Center of mass

This toy uses the principles of center of mass to keep balance on a finger
In physics, the center of mass of a distribution of mass in space is the unique point where the weighted relative position of the distributed mass sums to zero, or the point where if a force is applied it moves in the direction of the force without rotating. The distribution of mass is balanced around the center of mass and the average of the weighted position coordinates of the distributed mass defines its coordinates. Calculations in mechanics are often simplified when formulated with respect to the center of mass.
It is a hypothetical point where entire mass of an object may be assumed to be concentrated to visualise its motion.
In other words, the center of mass is the particle equivalent of a given object for application of Newton's laws of motion.
In the case of a single rigid body, the center of mass is fixed in relation to the body, and if the body has uniform density, it will be located at the centroid. The center of mass may be located outside the physical body, as is sometimes the case for hollow or open-shaped objects, such as a horseshoe. In the case of a distribution of separate bodies, such as the planets of the Solar System, the center of mass may not correspond to the position of any individual member of the system.
The center of mass is a useful reference point for calculations in mechanics that involve masses distributed in space, such as the linear and angular momentum of planetary bodies and rigid body dynamics. In orbital mechanics, the equations of motion of planets are formulated as point masses located at the centers of mass. The center of mass frame is an inertial frame in which the center of mass of a system is at rest with respect to the origin of the coordinate system.
Contents
1 History
2 Definition
2.1 A system of particles
2.2 A continuous volume
2.3 Barycentric coordinates
2.4 Systems with periodic boundary conditions
3 Center of gravity
4 Linear and angular momentum
5 Locating the center of mass
5.1 In two dimensions
5.2 In three dimensions
6 Applications
6.1 Engineering designs
6.1.1 Automotive applications
6.1.2 Aeronautics
6.2 Astronomy
6.3 Body motion
7 See also
8 Notes
9 References
10 External links
History
The concept of "center of mass" in the form of the center of gravity was first introduced by the great ancient Greek physicist, mathematician, and engineer Archimedes of Syracuse. He worked with simplified assumptions about gravity that amount to a uniform field, thus arriving at the mathematical properties of what we now call the center of mass. Archimedes showed that the torque exerted on a lever by weights resting at various points along the lever is the same as what it would be if all of the weights were moved to a single point—their center of mass. In work on floating bodies he demonstrated that the orientation of a floating object is the one that makes its center of mass as low as possible. He developed mathematical techniques for finding the centers of mass of objects of uniform density of various well-defined shapes.[1]
Later mathematicians who developed the theory of the center of mass include Pappus of Alexandria, Guido Ubaldi, Francesco Maurolico,[2]Federico Commandino,[3]Simon Stevin,[4]Luca Valerio,[5]Jean-Charles de la Faille, Paul Guldin,[6]John Wallis, Louis Carré, Pierre Varignon, and Alexis Clairaut.[7]
Newton's second law is reformulated with respect to the center of mass in Euler's first law.[8]
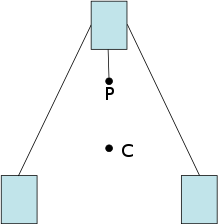
Diagram of an educational toy that balances on a point: the center of mass (C) settles below its support (P)
Definition
The center of mass is the unique point at the center of a distribution of mass in space that has the property that the weighted position vectors relative to this point sum to zero. In analogy to statistics, the center of mass is the mean location of a distribution of mass in space.
A system of particles
In the case of a system of particles Pi, i = 1, …, n , each with mass mi that are located in space with coordinates ri, i = 1, …, n , the coordinates R of the center of mass satisfy the condition
- ∑i=1nmi(ri−R)=0.displaystyle sum _i=1^nm_i(mathbf r _i-mathbf R )=0.
Solving this equation for R yields the formula
- R=1M∑i=1nmiri,displaystyle mathbf R =frac 1Msum _i=1^nm_imathbf r _i,
where M is the sum of the masses of all of the particles.
A continuous volume
If the mass distribution is continuous with the density ρ(r) within a solid Q, then the integral of the weighted position coordinates of the points in this volume relative to the center of mass R over the volume V is zero, that is
- ∭Qρ(r)(r−R)dV=0.displaystyle iiint limits _Qrho (mathbf r )(mathbf r -mathbf R )dV=0.
Solve this equation for the coordinates R to obtain
- R=1M∭Qρ(r)rdV,displaystyle mathbf R =frac 1Miiint limits _Qrho (mathbf r )mathbf r dV,
where M is the total mass in the volume.
If a continuous mass distribution has uniform density, which means ρ is constant, then the center of mass is the same as the centroid of the volume.[9]
Barycentric coordinates
The coordinates R of the center of mass of a two-particle system, P1 and P2, with masses m1 and m2 is given by
- R=1m1+m2(m1r1+m2r2).displaystyle mathbf R =frac 1m_1+m_2(m_1mathbf r _1+m_2mathbf r _2).
Let the percentage of the total mass divided between these two particles vary from 100% P1 and 0% P2 through 50% P1 and 50% P2 to 0% P1 and 100% P2, then the center of mass R moves along the line from P1 to P2. The percentages of mass at each point can be viewed as projective coordinates of the point R on this line, and are termed barycentric coordinates. Another way of interpreting the process here is the mechanical balancing of moments about an arbitrary point. The numerator gives the total moment that is then balanced by an equivalent total force at the center of mass. This can be generalized to three points and four points to define projective coordinates in the plane, and in space, respectively.
Systems with periodic boundary conditions
For particles in a system with periodic boundary conditions two particles can be neighbours even though they are on opposite sides of the system. This occurs often in molecular dynamics simulations, for example, in which clusters form at random locations and sometimes neighbouring atoms cross the periodic boundary. When a cluster straddles the periodic boundary, a naive calculation of the center of mass will be incorrect. A generalized method for calculating the center of mass for periodic systems is to treat each coordinate, x and y and/or z, as if it were on a circle instead of a line.[10]
The calculation takes every particle's x coordinate and maps it to an angle,
- θi=xixmax2πdisplaystyle theta _i=frac x_ix_max2pi
where xmax is the system size in the x direction and xi∈[0,xmax)displaystyle x_iin [0,x_max)


- ξi=cos(θi)displaystyle xi _i=cos(theta _i)
- ζi=sin(θi)displaystyle zeta _i=sin(theta _i)
In the (ξ,ζ)displaystyle (xi ,zeta )




- ξ¯=1M∑i=1nmiξi,displaystyle overline xi =frac 1Msum _i=1^nm_ixi _i,
- ζ¯=1M∑i=1nmiζi,displaystyle overline zeta =frac 1Msum _i=1^nm_izeta _i,
where M is the sum of the masses of all of the particles.
These values are mapped back into a new angle, θ¯displaystyle overline theta 
- θ¯=atan2(−ζ¯,−ξ¯)+πdisplaystyle overline theta =mathrm atan2 (-overline zeta ,-overline xi )+pi
- xcom=xmaxθ¯2πdisplaystyle x_com=x_maxfrac overline theta 2pi
The process can be repeated for all dimensions of the system to determine the complete center of mass. The utility of the algorithm is that it allows the mathematics to determine where the "best" center of mass is, instead of guessing or using cluster analysis to "unfold" a cluster straddling the periodic boundaries. If both average values are zero, (ξ¯,ζ¯)=(0,0)displaystyle (overline xi ,overline zeta )=(0,0)

Center of gravity
A body's center of gravity is the point around which the resultant torque due to gravity forces vanishes. Where a gravity field can be considered to be uniform, the mass-center and the center-of-gravity will be the same. However, for satellites in orbit around a planet, in the absence of other torques being applied to a satellite, the slight variation (gradient) in gravitational field between closer-to (stronger) and further-from (weaker) the planet can lead to a torque that will tend to align the satellite such that its long axis is vertical. In such a case, it is important to make the distinction between the center-of-gravity and the mass-center. Any horizontal offset between the two will result in an applied torque.
It is useful to note that the mass-center is a fixed property for a given rigid body (e.g. with no slosh or articulation), whereas the center-of-gravity may, in addition, depend upon its orientation in a non-uniform gravitational field. In the latter case, the center-of-gravity will always be located somewhat closer to the main attractive body as compared to the mass-center, and thus will change its position in the body of interest as its orientation is changed.
In the study of the dynamics of aircraft, vehicles and vessels, forces and moments need to be resolved relative to the mass center. That is true independent of whether gravity itself is a consideration. Referring to the mass-center as the center-of-gravity is something of a colloquialism, but it is in common usage and when gravity gradient effects are negligible, center-of-gravity and mass-center are the same and are used interchangeably.
In physics the benefits of using the center of mass to model a mass distribution can be seen by considering the resultant of the gravity forces on a continuous body. Consider a body Q of volume V with density ρ(r) at each point r in the volume. In a parallel gravity field the force f at each point r is given by,
- f(r)=−dmgk→=−ρ(r)dVgk→,displaystyle mathbf f (mathbf r )=-dm,gvec k=-rho (mathbf r )dV,gvec k,
where dm is the mass at the point r, g is the acceleration of gravity, and k is a unit vector defining the vertical direction.
Choose a reference point R in the volume and compute the resultant force and torque at this point,
- F=∭Qf(r)=∭Qρ(r)dV(−gk→)=−Mgk→,displaystyle mathbf F =iiint limits _Qmathbf f (mathbf r )=iiint limits _Qrho (mathbf r )dV(-gvec k)=-Mgvec k,
and
- T=∭Q(r−R)×f(r)=∭Q(r−R)×(−gρ(r)dVk→)=(∭Qρ(r)(r−R)dV)×(−gk→).displaystyle mathbf T =iiint limits _Q(mathbf r -mathbf R )times mathbf f (mathbf r )=iiint limits _Q(mathbf r -mathbf R )times (-grho (mathbf r )dVvec k)=left(iiint limits _Qrho (mathbf r )(mathbf r -mathbf R )dVright)times (-gvec k).
If the reference point R is chosen so that it is the center of mass, then
- ∭Qρ(r)(r−R)dV=0,displaystyle iiint limits _Qrho (mathbf r )(mathbf r -mathbf R )dV=0,
which means the resultant torque T=0. Because the resultant torque is zero the body will move as though it is a particle with its mass concentrated at the center of mass.
By selecting the center of gravity as the reference point for a rigid body, the gravity forces will not cause the body to rotate, which means the weight of the body can be considered to be concentrated at the center of mass.
Linear and angular momentum
The linear and angular momentum of a collection of particles can be simplified by measuring the position and velocity of the particles relative to the center of mass. Let the system of particles Pi, i=1,...,n of masses mi be located at the coordinates ri with velocities vi. Select a reference point R and compute the relative position and velocity vectors,
- ri=(ri−R)+R,vi=ddt(ri−R)+v.displaystyle mathbf r _i=(mathbf r _i-mathbf R )+mathbf R ,quad mathbf v _i=frac ddt(mathbf r _i-mathbf R )+mathbf v .
The total linear and angular momentum vectors relative to the reference point R are
- p=ddt(∑i=1nmi(ri−R))+(∑i=1nmi)v,displaystyle mathbf p =frac ddtleft(sum _i=1^nm_i(mathbf r _i-mathbf R )right)+left(sum _i=1^nm_iright)mathbf v ,
and
- L=∑i=1nmi(ri−R)×ddt(ri−R)+(∑i=1nmi(ri−R))×v.displaystyle mathbf L =sum _i=1^nm_i(mathbf r _i-mathbf R )times frac ddt(mathbf r _i-mathbf R )+left(sum _i=1^nm_i(mathbf r _i-mathbf R )right)times mathbf v .
If R is chosen as the center of mass these equations simplify to
- p=mv,L=∑i=1nmi(ri−R)×ddt(ri−R),displaystyle mathbf p =mmathbf v ,quad mathbf L =sum _i=1^nm_i(mathbf r _i-mathbf R )times frac ddt(mathbf r _i-mathbf R ),
where m is the total mass of all the particles, p is the linear momentum, and L is the angular momentum
The Law of Conservation of Momentum predicts that for any system not subjected to external forces the momentum of the system will remain constant, which means the center of mass will move with constant velocity. This applies for all systems with classical internal forces, including magnetic fields, electric fields, chemical reactions, and so on. More formally, this is true for any internal forces that cancel in accordance with Newton's Third Law.[11]
Locating the center of mass

Plumb line method
The experimental determination of the center of mass of a body uses gravity forces on the body and relies on the fact that in the parallel gravity field near the surface of the earth the center of mass is the same as the center of gravity.
The center of mass of a body with an axis of symmetry and constant density must lie on this axis. Thus, the center of mass of a circular cylinder of constant density has its center of mass on the axis of the cylinder. In the same way, the center of mass of a spherically symmetric body of constant density is at the center of the sphere. In general, for any symmetry of a body, its center of mass will be a fixed point of that symmetry.[12]
In two dimensions
An experimental method for locating the center of mass is to suspend the object from two locations and to drop plumb lines from the suspension points. The intersection of the two lines is the center of mass.[13]
The shape of an object might already be mathematically determined, but it may be too complex to use a known formula. In this case, one can subdivide the complex shape into simpler, more elementary shapes, whose centers of mass are easy to find. If the total mass and center of mass can be determined for each area, then the center of mass of the whole is the weighted average of the centers.[14] This method can even work for objects with holes, which can be accounted for as negative masses.[15]
A direct development of the planimeter known as an integraph, or integerometer, can be used to establish the position of the centroid or center of mass of an irregular two-dimensional shape. This method can be applied to a shape with an irregular, smooth or complex boundary where other methods are too difficult. It was regularly used by ship builders to compare with the required displacement and center of buoyancy of a ship, and ensure it would not capsize.[16][17]
In three dimensions
An experimental method to locate the three-dimensional coordinates of the center of mass begins by supporting the object at three points and measuring the forces, F1, F2, and F3 that resist the weight of the object, W=−Wk^displaystyle mathbf W =-Wmathbf hat k 

- T=(r1−R)×F1+(r2−R)×F2+(r3−R)×F3=0,displaystyle mathbf T =(mathbf r _1-mathbf R )times mathbf F _1+(mathbf r _2-mathbf R )times mathbf F _2+(mathbf r _3-mathbf R )times mathbf F _3=0,
or
- R×(−Wk^)=r1×F1+r2×F2+r3×F3.displaystyle mathbf R times (-Wmathbf hat k )=mathbf r _1times mathbf F _1+mathbf r _2times mathbf F _2+mathbf r _3times mathbf F _3.
This equation yields the coordinates of the center of mass R* in the horizontal plane as,
- R∗=−1Wk^×(r1×F1+r2×F2+r3×F3).displaystyle mathbf R ^*=-frac 1Wmathbf hat k times (mathbf r _1times mathbf F _1+mathbf r _2times mathbf F _2+mathbf r _3times mathbf F _3).
The center of mass lies on the vertical line L, given by
- L(t)=R∗+tk^.displaystyle mathbf L (t)=mathbf R ^*+tmathbf hat k .
The three-dimensional coordinates of the center of mass are determined by performing this experiment twice with the object positioned so that these forces are measured for two different horizontal planes through the object. The center of mass will be the intersection of the two lines L1 and L2 obtained from the two experiments.
Applications
Engineering designs
Automotive applications
Engineers try to design a sports car so that its center of mass is lowered to make the car handle better, that is maintaining traction while executing relatively sharp turns.
The characteristic low profile of the U. S. military Humvee was designed in part to allow it tilt farther than taller vehicles, without a rollover, because its low center of mass would stay over the space bounded the four wheels even at angles far from the horizontal.
Aeronautics
The center of mass is an important point on an aircraft, which significantly affects the stability of the aircraft. To ensure the aircraft is stable enough to be safe to fly, the center of mass must fall within specified limits. If the center of mass is ahead of the forward limit, the aircraft will be less maneuverable, possibly to the point of being unable to rotate for takeoff or flare for landing.[18] If the center of mass is behind the aft limit, the aircraft will be more maneuverable, but also less stable, and possibly so unstable that it is impossible to fly. The moment arm of the elevator will also be reduced, which makes it more difficult to recover from a stalled condition.[19]
For helicopters in hover, the center of mass is always directly below the rotorhead. In forward flight, the center of mass will move forward to balance the negative pitch torque produced by applying cyclic control to propel the helicopter forward; consequently a cruising helicopter flies "nose-down" in level flight.[20]
Astronomy
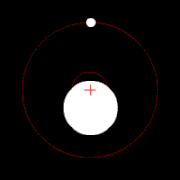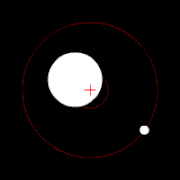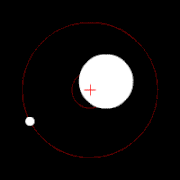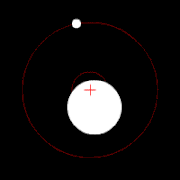
Two bodies orbiting their barycenter (red cross)
The center of mass plays an important role in astronomy and astrophysics, where it is commonly referred to as the barycenter. The barycenter is the point between two objects where they balance each other; it is the center of mass where two or more celestial bodies orbit each other. When a moon orbits a planet, or a planet orbits a star, both bodies are actually orbiting around a point that lies away from the center of the primary (larger) body.[21] For example, the Moon does not orbit the exact center of the Earth, but a point on a line between the center of the Earth and the Moon, approximately 1,710 km (1,062 miles) below the surface of the Earth, where their respective masses balance. This is the point about which the Earth and Moon orbit as they travel around the Sun. If the masses are more similar, e.g., Pluto and Charon, the barycenter will fall outside both bodies.
Body motion

Estimated center of mass/gravity of a high jumper doing a Fosbury Flop. Note that it is below the bar in this position.
When high jumpers perform a "Fosbury Flop", they bend their respective bodies in such a way that they clear the bar while their respective centers of mass do not necessarily do so.[22] Because it is the height of the center of gravity (rather than of the highest part of the body) that constrains the minimum energy investment for "clearing" the bar, "snaking over" the bar can reduce the energy expended in propelling the body upward.
In kinesiology and biomechanics, the center of mass is an important parameter that assists people in understanding their human locomotion. Typically, a human’s center of mass is detected with one of two methods: The reaction board method is a static analysis that involves the person lying down on that instrument, and use of their static equilibrium equation to find their center of mass; the segmentation method relies on a mathematical solution based on the physical principle that the summation of the torques of individual body sections, relative to a specified axis, must equal the torque of the whole system that constitutes the body, measured relative to the same axis.[23]
See also
- Barycenter
- Buoyancy
- Center of mass (relativistic)
- Center of percussion
- Center of pressure (fluid mechanics)
- Center of pressure (terrestrial locomotion)
- Centroid
- Circumcenter of mass
- Expected value
- Mass point geometry
- Metacentric height
- Roll center
- Weight distribution
Notes
^ Shore 2008, pp. 9–11.
^ Baron 2004, pp. 91–94.
^ Baron 2004, pp. 94–96.
^ Baron 2004, pp. 96–101.
^ Baron 2004, pp. 101–106.
^ Mancosu 1999, pp. 56–61.
^ Walton 1855, p. 2.
^ Beatty 2006, p. 29.
^ Levi 2009, p. 85.
^ Bai, Linge; Breen, David (2008). "Calculating Center of Mass in an Unbounded 2D Environment". Journal of Graphics, GPU, and Game Tools. 13 (4): 53–60. doi:10.1080/2151237X.2008.10129266..mw-parser-output cite.citationfont-style:inherit.mw-parser-output qquotes:"""""""'""'".mw-parser-output code.cs1-codecolor:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registrationcolor:#555.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration spanborder-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-errordisplay:none;font-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-errorfont-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-formatfont-size:95%.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-leftpadding-left:0.2em.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-rightpadding-right:0.2em
^ Kleppner & Kolenkow 1973, p. 117.
^ Feynman, Leighton & Sands 1963, p. 19.3.
^ Kleppner & Kolenkow 1973, pp. 119–120.
^ Feynman, Leighton & Sands 1963, pp. 19.1–19.2.
^ Hamill 2009, pp. 20–21.
^ "The theory and design of British shipbuilding". Amos Lowrey Ayre. p. 3 of 14. Retrieved 20 August 2012.
^ Sangwin 2006, p. 7.
^ Federal Aviation Administration 2007, p. 1.4.
^ Federal Aviation Administration 2007, p. 1.3.
^ "Helicopter Aerodynamics" (PDF). p. 82. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 March 2012. Retrieved 23 November 2013.
^ Murray & Dermott 1999, pp. 45–47.
^ Van Pelt 2005, p. 185.
^ Vint 2003, pp. 1–11.
References
Baron, Margaret E. (2004) [1969], The Origins of the Infinitesimal Calculus, Courier Dover Publications, ISBN 0-486-49544-2
Beatty, Millard F. (2006), Principles of Engineering Mechanics, Volume 2: Dynamics—The Analysis of Motion, Mathematical Concepts and Methods in Science and Engineering, 33, Springer, ISBN 0-387-23704-6
Feynman, Richard; Leighton, Robert; Sands, Matthew (1963), The Feynman Lectures on Physics, Addison Wesley, ISBN 0-201-02116-1
Federal Aviation Administration (2007), Aircraft Weight and Balance Handbook (PDF), United States Government Printing Office, archived from the original (PDF) on 19 October 2011, retrieved 23 October 2011
Giambattista, Alan; Richardson, Betty McCarthy; Richardson, Robert Coleman (2007), College physics, 1 (2nd ed.), McGraw-Hill Higher Education, ISBN 0-07-110608-1
Goldstein, Herbert; Poole, Charles; Safko, John (2001), Classical Mechanics (3rd ed.), Addison Wesley, ISBN 0-201-65702-3
Hamill, Patrick (2009), Intermediate Dynamics, Jones & Bartlett Learning, ISBN 978-0-7637-5728-1
Kleppner, Daniel; Kolenkow, Robert (1973), An Introduction to Mechanics (2nd ed.), McGraw-Hill, ISBN 0-07-035048-5
Levi, Mark (2009), The Mathematical Mechanic: Using Physical Reasoning to Solve Problems, Princeton University Press, ISBN 978-0-691-14020-9
Mancosu, Paolo (1999), Philosophy of mathematics and mathematical practice in the seventeenth century, Oxford University Press, ISBN 0-19-513244-0
Murray, Carl; Dermott, Stanley (1999), Solar System Dynamics, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-521-57295-9
Sangwin, Christopher J. (2006), "Locating the centre of mass by mechanical means" (PDF), Journal of the Oughtred Society, 15 (2), archived from the original (PDF) on 5 October 2011, retrieved 23 October 2011
Shore, Steven N. (2008), Forces in Physics: A Historical Perspective, Greenwood Press, ISBN 978-0-313-33303-3
Symon, Keith R. (1971), Mechanics (3rd ed.), Addison-Wesley, ISBN 0-201-07392-7
Van Pelt, Michael (2005), Space Tourism: Adventures in Earth Orbit and Beyond, Springer, ISBN 0-387-40213-6
Walton, William (1855), A collection of problems in illustration of the principles of theoretical mechanics (2nd ed.), Deighton, Bell & Co.
Asimov, Isaac (1988) [1966], Understanding Physics, Barnes & Noble Books, ISBN 0-88029-251-2
Beatty, Millard F. (2006), Principles of Engineering Mechanics, Volume 2: Dynamics—The Analysis of Motion, Mathematical Concepts and Methods in Science and Engineering, 33, Springer, ISBN 0-387-23704-6
Feynman, Richard; Leighton, Robert B.; Sands, Matthew (1963), The Feynman Lectures on Physics, 1 (Sixth printing, February 1977 ed.), Addison-Wesley, ISBN 0-201-02010-6
Frautschi, Steven C.; Olenick, Richard P.; Apostol, Tom M.; Goodstein, David L. (1986), The Mechanical Universe: Mechanics and heat, advanced edition, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-521-30432-6
Goldstein, Herbert; Poole, Charles; Safko, John (2002), Classical Mechanics (3rd ed.), Addison-Wesley, ISBN 0-201-65702-3
Goodman, Lawrence E.; Warner, William H. (2001) [1964], Statics, Dover, ISBN 0-486-42005-1
Hamill, Patrick (2009), Intermediate Dynamics, Jones & Bartlett Learning, ISBN 978-0-7637-5728-1
Jong, I. G.; Rogers, B. G. (1995), Engineering Mechanics: Statics, Saunders College Publishing, ISBN 0-03-026309-3
Millikan, Robert Andrews (1902), Mechanics, molecular physics and heat: a twelve weeks' college course, Chicago: Scott, Foresman and Company, retrieved 25 May 2011
O'Donnell, Peter J. (2015), Essential Dynamics and Relativity, CRC Press, ISBN 978-1-466-58839-4
Pollard, David D.; Fletcher, Raymond C. (2005), Fundamentals of Structural Geology, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-521-83927-0
Pytel, Andrew; Kiusalaas, Jaan (2010), Engineering Mechanics: Statics, 1 (3rd ed.), Cengage Learning, ISBN 978-0-495-29559-4
Rosen, Joe; Gothard, Lisa Quinn (2009), Encyclopedia of Physical Science, Infobase Publishing, ISBN 978-0-8160-7011-4
Serway, Raymond A.; Jewett, John W. (2006), Principles of physics: a calculus-based text, 1 (4th ed.), Thomson Learning, ISBN 0-534-49143-X
Shirley, James H.; Fairbridge, Rhodes Whitmore (1997), Encyclopedia of planetary sciences, Springer, ISBN 0-412-06951-2
De Silva, Clarence W. (2002), Vibration and shock handbook, CRC Press, ISBN 978-0-8493-1580-0
Symon, Keith R. (1971), Mechanics, Addison-Wesley, ISBN 978-0-201-07392-8
Tipler, Paul A.; Mosca, Gene (2004), Physics for Scientists and Engineers, 1A (5th ed.), W. H. Freeman and Company, ISBN 0-7167-0900-7
Vint, Peter (2003), "LAB: Center of Mass (Center of Gravity) of the Human Body" (PDF), KIN 335 - Biomechanics, retrieved 18 October 2013
External links
| Look up barycenter in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
Motion of the Center of Mass shows that the motion of the center of mass of an object in free fall is the same as the motion of a point object.
The Solar System's barycenter, simulations showing the effect each planet contributes to the Solar System's barycenter.
Center of Gravity at Work, video showing objects climbing up an incline by themselves.























