined to turn popular opinion sharply against the queen, and the image of a licentious, spendthrift, empty-headed foreign queen was quickly taking root in the French psyche.[109]
A second daughter, her last child, Marie Sophie Hélène Béatrix, Madame Sophie, was born on 9 July 1786 and lived only eleven months until 19 June 1787.
Marie Antoinette's four live-born children were:
Marie-Thérèse-Charlotte, Madame Royale (19 December 1778 – 19 October 1851)
Louis-Joseph-Xavier-François, Dauphin (22 October 1781 – 4 June 1789)
Louis-Charles, Dauphin after the death of his elder brother, future titular king Louis XVII of France (27 March 1785 – 8 June 1795)
Sophie-Hélène-Béatrix, died in infancy (9 July 1786 – 19 June 1787)
Prelude to the Revolution: scandals and the failure of reforms (1786–89)
Diamond necklace scandal

Copy of the diamond necklace, Le Collier de la Reine, at Château de Breteuil
Marie Antoinette began to abandon her more carefree activities to become increasingly involved in politics in her role as Queen of France.[110] By publicly showing her attention to the education and care of her children, the queen sought to improve the dissolute image she had acquired in 1785 from the "Diamond Necklace Affair", in which public opinion had falsely accused her of criminal participation in defrauding the jewelers Boehmer and Bassenge of the price of an expensive diamond necklace they had originally created for Madame du Barry. The main actors in the scandal were Cardinal de Rohan, prince de Rohan-Guéméné, Great Almoner of France, and Jeanne de Valois-Saint-Rémy, comtesse de La Motte, a descendant of an illegitimate child of Henry II of France of the House of Valois. Marie Antoinette had profoundly disliked Rohan since the time he had been the French ambassador to Vienna when she was a child. Despite his high clerical position at the Court, she never addressed a word to him. Others involved were Nicole Lequay, alias Baronne d'Oliva, a prostitute who happened to look like Marie Antoinette; Rétaux de Villette, a forger; Alessandro Cagliostro, an Italian adventurer; and the comte de La Motte, Jeanne de Valois' husband. Mme de La Motte tricked Rohan into buying the necklace as a gift to Marie Antoinette, in order for him to gain the queen's favor.
When the affair was discovered, those involved (except de La Motte and Réaux de Villette, who both managed to flee) were arrested, tried, convicted, and either imprisoned or exiled. Mme de La Motte was sentenced for life to confinement in the Pitié-Salpêtrière Hospital, which also served as a prison for women. Judged by the Parlement, Rohan was found innocent of any wrongdoing and allowed to leave the Bastille. Marie Antoinette, who had insisted on the arrest of the Cardinal, was dealt a heavy personal blow, as was the monarchy, and despite the fact that the guilty parties were tried and convicted, the affair proved to be extremely damaging to her reputation, which never recovered from it.[citation needed]
Failure of political and financial reforms
Suffering from an acute case of depression, the king began to seek the advice of his wife. In her new role and with increasing political power, the queen tried to improve the awkward situation brewing between the assembly and the king.[111] This change of the queen's position signalled the end of the Polignacs' influence and their impact on the finances of the Crown.

Miniature of Marie Antoinette (by Louis Marie Sicard, 1787)
Continuing deterioration of the financial situation despite cutbacks to the royal retinue and court expenses ultimately forced the king, the queen and the Minister of Finance, Calonne, at the urging of Vergennes, to call a session of the Assembly of Notables, after a hiatus of 160 years. The assembly was held for the purpose of initiating necessary financial reforms, but the Parlement refused to cooperate. The first meeting took place on 22 February 1787, nine days after the death of Vergennes on 13 February. Marie Antoinette did not attend the meeting and her absence resulted in accusations that the queen was trying to undermine its purpose.[112][113] The Assembly was a failure. It did not pass any reforms and, instead, fell into a pattern of defying the king. On the urging of the queen, Louis XVI dismissed Calonne on 8 April 1787.[111]
On 1 May 1787, Étienne Charles de Loménie de Brienne, archbishop of Toulouse and one of the queen's political allies, was appointed by the king at her urging to replace Calonne, first as Controller-General of Finances and then as Prime Minister. He began to institute more cutbacks at court, while trying to restore the royal absolute power weakened by parliament.[114] Brienne was unable to improve the financial situation, and since he was the queen's ally, this failure adversely affected her political position. The continued poor financial climate of the country resulted in the 25 May dissolution of the Assembly of Notables because of its inability to function, and the lack of solutions was blamed on the queen.[115]
France's financial problems were the result of a combination of factors: several expensive wars; a large royal family whose expenditures were paid for by the state; and an unwillingness on the part of most members of the privileged classes, aristocracy and clergy, to help defray the costs of the government out of their own pockets by relinquishing some of their financial privileges. As a result of the public perception that she had single-handedly ruined the national finances, Marie Antoinette was given the nickname of "Madame Déficit" in the summer of 1787.[116] While the sole fault for the financial crisis did not lie with her, Marie Antoinette was the biggest obstacle to any major reform effort. She had played a decisive role in the disgrace of the reformer ministers of finance, Turgot (in 1776), and Jacques Necker (first dismissal in 1781). If the secret expenses of the queen were taken into account, court expenses were much higher than the official estimate of 7% of the state budget.[117]

This State Portrait of Marie Antoinette and her three surviving children, Marie Thérèse, Louis Charles (on her lap), and Louis Joseph holding up the drape of an empty bassinet signifying the recent death of Marie's fourth child, Sophie, was meant to improve her reputation by depicting her as a mother in simple, yet stately attire (by Vigée-Lebrun, 1787).
The queen attempted to fight back with propaganda portraying her as a caring mother, most notably in the painting by Élisabeth Vigée Le Brun exhibited at the Royal Académie Salon de Paris in August 1787, showing her with her children.[118][119] Around the same time, Jeanne de Valois-Saint-Rémy escaped from prison and fled to London, where she published damaging slander concerning her supposed amorous affair with the queen.[120]
The political situation in 1787 worsened when, at Marie Antoinette's urging, the Parlement was exiled to Troyes on 15 August. It further deteriorated when Louis XVI tried to use a lit de justice on 11 November to impose legislation. The new duc d'Orléans publicly protested the king's actions, and was subsequently exiled to his estate at Villers-Cotterêts.[121] The May Edicts issued on 8 May 1788 were also opposed by the public and parliament. Finally, on 8 August, Louis XVI announced his intention to bring back the Estates General, the traditional elected legislature of the country, which had not been convened since 1614.[122]
While from late 1787 up to his death in June 1789, Marie Antoinette's primary concern was the continued deterioration of the health of the Dauphin, who suffered from tuberculosis,[123] she was directly involved in the exile of the Parlement, the May Edicts, and the announcement regarding the Estates General. She did participate in the King Council, the first queen to do this in over 175 years (since Marie de' Medici had been named Chef du Conseil du Roi, between 1614 and 1617), and she was making the major decisions behind the scene and in the Royal Council.
Marie Antoinette was instrumental in the reinstatement of Jacques Necker as Finance Minister on 26 August, a popular move, even though she herself was worried that it would go against her if Necker proved unsuccessful in reforming the country's finances. She accepted Necker's proposition to double the representation of the Third Estate (tiers état) in an attempt to check the power of the aristocracy.[124][125]
On the eve of the opening of the Estates General, the queen attended the mass celebrating its return. As soon as it opened on 5 May 1789, the fracture between the democratic Third Estate (consisting of bourgeois and radical aristocrats) and the conservative nobility of the Second Estate widened, and Marie Antoinette knew that her rival, the duc d'Orléans, who had given money and bread to the people during the winter, would be acclaimed by the crowd, much to her detriment.[126]
The death of the Dauphin on 4 June, which deeply affected his parents, was virtually ignored by the French people,[127] who were instead preparing for the next meeting of the Estates General and hoping for a resolution to the bread crisis. As the Third Estate declared itself a National Assembly and took the Tennis Court Oath, and as people either spread or believed rumors that the queen wished to bathe in their blood, Marie Antoinette went into mourning for her eldest son.[128] Her role was decisive in urging the king to remain firm and not concede to popular demands for reforms. In addition, she showed her determination to use force to crush the forthcoming revolution.[129][130]
French Revolution before Varennes (1789–91)

Storming of the Bastille and arrest of Governor Bernard-René de Launay, 14 July 1789
The situation escalated on 20 June as the Third Estate, which had been joined by several members of the clergy and radical nobility, found the door to its appointed meeting place closed by order of the king. It thus met at the tennis court in Versailles and took the Tennis Court Oath not to separate before it had given a constitution to the nation.
On 11 July at Marie Antoinette's urging Necker was dismissed and replaced by Breteuil, the queen's choice to crush the Revolution with mercenary Swiss troops under the command of one of her favorites, Pierre Victor, baron de Besenval de Brünstatt.[131][132][133] At the news, Paris was besieged by riots that culminated in the storming of the Bastille on 14 July.[134][135]
On 15 July Gilbert du Motier, Marquis de Lafayette was named commander-in-chief of the newly formed Garde nationale.[136][137]
In the days following the storming of the Bastille, for fear of assassination, and ordered by the king, the emigration of members of the high aristocracy began on 17 July with the departure of the comte d'Artois, the Condés, cousins of the king,[138] and the unpopular Polignacs. Marie Antoinette, whose life was as much in danger, remained with the king, whose power was gradually being taken away by the National Constituent Assembly.[136][139][140]

Representation of the "Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen" in 1789, with the "Eye of Providence" symbol in the triangle at the top (by Jean-Jacques-François Le Barbier, 1789)
The abolition of feudal privileges by the National Constituent Assembly on 4 August 1789 and the Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen (La Déclaration des Droits de l'Homme et du Citoyen), drafted by Lafayette with the help of Thomas Jefferson and adopted on 26 August, paved the way to a Constitutional Monarchy (4 September 1791 – 21 September 1792).[141][142] Despite these dramatic changes, life at court continued, while the situation in Paris was becoming critical because of bread shortages in September. On 5 October, a crowd from Paris descended upon Versailles and forced the royal family to move to the Tuileries Palace in Paris, where they lived under a form of house arrest under the watch of Lafayette's Garde nationale, while the comte de Provence and his wife were allowed to reside in the Petit Luxembourg, where they remained until they went into exile on 20 June 1791.[143]
Marie Antoinette continued to perform charitable functions and attend religious ceremonies, but dedicated most of her time to her children.[144] She also played an important political, albeit not public, role between 1789 and 1791 when she had a complex set of relationships with several key actors of the early period of the French Revolution. One of the most important was Necker, the Prime Minister of Finances (Premier ministre des finances).[145] Despite her dislike of him, she played a decisive role in his return to office. She blamed him for his support of the Revolution and did not regret his resignation in 1790.[146][147]
Lafayette, one of the former military leaders in the American War of Independence (1775–83), served as the warden of the royal family in his position as commander-in-chief of the Garde nationale. Despite his dislike of the queen—he detested her as much as she detested him and at one time had even threatened to send her to a convent—he was persuaded by the mayor of Paris, Jean Sylvain Bailly, to work and collaborate with her, and allowed her to see Fersen a number of times. He even went as far as exiling the Duke of Orléans, who was accused by the queen of fomenting trouble. His relationship with the king was more cordial. As a liberal aristocrat he did not want the fall of the monarchy but rather the establishment of a liberal one, similar to that of the United Kingdom, based on cooperation between the king and the people, as was to be defined in the Constitution of 1791.
Despite her attempts to remain out of the public eye, Marie Antoinette was falsely accused in the libelles of having an affair with Lafayette, whom she loathed,[148] and, as was published in "Le Godmiché Royal" (translated, "The Royal Dildo"), and of having a sexual relationship with the English Baroness 'Lady Sophie Farrell' of Bournemouth, a well-known lesbian of the time. Publication of such calumnies continued to the end, climaxing at her trial with an accusation of incest with her son. There is no evidence to support the accusations.
Mirabeau

Marie Antoinette at the Tuileries Palace in 1790 (Pastel by Alexandre Kucharski)
A significant achievement of Marie Antoinette in that period was the establishment of an alliance with Honoré Gabriel Riqueti, comte de Mirabeau, the most important lawmaker in the assembly. Like Lafayette, Mirabeau was a liberal aristocrat. He had joined the Third Estate and was not against the monarchy, but wanted to reconcile it with the Revolution. He also wanted to be a minister and was not immune to corruption. On the advice of Mercy, Marie Antoinette opened secret negotiations with him and both agreed to meet privately at the château of Saint-Cloud on 3 July 1790, where the royal family was allowed to spend the summer, free of the radical elements who watched their every move in Paris.[149][150] At the meeting, Mirabeau was much impressed by the queen, and remarked in a letter to Auguste Marie Raymond d'Arenberg, comte de La Marck, that she was the only person the king had by him: La reine est le seul homme que le roi ait auprès de lui.[151] An agreement was reached turning Mirabeau into one of her political allies: Marie Antoinette promised to pay him 6000 livres per month and one million if he succeeded in his mission to restore the king's authority.[152]
The only time the royal couple returned to Paris in that period was on 14 July to attend the Fête de la Fédération, an official ceremony held at the Champ de Mars in commemoration of the fall of the Bastille one year earlier. At least 300,000 persons participated from all over France, including 18,000 national guards, with Talleyrand, bishop of Autun, celebrating a mass at the autel de la patrie ("altar of the fatherland"). The king was greeted at the event with loud cheers of "Long live the king!", especially when he took the oath to protect the nation and to enforce the laws voted by the Constitutional Assembly. There were even cheers for the queen, particularly when she presented the Dauphin to the public.[153][154]
Mirabeau sincerely wanted to reconcile the queen with the people, and she was happy to see him restoring much of the king's powers, such as his authority over foreign policy, and the right to declare war. Over the objections of Lafayette and his allies, the king was given a suspensive veto allowing him to veto any laws for a period of four years. With time, Mirabeau would support the queen even more, going as far as to suggest that Louis XVI "adjourn" to Rouen or Compiègne.[155] This leverage with the Assembly ended with the death of Mirabeau in April 1791, despite the attempt of several moderate leaders of the Revolution to contact the queen to establish some basis of cooperation with her.
Civil Constitution of the Clergy
In March 1791 Pope Pius VI had condemned the Civil Constitution of the Clergy, reluctantly signed by Louis XVI, which reduced the number of bishops from 132 to 93, imposed the election of bishops and all members of the clergy by departmental or district assemblies of electors, and reduced the Pope's authority over the Church. Religion played an important role in the life of Marie Antoinette and Louis XVI, both raised in the Roman Catholic faith. The queen's political ideas and her belief in the absolute power of monarchs were based on France's long established tradition of the divine right of kings. On 18 April, as the royal family prepared to leave for Saint-Cloud to attend Easter mass celebrated by a refractory priest, a crowd, soon joined by the Garde nationale (disobeying Lafayette's orders), prevented their departure from Paris, prompting Marie Antoinette to declare to Lafayette that she and her family were no longer free. This incident fortified her in her determination to leave Paris for personal and political reasons, not alone, but with her family. Even the king, who had been hesitant, accepted his wife's decision to flee with the help of foreign powers and counter-revolutionary forces.[156][157][158] Fersen and Breteuil, who represented her in the courts of Europe, were put in charge of the escape plan, while Marie Antoinette continued her negotiations with some of the moderate leaders of the French Revolution.[159][160]
Flight, arrest at Varennes and return to Paris (21–25 June 1791)

Arrest of the royal family at the house of the registrar of passports at Varennes night of 21–22 June 1791 (by Thomas Falcon Marshall, 1854)
There had been several plots designed to help the royal family escape, which the queen had rejected because she would not leave without the king, or which had ceased to be viable because of the king's indecision. Once Louis XVI finally did commit to a plan, its poor execution was the cause of its failure. In an elaborate attempt known as the Flight to Varennes to reach the royalist stronghold of Montmédy, some members of the royal family were to pose as the servants of an imaginary "Mme de Korff", a wealthy Russian baroness, a role played by Louise-Élisabeth de Croÿ de Tourzel, governess of the royal children.
After many delays, the escape was ultimately attempted on 21 June 1791, but the entire family was arrested less than twenty-four hours later at Varennes and taken back to Paris within a week. The escape attempt destroyed much of the remaining support of the population for the king.[161][162]

Return of the royal family to Paris on 25 June 1791, after the flight to Varennes (colored engraving, Carnavalet Museum, Paris)
Upon learning of the capture of the royal family, the National Constituent Assembly sent three representatives, Antoine Barnave, Jérôme Pétion de Villeneuve and Charles César de Fay de La Tour-Maubourg to Varennes to escort Marie Antoinette and her family back to Paris. On the way to the capital they were jeered and insulted by the people as never before. The prestige of the French monarchy had never been at such a low level. During the trip, Barnave, the representative of the moderate party in the Assembly, protected Marie Antoinette from the crowds, and even Pétion took pity on the royal family. Brought safely back to Paris, they were met with total silence by the crowd. Thanks to Barnave, the royal couple was not brought to trial and was publicly exonerated of any crime in relation with the attempted escape.[163][164]
Marie Antoinette's first Lady of the Bedchamber, Mme Campan, wrote about what happened to the queen's hair on the night of 21–22 June, "...in a single night, it had turned white as that of a seventy-year old woman." (En une seule nuit ils étaient devenus blancs comme ceux d'une femme de soixante-dix ans.)[165]
Radicalization of the Revolution after Varennes (1791–92)

Marie-Antoinette, c. 1792. A blow from a pike struck by a revolutionary is visible on the lower part of the work (unfinished pastel portrait by Alexandre Kucharski).
After their return from Varennes and until the storming of the Tuileries on 10 August 1792, the queen, her family and entourage were held under tight surveillance by the Garde nationale in the Tuileries, where the royal couple was guarded night and day. Four guards accompanied the queen wherever she went, and her bedroom door had to be left open at night. Her health also began to deteriorate, thus further reducing her physical activities.[166][167]
On 17 July 1791, with the support of Barnave and his friends, Lafayette's Garde nationale opened fire on the crowd that had assembled on the Champ de Mars to sign a petition demanding the deposition of the king. The estimated number of those killed varies between 12 and 50. Lafayette's reputation never recovered from the event and, on 8 October, he resigned as commander of the Garde nationale. Their enmity continuing, Marie Antoinette played a decisive role in defeating him in his aims to become the mayor of Paris in November 1791.[168]

Miniature of Marie Antoinette (by François Dumont, 1792)
As her correspondence shows, while Barnave was taking great political risks in the belief that the queen was his political ally and had managed, despite her unpopularity, to secure a moderate majority ready to work with her, Marie Antoinette was not considered sincere in her cooperation with the moderate leaders of the French Revolution, which ultimately ended any chance to establish a moderate government.[169] Moreover, the view that the unpopular queen was controlling the king further degraded the royal couple's standing with the people, which the Jacobins successfully exploited after their return from Varennes to advance their radical agenda to abolish the monarchy.[170] This situation lasted until the spring of 1792.[171][172]
Marie Antoinette continued to hope that the military coalition of European kingdoms would succeed in crushing the Revolution. She counted most on the support of her Austrian family. After the death of her brother Joseph in 1790, his successor, Leopold, was willing to support her to a limited degree.[citation needed] Upon Leopold's death in 1792, his son, Francis, a conservative ruler, was ready to support the cause of the French royal couple more vigorously because he feared the consequences of the French Revolution and its ideas for the monarchies of Europe, particularly, for Austria's influence in the continent.[citation needed]
Barnave had advised the queen to call back Mercy, who had played such an important role in her life before the Revolution, but Mercy had been appointed to another foreign diplomatic position[where?] and could not return to France. At the end of 1791, ignoring the danger she faced, the princesse de Lamballe, who was in London, returned to the Tuileries. As to Fersen, despite the strong restriction imposed on the queen, he was able to see her a final time in February 1792.[173]
Events leading to the abolition of the monarchy on 10 August 1792
Leopold's and Francis II's strong action on behalf of Marie Antoinette led to France's declaration of war on Austria on 20 April 1792. This resulted in the queen being viewed as an enemy, although she was personally against Austrian claims to French territories on European soil. That summer, the situation was compounded by multiple defeats of the French armies by the Austrians, in part because Marie Antoinette passed on military secrets to them.[174] In addition, at the insistence of his wife, Louis XVI vetoed several measures that would have further restricted his power, earning the royal couple the nicknames "Monsieur Veto" and "Madame Veto",[175][176] nicknames then prominently featured in different contexts, including La Carmagnole.

Plate with the beginning of the text of the song La Carmagnole: Madame Veto…
Barnave remained the most important advisor and supporter of the queen, who was willing to work with him as long as he met her demands, which he did to a large extent. Barnave and the moderates comprised about 260 lawmakers in the new Legislative Assembly; the radicals numbered around 136, and the rest around 350. Initially, the majority was with Barnave, but the queen's policies led to the radicalization of the Assembly and the moderates lost control of the legislative process. The moderate government collapsed in April 1792 to be replaced by a radical majority headed by the Girondins. The Assembly then passed a series of laws concerning the Church, the aristocracy and the formation of new national guard units; all were vetoed by Louis XVI. While Barnave's faction had dropped to 120 members, the new Girondin majority controlled the legislative assembly with 330 members. The two strongest members of that government were Jean Marie Roland, who was minister of interior, and General Dumouriez, the minister of foreign affairs. Dumouriez sympathised with the royal couple and wanted to save them but he was rebuffed by the queen.[177][178]
Marie Antoinette's actions in refusing to collaborate with the Girondins, in power between April and June 1792, led them to denounce the treason of the Austrian comity, a direct allusion to the queen. After Madame Roland sent a letter to the king denouncing the queen's role in these matters, urged by the queen, Louis XVI disbanded[citation needed] the government, thus losing his majority in the Assembly. Dumouriez resigned and refused a post in any new government. At this point, the tide against royal authority intensified in the population and political parties, while Marie Antoinette encouraged the king to veto the new laws voted by the Legislative Assembly in 1792.[179] In August 1791, the Declaration of Pillnitz threatened an invasion of France. This led in turn to a French declaration of war in April 1792, which led to the French Revolutionary Wars and to the events of August 1792, which ended the monarchy.[180]

Marie Antoinette with her children and Madame Élisabeth, facing the mob that had broken into the Tuileries Palace on 20 June 1792, (Musée de la Révolution française)
On 20 June 1792, "a mob of terrifying aspect" broke into the Tuileries, made the king wear the bonnet rouge (red Phrygian cap) to show his loyalty to the Republic, insulted Marie Antoinette, accusing her of betraying France, and threatened her life. In consequence, the queen asked Fersen to urge the foreign powers to carry out their plans to invade France and to issue a manifesto in which they threatened to destroy Paris if anything happened to the royal family. The Brunswick Manifesto, issued on 25 July 1792, triggered the events of 10 August[181] when the approach of an armed mob on its way to the Tuileries Palace forced the royal family to seek refuge at the Legislative Assembly. Ninety minutes later, the palace was invaded by the mob, who massacred the Swiss Guards.[182][183] On 13 August the royal family was imprisoned in the tower of the Temple in the Marais under conditions considerably harsher than those of their previous confinement in the Tuileries.[184]
A week later, several of the royal family's attendants, among them the princesse de Lamballe, were taken for interrogation by the Paris Commune. Transferred to the La Force prison, after a rapid judgment, Marie Louise de Lamballe was savagely killed on 3 September. Her head was affixed on a pike and paraded through the city to the Temple for the queen to see. Marie Antoinette was prevented from seeing it, but fainted upon learning of it.[185][186]
On 21 September 1792, the fall of the monarchy was officially declared and the National Convention became the governing body of the French Republic. The royal family name was downgraded to the non-royal "Capets". Preparations began for the trial of the king in a court of law.[187]

"Day of 21 January 1793 the death of Louis Capet on the Place de la Révolution (engraving by Helman, Duclos, Monnet)
Louis XVI's trial and execution
Charged with undermining the First French Republic, Louis XVI was separated from his family and tried in December. He was found guilty by the Convention, led by the Jacobins who rejected the idea of keeping him as a hostage. On 15 January 1793, by a majority of one vote, that of Philippe Égalité, he was condemned to death by guillotine and executed on 21 January 1793.[188][189]
Marie Antoinette in the Temple

Marie Antoinette prisoner in the Temple Tower (attributed to Alexandre Kucharski, ca. 1792)
The queen, now called "Widow Capet", plunged into deep mourning. She still hoped her son Louis-Charles, whom the exiled Comte de Provence, Louis XVI's brother, had recognised as Louis XVI's successor, would one day rule France. The royalists and the refractory clergy, including those preparing the insurrection in Vendée, supported Marie Antoinette and the return to the monarchy. Throughout her imprisonment and up to her execution, Marie Antoinette could count on the sympathy of conservative factions and social-religious groups which had turned against the Revolution, and also on wealthy individuals ready to bribe republican officials in order to facilitate her escape;[190] These plots all failed. While imprisoned in the Tower of the Temple, Marie Antoinette, her children, and Élisabeth were insulted, some of the guards going as far as blowing smoke in the ex-queen's face. Strict security measures were taken to assure that Marie Antoinette was not able to communicate with the outside world. Despite these measures, several of her guards were open to bribery and a line of communication was kept with the outside world.
After Louis' execution, Marie Antoinette's fate became a central question of the National Convention. While some advocated her death, others proposed exchanging her for French prisoners of war or for a ransom from the Holy Roman Emperor. Thomas Paine advocated exile to America.[191] In April 1793, during the Reign of Terror, a Committee of Public Safety dominated by Robespierre was formed, and men such as Jacques Hébert began to call for Marie-Antoinette's trial. By the end of May, the Girondins had been chased from power.[192] Calls were also made to "retrain" the eight-year old Louis XVII, to make him pliant to revolutionary ideas. To carry this out, Louis Charles was separated from his mother on 3 July after a struggle during which his mother fought in vain to retain her son, who was handed over to Antoine Simon, a cobbler and representative of the Paris Commune. Until her removal from the Temple, Marie Antoinette spent hours trying to catch a glimpse of her son, who, within weeks, had been made to turn against her, accusing his mother of wrongdoing.[193]

Marie Antoinette's cell in the Conciergerie where she was allowed no privacy.
Conciergerie
On the night of 1 August, at 1:00 in the morning, Marie Antoinette was transferred from the Temple to an isolated cell in the Conciergerie as 'Prisoner n° 280'. Leaving the tower she bumped her head against the lintel of a door, which prompted one of her guards to ask her if she was hurt, to which she answered, "No! Nothing now can hurt me."[194] This was the most difficult period of her captivity. She was under constant surveillance, with no privacy. The "Carnation Plot" (Le complot de l'œillet), an attempt to help her escape at the end of August, was foiled due to the inability to corrupt all the guards.[195] She was attended by Rosalie Lamorlière, who took care of her as much as she could. At least once she received a visit by a Catholic priest.[196][197]
Trial and execution (14–16 October 1793)

Marie Antoinette au Tribunal révolutionnaire (engraving by Alphonse François, from a painting by Paul Delaroche, (1857)
Marie Antoinette was tried by the Revolutionary Tribunal on 14 October 1793. Some historians believe the outcome of the trial had been decided in advance by the Committee of Public Safety around the time the Carnation Plot was uncovered.[198] She and her lawyers were given less than one day to prepare her defense. Among the accusations, many previously published in the libelles, were: orchestrating orgies in Versailles, sending millions of livres of treasury money to Austria, planning the massacre of the gardes françaises (National Guards) in 1792,[199] declaring her son to be the new king of France, and incest, a charge made by her son Louis Charles, pressured into doing so by the radical Jacques Hébert who controlled him. This last accusation drew an emotional response from Marie Antoinette, who refused to respond to this charge, instead appealing to all mothers present in the room; their reaction comforted her, since these women were not otherwise sympathetic to her.[200][201]

Marie Antoinette on her way to the guillotine (pen and ink by Jacques-Louis David, 16 October 1793)

Marie Antoinette's execution on 16 October 1793: Sanson, the executioner, showing Marie Antoinette's head to the people (anonymous, 1793).
Early on 16 October, Marie Antoinette was declared guilty of the three main charges against her: depletion of the national treasury, conspiracy against the internal and external security of the State, and high treason because of her intelligence activities in the interest of the enemy; the latter charge alone was enough to condemn her to death.[202] At worst, she and her lawyers had expected life imprisonment.[203] In the hours left to her, she composed a letter to her sister-in-law, Madame Élisabeth, affirming her clear conscience, her Catholic faith, and her love and concern for her children. The letter did not reach Élisabeth.[204] Preparing for her execution, she had to change clothes in front of her guards. She put on a plain white dress, white being the color worn by widowed queens of France. Her hair was shorn, her hands bound painfully behind her back and she was put on a rope leash. Unlike her husband, who had been taken to his execution in a carriage (carrosse), she had to sit in an open cart (charrette) for the hour it took to convey her from the Conciergerie via the rue Saint-Honoré thoroughfare to reach the guillotine erected in the Place de la Révolution, (the present-day Place de la Concorde).[205] She maintained her composure, despite the insults of the jeering crowd. A constitutional priest was assigned to her to hear her final confession. He sat by her in the cart, but she ignored him all the way to the scaffold.[206][207]
Marie Antoinette was guillotined at 12:15 p.m. on 16 October 1793.[208][209] Her last words are recorded as, "Pardonnez-moi, monsieur. Je ne l’ai pas fait exprès." or "Pardon me, sir, I did not do it on purpose.", after accidentally stepping on her executioner's shoe.[210] Her head was one of those that Marie Tussaud was employed to make death masks of.[211] Her body was thrown into an unmarked grave in the Madeleine cemetery located close by in rue d'Anjou. Because its capacity was exhausted the cemetery was closed the following year, on 25 March 1794.[212]
Both Marie Antoinette's and Louis XVI's bodies were exhumed on 18 January 1815, during the Bourbon Restoration, when the comte de Provence ascended the newly reestablished throne as Louis XVIII, King of France and of Navarre. Christian burial of the royal remains took place three days later, on 21 January, in the necropolis of French kings at the Basilica of St Denis.[213]
Legacy

Funerary monument to King Louis XVI and Queen Marie Antoinette in the Basilica of St Denis (sculptures by Edme Gaulle and Pierre Petitot, (1830))
For many revolutionary figures, Marie Antoinette was the symbol of what was wrong with the old regime in France. The onus of having caused the financial difficulties of the nation were placed on her shoulders by the revolutionary tribunal,[214] and under the new republican ideas of what it meant to be a member of a nation, her Austrian descent and continued correspondence with the competing nation made her a traitor.[215] The people of France saw her death as a necessary step toward completing the revolution. Furthermore, her execution was seen as a sign that the revolution had done its work.[216]
Long after her death, Marie Antoinette remains a major historical figure linked with conservatism, the Catholic Church, wealth, and fashion. She has been the subject of a number of books, films and other media. Politically engaged authors have deemed her the quintessential representative of class conflict, western aristocracy and absolutism. Some of her contemporaries, such as Jefferson, attributed to her the start of the French Revolution.[217] For others, Marie Antoinette was a victim of her family's ambition and the general situation in France. Even her critics have recognized her qualities as a mother and her courage in dying.
In popular culture
The phrase "Let them eat cake" is often attributed to Marie Antoinette, but there is no evidence that she ever uttered it, and it is now generally regarded as a journalistic cliché.[218] This phrase originally appeared in Book VI of the first part of Jean-Jacques Rousseau's autobiographical work Les Confessions, finished in 1767 and published in 1782: "Enfin je me rappelai le pis-aller d'une grande princesse à qui l'on disait que les paysans n'avaient pas de pain, et qui répondit: Qu'ils mangent de la brioche" ("Finally I recalled the stop-gap solution of a great princess who was told that the peasants had no bread, and who responded: 'Let them eat brioche'"). Rousseau ascribes these words to a "great princess", but the purported writing date precedes Marie Antoinette's arrival in France. Some think that he invented it altogether.[219]
In the United States, expressions of gratitude to France for its help in the American Revolution included naming a city Marietta, Ohio in 1788.[220] Her life has been the subject of many films, such as the 2006 film Marie Antoinette.[221]
Ancestry
.mw-parser-output table.ahnentafelborder-collapse:separate;border-spacing:0;line-height:130%.mw-parser-output .ahnentafel trtext-align:center.mw-parser-output .ahnentafel-tborder-top:#000 solid 1px;border-left:#000 solid 1px.mw-parser-output .ahnentafel-bborder-bottom:#000 solid 1px;border-left:#000 solid 1px
| Ancestors of Marie Antoinette[222] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Children
| Name | Portrait | Lifespan | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
Marie Thérèse Charlotte Madame Royale |  | 19 December 1778 – 19 October 1851 | Married her cousin, Louis Antoine, Duke of Angoulême, the eldest son of the future Charles X of France. No issue. |
Louis Joseph Xavier François Dauphin de France |  | 22 October 1781 – 4 June 1789 | Died in childhood on the very day the Estates General convened. |
Louis XVII of France (Nominally) King of France and Navarre |  | 27 March 1785 – 8 June 1795 | Died in childhood; no issue. He was never officially king, nor did he rule. His title was bestowed by his royalist supporters and acknowledged implicitly by his uncle's later adoption of the regnal name Louis XVIII rather than Louis XVII, upon the restoration of the Bourbon monarchy in 1814. |
Sophie Hélène Béatrix |  | 9 July 1786 – 19 June 1787 | Died in childhood. |
In addition to her biological children, Marie Antoinette adopted four children: "Armand" Francois-Michel Gagné (c. 1771 – 1792), a poor orphan adopted in 1776; Jean Amilcar (c. 1781 – 1793), a Senegalese slave boy given to the queen as a present by Chevalier de Boufflers in 1787, but whom she instead had freed, baptized, adopted and placed in a pension; Ernestine Lambriquet (1778–1813), daughter of two servants at the palace, who was raised as the playmate of her daughter and whom she adopted after the death of her mother in 1788; and finally "Zoe" Jeanne Louise Victoire (born in 1787), who was adopted in 1790 along with her two older sisters when her parents, an usher and his wife in service of the king, had died.[223]
Of these, only Armand, Ernestine and Zoe actually lived with the royal family: Jean Amilcar, along with the elder siblings of Zoe and Armand who were also formally foster children of the royal couple, simply lived on the queen's expense until her imprisonment, which proved fatal for at least Amilcar, as he was evicted from the boarding school when the fee was no longer paid, and reportedly starved to death on the street.[223] Armand and Zoe had a position which was more similar to that of Ernestine; Armand lived at court with the king and queen until he left them at the outbreak of the revolution because of his republican sympathies, and Zoe was chosen to be the playmate of the Dauphin, just as Ernestine had once been selected as the playmate of Marie-Therese, and sent away to her sisters in a convent boarding school before the Flight to Varennes in 1791.[223]
See also
- French Revolution
References
Notes
^ Jones, Daniel (2003) [1917], Peter Roach, James Hartmann and Jane Setter, eds., English Pronouncing Dictionary, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, ISBN 3-12-539683-2CS1 maint: Uses editors parameter (link) .mw-parser-output cite.citationfont-style:inherit.mw-parser-output qquotes:"""""""'""'".mw-parser-output code.cs1-codecolor:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registrationcolor:#555.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration spanborder-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-errordisplay:none;font-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-errorfont-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-formatfont-size:95%.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-leftpadding-left:0.2em.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-rightpadding-right:0.2em
^ Fraser 2002, p. 5
^ Fraser 2002, pp. 5–6
^ Michel de Decker: Marie-Antoinette, les dangereuses liaisons de la reine, France Loisirs, 2005, p. 12.
^ Marie Célestine Amélie de Ségur d'Armaillé: Marie-Thérèse et Marie-Antoinette, Didier, 1870, p. 47.
^ Lever 2006, p. 10
^ ab Fraser 2001, pp. 22–23,166–170
^ Michel de Decker: Marie-Antoinette, les dangereuses liaisons de la reine, France Loisirs, 2005, p. 14.
^ Philippe Delorme: Marie-Antoinette. Épouse de Louis XVI, mère de Louis XVII, Pygmalion Éditions, 1999, p. 13.
^ Michel de Decker: Marie-Antoinette, les dangereuses liaisons de la reine, France Loisirs, 2005, p. 15.
^ Marie Célestine Amélie de Ségur d'Armaillé: Marie-Thérèse et Marie-Antoinette, Didier, 1870, p. 34.
^ Évelyne Lever: C'était Marie-Antoinette, Fayard, 2006, p. 14.
^ ab Cronin 1989, p. 45
^ France Loisirs, Michel de Decker, 2005, p.16
^ Fraser 2002, pp. 32–33
^ France Loisirs, Michel de Decker, 2005, p.17
^ Cronin 1989, p. 46
^ Weber 2007[page needed]
^ de Decker, Michel, France Loisirs, 2005, p. 20.
^ Fraser 2001, pp. 51–53
^ Pierre Nolhac & La Dauphine Marie Antoinette,1929, pp. 46–48
^ France Loisirs, Michel de Decker, 2005, p. 21.
^ Fraser 2001, pp. 70–71
^ Nolhac 1929, pp. 55–61
^ Fraser 2001, p. 157
^ Alfred et Geffroy D'Arneth & Correspondance Secrete entre Marie-Therese et le Comte de Mercy-Argenteau,vol 3 1874, pp. 80–90,110–115
^ Cronin 1974, pp. 61–63
^ Cronin 1974, p. 61
^ Fraser 2001, pp. 80–81
^ ALfred and Geffroy d'Arneth 1874, pp. 65–75
^ Lever 2006
^ Fraser, Marie Antoinette, 2001, p. 124.
^ Jackes Levron & Madame du Barry 1973, pp. 75–85
^ Evelyne Lever & Marie Antoinette 1991, pp. 124
^ Goncourt, Edmond de, La Du Barry, Ed. G. Charpentier, Paris, 1880, pp. 195-196
^ Lever, Evelyne, Louis XV, Fayard, Paris, 1985, p. 96
^ Vatel, Charles, Histoire de Madame du Barry: d'après ses papiers personnels et les documents d'archives, Paris, 1883, p. 410
^ Fraser 2001, pp. 136–137
^ Arneth and Geffroy ii, 1874 & pp475-480
^ Castelot, André, Marie-Antoinette, Librairie académique Perrin, Paris, 1962, pp. 107-108
^ Fraser 2001, pp. 124–127
^ Lever & Marie Antoinette 1991, pp. 125
^ Cronin 1974, p. 215
^ Fashion, the mirror of history, page 190, Michael Batterberry, Ariane Ruskin Batterberry, Greenwich House, 1977.
ISBN 978-0-517-38881-5
^ Fraser 2001, pp. 150–151
^ Carolly Erickson, To the Scaffold: The Life of Marie Antoinette. William and Morrow and Company, New York, pp. 163.
^ Thomas, Chantal. The Wicked Queen: The Origins of the Myth of Marie Antoinette. Translated by Julie Rose. New York: Zone Books, 2001, pp. 51.
^ Fraser 2001, pp. 140–145
^ Arneth and Geffroy i 1874, pp. 400–410
^ Fraser 2001, pp. 129–131
^ Fraser 2001, pp. 131–132; Bonnet 1981
^ Fraser 2001, pp. 111–113
^ Howard Patricia, Gluck 1995, pp. 105–115,240–245
^ Lever, Evelyne, Louis XVI, Fayard, Paris, 1985, pp. 289-291
^ Cronin 1974, pp. 158–159
^ "Circumcision and phimosis in eighteenth century France". History of Circumcision. Retrieved 16 December 2016.
^ Cronin 1974, p. 159
^ Fraser 2001, pp. 160–161
^ Cronin 1974, p. 161
^ Hibbert 2002, p. 23
^ Fraser 2001, p. 169
^ Cronin 1974, pp. 162–164
^ Fraser 2001, pp. 158–171
^ Arneth and Geoffroy,iii 1874, pp. 168–170,180–182,210–212
^ [1] Kelly Hall: "Impropriety, Informality
and Intimacy in Vigée Le Brun’s Marie Antoinette en Chemise", pp. 21–28. Providence College Art Journal, 2014.
^ Kindersley, Dorling (2012). Fashion: The Definitive History of Costume and Style. New York: DK Publishing. pp. 146–149.
^ Cronin 1974, pp. 127–128
^ Fraser 2001, pp. 174–179
^ "Marie-Antoinette | Biography & French Revolution". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 2018-02-03.
^ Fraser 2001, pp. 152,171,194–195
^ Fraser, 2001 & pp218-220
^ Price Munro & Preserving the Monarchy: The Comte de Vergennes, 1774–1787 1995, pp. 30–35,145–150
^ Meagen Elizabeth Moreland: The Performance of Motherhood in the Correspondence of Madame de Sévigné, Marie-Thérèse of Austria and Joséphine Bonaparte to their Daughters - Chapter I Contextualizing the correspondence, p. 11 [retrieved 1 October 2016].
^ Arneth, Alfred (1866). Marie Antoinette; Joseph II, und Leopold II (in French and German). The Ohio State University. Leipzig, K.F. Köhler, Paris, Ed. Jung-Treuttel etc. .. pp. 23 (footnote).CS1 maint: Date and year (link)
^ Fraser 2001, pp. 184–187
^ Price 1995, pp. 55–60
^ Fraser, pp.232-6
^ Lettres de Marie Antoinette et al., pp. 42–44
^ Lever, Marie Antoinette 1991, pp. 350–353
^ Cronin 1974, p. 193
^ Fraser 2001, pp. 198–201
^ Munro Price & The Road to Versailles 2003, pp. 14–15,72
^ Zweig Stephan & Marie Antoinette 1938, pp. 121
^ Farr, Evelyn, Marie Antoinette and Count Fersen: Untold Love Story
^ Fraser 2001, p. 202
^ Marie-Antoinette's torrid affair with Swedish count revealed in decoded letters.
^ Hunt, Lynn. “The Many Bodies of Marie Antoinette: Political Pornography and the Problem of the Feminine in the French Revolution.” In The French Revolution: Recent Debates and New Controversies 2nd edition, ed. Gary Kates, 201-218. New York and London: Routledge, 1998, pp 201-218.
^ Thomas, Chantal. The Wicked Queen: The Origins of the Myth of Marie Antoinette. Translated by Julie Rose. New York: Zone Books, 2001, pp. 51-52.
^ Lever 2006, p. 158
^ Fraser, pp=206-208
^ Gutwirth,Madelyn, The Twilight of the Goddesses: women and representation in the French revolutionary era 1992, pp. 103,178–185,400–405
^ Fraser 2001, p. 208
^ Bombelles, Marquis de & Journal, vol I 1977, pp. 258–265
^ Cronin 1974, pp. 204–205
^ Fraser 2001, pp. 214–215
^ Fraser 2001, pp. 216–220
^ Lever, Marie Antoinette 1991, pp. 358–360
^ Fraser 2001, pp. 224–225
^ Lever 2006, p. 189
^ Stefan Zweig, Marie Antoinette: The portrait of an average woman, New York, 1933, pp. 143, 244-247
^ Fraser 2001, pp. 267–269
^ Ian Dunlop, Marie-Antoinette: A Portrait, London, 1993
^ Évelyne Lever, Marie-Antoinette : la dernière reine, Fayard, Paris, 2000
^ Simone Bertière, Marie-Antoinette: l'insoumise, Le Livre de Poche, Paris, 2003
^ Jonathan Beckman, How to ruin a Queen: Marie Antoinette, the Stolen Diamonds and the Scandal that shook the French throne, London, 2014
^ Munro Price, The Fall of the French Monarchy: Louis XVI, Marie Antoinette and the baron de Breteuil, London, 2002
^ Deborah Cadbury, The Lost King of France: The tragic story of Marie-Antoinette's Favourite Son, London, 2003, pp. 22-24
^ Cadbury, p. 23
^ Fraser 2001, p. 226
^ Fraser 2001, pp. 248–252
^ ab Fraser 2001, pp. 248–250
^ Fraser 2001, pp. 246–248
^ Lever, Marie Antoinette 1991, pp. 419–420
^ Fraser 2001, pp. 250–260
^ Fraser
^ Fraser 2001, pp. 254–255
^ Fraser, 2001 & pp254-260
^ Facos, p. 12.
^ Schama, p. 221.
^ Fraser 2001, pp. 255–258
^ Fraser, 2001 & pp 257-258
^ Fraser 2001, pp. 258–259
^ Fraser 2001, pp. 260–261
^ Fraser 2001, pp. 263–265
^ Lever, Marie Antoinette 2001, pp. 448–453
^ A diary of the French Revolution 1789-93 & Morris Gouverneur 1939, pp. 66,67
^ Nicolardot, Louis, Journal de Louis Seize, 1873, pp. 133-138
^ Fraser 2001, pp. 274–278
^ Fraser, 2001 & pp279-282
^ Lever,Marie Antoinette 1991, pp. 462–467
^ iFraser, 2001 & pp280-285
^ Letters vol 2, pp. 130–140
^ Morris 1939, pp. 130–135
^ Fraser 2001, pp. 282–284
^ Lever, Marie Antoinette 1991, pp. 474–478
^ ab Fraser 2001, pp. 284–289
^ Despaches of Earl Grower, Oscar Browning & Cambridge 1885, pp. 70–75,245–250
^ Journal d'émigration du prince de Condé. 1789–1795, publié par le comte de Ribes, Bibliothèque nationale de France. [2]
^ Castelot, Charles X, Librairie Académique Perrin, Paris, 1988, pp. 78-79.
^ Despaches of Earl Grower, Oscar Browning & Cambridge,1885, pp. 70–75,245–250
^ Fraser 2001, p. 289
^ Lever, Marie Antoinette 1991, pp. 484–485
^ http://www.senat.fr/evenement/archives/presidence1.html
^ Fraser 2001, pp. 304–308
^ Discours prononcé par M. Necker, Premier Ministre des Finances, à l'Assemblée Nationale, le 24. Septembre 1789.[3]
^ Fraser 2001, p. 315
^ Lever, Marie Antoinette 1991, pp. 536,537
^ Fraser 2001, p. 319
^ Castelot, Marie Antoinette 1962, p. 334
^ Lever, Marie Antoinette 1991, pp. 528–530
^ Mémoires de Mirabeau, tome VII, p. 342.
^ Lever, Marie Antoinette 1991, pp. 524–527
^ 2001 & Fraser, pp. 314–316
^ Castelot, Marie Antoinette 1962, pp. 335
^ Fraser, 2001 & p. 313
^ Fraser, 2001 & pp321-323
^ Lever, Marie Antoinette 1991, pp. 542–552
^ Castelot, Marie Antoinette 1962, pp. 336–339
^ Fraser, 2001 & pp321-325
^ Castelot, Marie Antoinette 1962, pp. 340–341
^ Fraser 2001, pp. 325–348
^ Lever, Marie Antoinette 1991, pp. 555–568
^ Lever, Marie Antoinette 1991, pp. 569–575
^ Castelot, Marie Antoinette 1962, pp. 385–398
^ Mémoires de Madame Campan, première femme de chambre de Marie-Antoinette, Le Temps retrouvé, Mercure de France, Paris, 1988, p.272,
ISBN 2-7152-1566-5
^ Lettres de Marie Antoinette vol 2 1895, pp. 364–378
^ Lever, Marie Antoinette 1991, pp. 576–580
^ Fraser 2001, pp. 350,360–371
^ Fraser 2001, pp. 353–354
^ Fraser 2001, pp. 350–352
^ Fraser, 2001 & pp357-358
^ Castelot, Marie Antoinette 1962, pp. 408,409
^ Lever, Marie Antoinette 1991, pp. 599–601
^ 2001 & pp365-368
^ Fraser 2001, pp. 365–368
^ Lever, Marie Antoinette 1991, pp. 607–609
^ Castelot 1962, pp. 415,416
^ Lever, Marie Antoinette 1991, pp. 591,592
^ Castelot 1962, pp. 418
^ Fraser, 2001 & pp371-373
^ Fraser 2001, pp. 368,375–378
^ Fraser 2001, pp. 373–379
^ Castelot, Marie Antoinette 1962, pp. 428–435
^ Fraser 2001, pp. 382–386
^ Fraser 2001, p. 389
^ Castelot, Marie Antoinette 1962, pp. 442–446
^ Fraser 2001, p. 392
^ Fraser 2001, pp. 395–399
^ Castelot, Marie Antoinette 1962, pp. 447–453
^ Castelot, Marie Antoinette 1962, pp. 453–457
^ Fraser 2001, pp. 398, 408
^ Fraser 2001, pp. 411–412
^ Fraser 2001, pp. 412–414
^ Funck-Brentano, Frantz: Les derniers jours de Marie-Antoinette, Flammarion, Paris, 1933
^ Furneaux & 19711, pp. 139–142
^ G. Lenotre: The Last Days of Marie Antoinette, 1907.
^ Fraser 2001, pp. 416–420
^ Castelot, Marie Antoinette 1962, pp. 496–500
^ Procès de Louis XVI, de Marie-Antoinette, de Marie-Elisabeth et de Philippe d'Orléans, Recueil de pièces authentiques, Années 1792, 1793 et 1794, De Mat, imprimeur-libraire, Bruxelles, 1821, p. 473
^ Castelot 1957, pp. 380–385
^ Fraser 2001, pp. 429–435
^ Le procès de Marie-Antoinette, Ministère de la Justice, 17 October 2011, (French) [4]
^ Furneaus 1971, pp. 150–154
^ "Last Letter of Marie-Antoinette", Tea at Trianon, 26 May 2007
^ Furneaus 1971, pp. =155–156
^ Castelot 1957, pp. 550–558
^ Lever & Marie Antoinette 1991, pp. 660
^ Fraser 2001, p. 440
^ The Times 23 October 1793, The Times.
^ https://thoughtcatalog.com/oliver-miller/2012/05/famous-last-words-2/
^ "Marie Tussaud Facts, information, pictures | Encyclopedia.com articles about Marie Tussaud". www.encyclopedia.com. Retrieved 2016-03-28.
^ Ragon, Michel, L'espace de la mort, Essai sur l'architecture, la décoration et l'urbanisme funéraires, Michel Albin, Paris, 1981,
ISBN 978-2-226-22871-0 [5]
^ Fraser 2001, pp. 411, 447
^ Hunt, Lynn. “The Many Bodies of Marie Antoinette: Political Pornography and the Problem of the Feminine in the French Revolution.” In The French Revolution: Recent Debates and New Controversies 2nd edition, ed. Gary Kates, 201-218. New York and London: Routledge, 1998, pp 202.
^ Kaiser, Thomas. “From the Austrian Committee to the Foreign Plot: Marie-Antoinette, Austrophobia, and the Terror.” French Historical Studies 26 no. 4 (Fall 2003): 579-617, https://muse.jhu.edu
^ Thomas, Chantal. The Wicked Queen: The Origins of the Myth of Marie Antoinette. Translated by Julie Rose. New York: Zone Books, 2001, pp 149
^ Jefferson, Thomas. Autobiography of Thomas Jefferson. Courier Dover Publications. Retrieved March 29, 2013.I have ever believed that had there been no queen, there would have been no revolution.
^ Fraser 2001, pp. xviii, 160; Lever 2006, pp. 63–5; Lanser 2003, pp. 273–290
^ Johnson 1990, p. 17
^ Sturtevant, pp. 14, 72.
^ luizhadsen Paulnewton (2016-09-24), Marie Antoinette 2006 Full Movie, retrieved 2016-12-01
^ Genealogie ascendante jusqu'au quatrieme degre inclusivement de tous les Rois et Princes de maisons souveraines de l'Europe actuellement vivans [Genealogy up to the fourth degree inclusive of all the Kings and Princes of sovereign houses of Europe currently living] (in French). Bourdeaux: Frederic Guillaume Birnstiel. 1768. p. 1.
^ abc Philippe Huisman, Marguerite Jallut: Marie Antoinette, Stephens, 1971
Bibliography
.mw-parser-output .refbeginfont-size:90%;margin-bottom:0.5em.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>ullist-style-type:none;margin-left:0.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>ul>li,.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>dl>ddmargin-left:0;padding-left:3.2em;text-indent:-3.2em;list-style:none.mw-parser-output .refbegin-100font-size:100%
Bonnet, Marie-Jo (1981). Un choix sans équivoque: recherches historiques sur les relations amoureuses entre les femmes, XVIe-XXe siècle (in French). Paris: Denoël. OCLC 163483785.
Castelot, André (1957). Queen of France: a biography of Marie Antoinette. trans. Denise Folliot. New York: Harper & Brothers. OCLC 301479745.
Cronin, Vincent (1989). Louis and Antoinette. London: The Harvill Press. ISBN 978-0-00-272021-2.
Dams, Bernd H.; Zega, Andrew (1995). La folie de bâtir: pavillons d'agrément et folies sous l'Ancien Régime. trans. Alexia Walker. Flammarion. ISBN 978-2-08-201858-6.
Facos, Michelle (2011). An Introduction to Nineteenth-Century Art. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-1-136-84071-5. Retrieved 1 September 2011.
Fraser, Antonia (2001). Marie Antoinette (1st ed.). New York: N.A. Talese/Doubleday. ISBN 978-0-385-48948-5.
Fraser, Antonia (2002). Marie Antoinette: The Journey (2nd ed.). Garden City: Anchor Books. ISBN 978-0-385-48949-2.
Hermann, Eleanor (2006). Sex With The Queen. Harper/Morrow. ISBN 0-06-084673-9.
Hibbert, Christopher (2002). The Days of the French Revolution. Harper Perennial. ISBN 0-688-16978-3.
Johnson, Paul (1990). Intellectuals. New York: Harper & Row. ISBN 978-0-06-091657-2.
Lanser, Susan S. (2003). "Eating Cake: The (Ab)uses of Marie-Antoinette". In Goodman, Dena. Marie-Antoinette: Writings on the Body of a Queen. Psychology Press. ISBN 978-0-415-93395-7.
Lever, Évelyne (2006). Marie Antoinette: The Last Queen of France. London: Portrait. ISBN 978-0-7499-5084-2.
Schama, Simon (1989). Citizens: A Chronicle of the French Revolution. New York: Vintage. ISBN 0-679-72610-1.
Seulliet, Philippe (July 2008). "Swan Song: Music Pavillion of the Last Queen of France". World Of Interiors (7).
Sturtevant, Lynne (2011). A Guide to Historic Marietta, Ohio. The History Press. ISBN 978-1-60949-276-2. Retrieved 1 September 2011.
Weber, Caroline (2007). Queen of Fashion: What Marie Antoinette Wore to the Revolution. Picador. ISBN 978-0-312-42734-4.
Wollstonecraft, Mary (1795). An Historical and Moral View of the Origin and Progress of the French Revolution and the Effect it Has Produced in Europe. St. Paul's.
Farr, Evelyn (2009). The Untold Love Story: Marie Antoinette & Count Fersen. Peter Owen Publishers.
Further reading
Bashor, Will (2013). Marie Antoinette's Head: The Royal Hairdresser, the Queen, and the Revolution. Lyons Press. p. 320. ISBN 978-0762791538.
Erickson, Carolly (1991). To the Scaffold. New York: William Morrow and Company, Inc.
Kaiser, Thomas. “From the Austrian Committee to the Foreign Plot: Marie-Antoinette, Austrophobia, and the Terror.” French Historical Studies 26 no. 4 (Fall 2003): 579-617.
Kates, Gary (1998). The French Revolution: Recent Debates and New Controversies 2nd ed. Routledge. pp. 201–218.
Lasky, Kathryn (2000). The Royal Diaries: Marie Antoinette, Princess of Versailles: Austria-France, 1769. New York: Scholastic. ISBN 978-0-439-07666-1.
Loomis, Stanley (1972). The Fatal Friendship: Marie Antoinette, Count Fersen and the flight to Varennes. London: Davis-Poynter. ISBN 978-0-7067-0047-3.
MacLeod, Margaret Anne (2008). There Were Three of Us in the Relationship: The Secret Letters of Marie Antoinette. Irvine, Scotland: Isaac MacDonald. ISBN 978-0-9559991-0-9.
Naslund, Sena Jeter (2006). Abundance: A Novel of Marie Antoinette. New York: William Morrow. ISBN 978-0-06-082539-3.
Romijn, André (2008). Vive Madame la Dauphine: A Biographical Novel. Ripon: Roman House. ISBN 978-0-9554100-2-4.
Thomas, Chantal (1999). The Wicked Queen: The Origins of the Myth of Marie-Antoinette. Trans. Julie Rose. New York: Zone Books. ISBN 978-0-942299-40-3.
Vidal, Elena Maria (1997). Trianon: A Novel of Royal France. Long Prairie, MN: Neumann Press. ISBN 978-0-911845-96-9.
Weber, Caroline (2006). Queen of Fashion: What Marie Antoinette Wore to the Revolution. New York: Henry Holt and Company.
Zweig, Stefan (2002). Marie Antoinette: The Portrait of an Average Woman. New York: Grove Press. ISBN 978-0-8021-3909-2.
External links
Marie-Antoinette at Encyclopædia Britannica
"Marie Antionette" in the Catholic Encyclopedia- Story of Marie Antoinette with Primary Sources
 Marie Antoinette public domain audiobook at LibriVox
Marie Antoinette public domain audiobook at LibriVox
Marie Antoinette at Find a Grave
Marie Antoinette's Head: The Royal Hairdresser, the Queen, and the Revolution – Lyons Press page- Marie Antoinette's official Versailles profile
Marie Antoinette Online – A site with a sympathetic bend, and contains a great deal of information.
The marais of Marie-Antoinette on parismarais.com
Tea At Trianon – Many articles on all things Antoinette, from Versailles to Trianon to the most obscure details of life in Royal France, by historian and author Elena Maria Vidal.
Online catalog of Marie Antoinette's personal reading library from the Petit-Trianon palace, based on 1863 printed catalog, online at LibraryThing.- If they have no bread, let them eat cake.
- 2015 Irish Examiner article
