Madeira
Madeira | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Autonomous Region | |||
 A January 2014 view of Funchal, the capital city of the autonomous region. | |||
| |||
| Etymology: madeira, Portuguese for wood | |||
| Motto(s): Das Ilhas as Mais Belas e Livres (English: Of all islands, the most beautiful and free) | |||
 Location of Madeira relative to Portugal (green) and the rest of the European Union (light green) | |||
| Country | |||
| Autonomous Region | |||
| Region | Atlantic Ocean | ||
| Subregion | Tore-Madeira Ridge | ||
| Position | Madeira Platform, Savage Islands submarine mount | ||
| Settlement | c. 1420 | ||
| Administrative autonomy | c. 1895 | ||
| Political autonomy | 1 July 1976 | ||
| Capital | Funchal | ||
| Municipalities | Calheta, Câmara de Lobos, Machico, Ponta do Sol, Porto Moniz, Porto Santo, Ribeira Brava, Santa Cruz, Santana, São Vicente | ||
| Government | |||
| • President (Government) | Miguel Albuquerque | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 741 km2 (286 sq mi) | ||
| Population (2016) | |||
| • Total | 289,000 | ||
| • Density | 390/km2 (1,000/sq mi) | ||
| Time zone | UTC+0 (WET) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+1 (WEST) | ||
| Postal code | 9XXX-XXX | ||
| Area code(s) | (+351) 291 XXX XXX | ||
HDI (2017) | 0.800[1] very high · 6th | ||
| Date format | dd-mm-yyyy | ||
| Drive | right-side | ||
| Demonym | Madeiran; Madeirense | ||
| Patron Saint | Nossa Senhora do Monte | ||
| Holiday | 1 July | ||
| Anthem |
| ||
| Currency | Euro (€)[2] | ||
| Website | www.madeira.gov.pt | ||
| Geographic detail from CAOP (2010)[3] produced by Instituto Geográfico Português (IGP) | |||
Madeira (/məˈdɪərə/ mə-DEER-ə, /məˈdɛərə/ mə-DAIR-ə; Portuguese: [mɐˈðejɾɐ, -ˈðɐj-]), officially the Autonomous Region of Madeira (Região Autónoma da Madeira), is one of the two autonomous regions of Portugal (along with the Azores). It is an archipelago situated in the north Atlantic Ocean, southwest of Portugal. Its total population was estimated in 2011 at 267,785. The capital of Madeira is Funchal, which is located on the main island's south coast.
The archipelago is just under 400 kilometres (250 mi) north of Tenerife, Canary Islands. Bermuda and Madeira, a few time zones apart, are the only land in the Atlantic on the 32nd parallel north. It includes the islands of Madeira, Porto Santo, and the Desertas, administered together with the separate archipelago of the Savage Islands. The region has political and administrative autonomy through the Administrative Political Statue of the Autonomous Region of Madeira provided for in the Portuguese Constitution. The autonomous region is an integral part of the European Union as an outermost region.[4]
Madeira was claimed by Portuguese sailors in the service of Prince Henry the Navigator in 1419 and settled after 1420. The archipelago is considered to be the first territorial discovery of the exploratory period of the Age of Discovery.
Today, it is a popular year-round resort, being visited every year by about 1.4 million tourists,[5] almost five times its population. The region is noted for its Madeira wine, gastronomy, historical and cultural value, flora and fauna, landscapes (laurel forest) which are classified as a UNESCO World Heritage Site, and embroidery artisans. The main harbour in Funchal has long been the leading Portuguese port in cruise liner dockings,[6] receiving more than half a million tourists though its main port in 2017,[7] being an important stopover for commercial and trans-Atlantic passenger cruises between Europe, the Caribbean and North Africa. In addition, the International Business Centre of Madeira also known as the Madeira Free Trade Zone, was created formally in the 1980s as a tool of regional economic policy. It consists of a set of incentives, mainly tax-related, granted with the objective of attracting foreign direct investment based on international services into Madeira.[8]
Contents
1 History
1.1 Exploration
1.2 Legend
1.3 Discovery
1.4 Settlement
1.5 World War I
1.6 Autonomy and modern history
2 Geography
2.1 Islands and islets
2.1.1 Madeira Island
3 Climate
4 Flora and fauna
4.1 Native flora gallery
4.2 Native birds gallery
4.3 Madeiran wall lizard
5 Levadas
6 Governance
6.1 Funchal
7 Population
7.1 Demographics
7.2 Diaspora
7.3 Immigration
8 Economy
8.1 Free Trade Zone and Public Administration
8.2 Tourism
8.2.1 Whale watching
9 Renewable energy
10 Transport
11 Culture
11.1 Music
11.2 Cuisine
11.3 Beverages
12 Sports
13 Sister provinces
14 Postage stamps
15 Notable people
16 See also
17 References
17.1 Bibliography
18 External links
History
Exploration
Plutarch in his Parallel Lives (Sertorius, 75 AD) referring to the military commander Quintus Sertorius (d. 72 BC), relates that after his return to Cádiz, he met sailors who spoke of idyllic Atlantic islands: "The islands are said to be two in number separated by a very narrow strait and lie 10,000 furlongs (2,011.68 km) from Africa. They are called the Isles of the Blest."[9]
Archeological evidence suggests that the islands may have been visited by the Vikings sometime between 900 and 1030.[10]
Legend
During the reign of King Edward III of England, lovers Robert Machim and Anna d'Arfet were said to have fleed from England to France in 1346. They were driven off their course by a violent storm, and their ship ran aground along the coast of an island that may have been Madeira. Later this legend was the basis of the naming of the city of Machico on the island, in memory of the young lovers.[11]
Discovery
Knowledge of some Atlantic islands, such as Madeira, existed before their formal discovery and settlement, as the islands were shown on maps as early as 1339.[12]

Statue of João Gonçalves Zarco
In 1418, two captains under service to Prince Henry the Navigator, João Gonçalves Zarco and Tristão Vaz Teixeira, were driven off course by a storm to an island which they named Porto Santo (English: holy harbour) in gratitude for divine deliverance from a shipwreck. The following year, an organised expedition, under the captaincy of Zarco, Vaz Teixeira, and Bartolomeu Perestrello, traveled to the island to claim it on behalf of the Portuguese Crown. Subsequently, the new settlers observed "a heavy black cloud suspended to the southwest."[13] Their investigation revealed it to be the larger island they called Madeira.[14]
Settlement

Cathedral of Funchal with its tower of 15th-century Gothic style in the background
The first Portuguese settlers began colonizing the islands around 1420 or 1425.[15]
Grain production began to fall and the ensuing crisis forced Henry the Navigator to order other commercial crops to be planted so that the islands could be profitable.[citation needed] These specialised plants, and their associated industrial technology, created one of the major revolutions on the islands and fuelled Portuguese industry. Following the introduction of the first water-driven sugar mill on Madeira, sugar production increased to over 6,000 arrobas (an arroba was equal to 11 to 12 kilograms) by 1455,[16] using advisers from Sicily and financed by Genoese capital. (Genoa acted as an integral part of the island economy until the 17th century.) The accessibility of Madeira attracted Genoese and Flemish traders, who were keen to bypass Venetian monopolies.
.mw-parser-output .templatequoteoverflow:hidden;margin:1em 0;padding:0 40px.mw-parser-output .templatequote .templatequoteciteline-height:1.5em;text-align:left;padding-left:1.6em;margin-top:0
"By 1480 Antwerp had some seventy ships engaged in the Madeira sugar trade, with the refining and distribution concentrated in Antwerp. By the 1490s Madeira had overtaken Cyprus as a producer of sugar."[17]
Sugarcane production was the primary engine of the island's economy, increasing the demand for labour. African slaves were used during portions of the island's history to cultivate sugar cane, and the proportion of imported slaves reached 10% of the total population of Madeira by the 16th century.[18]
Barbary corsairs from North Africa, who enslaved Europeans from ships and coastal communities throughout the Mediterranean region, captured 1,200 people in Porto Santo in 1617.[19][20] After the 17th century, as Portuguese sugar production was shifted to Brazil, São Tomé and Príncipe and elsewhere, Madeira's most important commodity product became its wine.[citation needed]
The British first amicably occupied the island in 1801 whereafter Colonel William Henry Clinton became governor.[21] A detachment of the 85th Regiment of Foot under Lieutenant-colonel James Willoughby Gordon garrisoned the island.[22]
After the Peace of Amiens, British troops withdrew in 1802, only to reoccupy Madeira in 1807 until the end of the Peninsular War in 1814.[23]
World War I
On 31 December 1916, during the Great War, a German U-boat, SM U-38, captained by Max Valentiner, entered Funchal harbour on Madeira. U-38 torpedoed and sank three ships, bringing the war to Portugal by extension. The ships sunk were:
- CS Dacia (1,856 tons), a British cable-laying vessel.[24]Dacia had previously undertaken war work off the coast of Casablanca and Dakar. It was in the process of diverting the German South American cable into Brest, France.[25]
SS Kanguroo (2,493 tons), a French specialized "heavy-lift" transport.[26]
Surprise (680 tons), a French gunboat. Her commander and 34 crewmen (including 7 Portuguese) were killed.[27]
After attacking the ships, U-38 bombarded Funchal for two hours from a range of about 2 miles (3 km). Batteries on Madeira returned fire and eventually forced U-38 to withdraw.[28]
On 12 December 1917, two German U-boats, SM U-156 and SM U-157 (captained by Max Valentiner), again bombarded Funchal.[29] This time the attack lasted around 30 minutes. The U-boats fired 40 4.7-and-5.9-inch (120 and 150 mm) shells. There were three fatalities and 17 wounded; a number of houses and Santa Clara church were hit.[citation needed]
Charles I (Karl I), the last Emperor of the Austro-Hungarian Empire, went to Madeira after the war. Determined to prevent an attempt to restore Charles to the throne, the Council of Allied Powers agreed he could go into exile on Madeira because it was isolated in the Atlantic and easily guarded.[30] He died there on 1 April 1922 and his coffin lies in a chapel of the church in Monte.
Autonomy and modern history
On 1 July 1976, following the democratic revolution of 1974, Portugal granted political autonomy to Madeira, celebrated on Madeira Day. The region now has its own government and legislative assembly.
On 20 February 2010 at least 42 people died[31] and 100 were injured[32] by the 2010 Madeira floods and mudslides that affected the Island.

NASA satellite image of wildfires on the island of Madeira from 19 July 2012
Drought conditions, coupled with hot and windy weather in summer, have caused numerous wildfires in recent years. The largest of the fires in August 2010 burned through 95 percent of the Funchal Ecological Park, a 1,000-hectare preserve set aside to restore native vegetation to the island.[33][34]
In July 2012 Madeira was suffering again from severe drought. Wildfires broke out on 18 July, in the midst of temperatures up to 40 °C (more than 100 °F) and high winds. By 20 July, fires had spread to the nearby island of Porto Santo, and firefighters were sent from mainland Portugal to contain the multiple blazes.[35][36][37][38]
In October 2012, it was reported that there was a dengue fever epidemic on the island.[39][40] There was a total of 2,168 cases reported of dengue fever since the start in October 2012. The number of cases was on the decline since mid November 2012 and by 4 February 2013, no new cases had been reported.[41]
In August 2013, a hospital and some private homes were evacuated as a wildfire approached Funchal. A number of homes were destroyed when the fire hit Monte, a suburb of Funchal.[42][43]
In August 2016, wildfires caused over 1,000 people to be evacuated, destroyed 150 homes, and led to the death of three people, all of whom are said to have been elderly.[44][45][46] The wildfires threatened Funchal and other administrative regions of Madeira, such as Calheta.
In August 2017, a falling tree killed at least 13 people and injured 49 at a religious ceremony. People had gathered outside the Church of Our Lady of Monte in Monte, to celebrate the Roman Catholic Feast of the Assumption, which takes place on Tuesday and is a public holiday. The Lady of the Mount festival is the island's biggest.[47]
In 2019 Madeira island will celebrate six centuries since its formal discovery by the Portuguese.[48][49]
Geography

Distribution of the islands of the archipelago (not including the Savage Islands)

Sights from Bica da Cana showing Madeira's high orography
The archipelago of Madeira is located 520 km (280 nmi) from the African coast and 1,000 km (540 nmi) from the European continent (approximately a one-and-a-half hour flight from the Portuguese capital of Lisbon).[50] Madeira is on the same parallel as Bermuda a few time zones farther west in the Atlantic. The two archipelagos are the only land in the Atlantic on the 32nd parallel north. Madeira is found in the extreme south of the Tore-Madeira Ridge, a bathymetric structure of great dimensions oriented along a north-northeast to south-southwest axis that extends for 1,000 kilometres (540 nmi). This submarine structure consists of long geomorphological relief that extends from the abyssal plain to 3500 metres; its highest submersed point is at a depth of about 150 metres (around latitude 36ºN). The origins of the Tore-Madeira Ridge are not clearly established, but may have resulted from a morphological buckling of the lithosphere.[51][52]
Islands and islets
Madeira (740.7 km²), including Ilhéu de Agostinho, Ilhéu de São Lourenço, Ilhéu Mole (northwest); Total population: 262,456 (2011 Census).
Porto Santo (42.5 km²), including Ilhéu de Baixo ou da Cal, Ilhéu de Ferro, Ilhéu das Cenouras, Ilhéu de Fora, Ilhéu de Cima; Total population: 5,483 (2011 Census).
Desertas Islands (14.2 km²), including the three uninhabited islands: Deserta Grande Island, Bugio Island and Ilhéu de Chão.
Savage Islands (3.6 km²), archipelago 280 km south-southeast of Madeira Island including three main islands and 16 uninhabited islets in two groups: the Northwest Group (Selvagem Grande Island, Ilhéu de Palheiro da Terra, Ilhéu de Palheiro do Mar) and the Southeast Group (Selvagem Pequena Island, Ilhéu Grande, Ilhéu Sul, Ilhéu Pequeno, Ilhéu Fora, Ilhéu Alto, Ilhéu Comprido, Ilhéu Redondo, Ilhéu Norte).
Madeira Island

Detailed, true-colour image of Madeira. The image shows that deep green forest Laurissilva survives intact on the steep northern slopes of the island, but in the south, where terrain is gentler, the terracotta colour of towns and the light green colour of agriculture are more dominant
The island of Madeira is at the top of a massive shield volcano that rises about 6 km (20,000 ft) from the floor of the Atlantic Ocean, on the Tore underwater mountain range. The volcano formed atop an east-west rift[53][54] in the oceanic crust along the African Plate, beginning during the Miocene epoch over 5 million years ago, continuing into the Pleistocene until about 700,000 years ago.[55] This was followed by extensive erosion, producing two large amphitheatres open to south in the central part of the island. Volcanic activity later resumed, producing scoria cones and lava flows atop the older eroded shield. The most recent volcanic eruptions were on the west-central part of the island only 6,500 years ago, creating more cinder cones and lava flows.[55]
It is the largest island of the group with an area of 741 km2 (286 sq mi), a length of 57 km (35 mi) (from Ponte de São Lourenço to Ponte do Pargo), while approximately 22 km (14 mi) at its widest point (from Ponte da Cruz to Ponte São Jorge), with a coastline of 150 km (90 mi). It has a mountain ridge that extends along the centre of the island, reaching 1,862 metres (6,109 feet) at its highest point (Pico Ruivo), while much lower (below 200 metres) along its eastern extent. The primitive volcanic foci responsible for the central mountainous area, consisted of the peaks: Ruivo (1,862 m), Torres (1,851 m), Arieiro (1,818 m), Cidrão (1,802 m), Cedro (1,759 m), Casado (1,725 m), Grande (1,657 m), Ferreiro (1,582 m). At the end of this eruptive phase, an island circled by reefs was formed, its marine vestiges are evident in a calcareous layer in the area of Lameiros, in São Vicente (which was later explored for calcium oxide production). Sea cliffs, such as Cabo Girão, valleys and ravines extend from this central spine, making the interior generally inaccessible.[56] Daily life is concentrated in the many villages at the mouths of the ravines, through which the heavy rains of autumn and winter usually travel to the sea.[57]
Climate
Madeira has been classified as a Mediterranean climate (Köppen climate classification: Csa/Csb).[58] Based on differences in sun exposure, humidity, and annual mean temperature, there are clear variations between north- and south-facing regions, as well as between some islands. The islands are strongly influenced by the Gulf Stream and Canary Current, giving mild year-round temperatures; according to the Instituto de Meteorologia (IM), the average annual temperature at Funchal weather station is 19.6 °C (67.3 °F) for the 1980–2010 period. Porto Santo has at least one weather station with a semiarid climate (BSh). On the highest windward slopes of Madeira, rainfall exceeds 1,250 mm (50 inches) per year, mostly falling between October and April. In most winters snowfall occurs in the mountains of Madeira.
View from Pico do Arieiro

Lava pools[59] in Porto Moniz

Porto Santo's lack of higher mountains results in a paradoxical landscape when comparing it with its sister island Madeira

The Desertas Islands in the distance at sunrise

In some winters snow can occasionally be seen from Funchal, while the temperatures in the city stay mild

Accentuated orography produces sui generis climate in Madeira Island
| Climate data for Funchal, capital of Madeira | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 25.5 (77.9) | 27.0 (80.6) | 30.5 (86.9) | 32.6 (90.7) | 34.2 (93.6) | 34.7 (94.5) | 37.7 (99.9) | 38.5 (101.3) | 38.4 (101.1) | 34.1 (93.4) | 29.5 (85.1) | 25.9 (78.6) | 38.5 (101.3) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 19.7 (67.5) | 19.7 (67.5) | 20.4 (68.7) | 20.6 (69.1) | 21.6 (70.9) | 23.4 (74.1) | 25.1 (77.2) | 26.4 (79.5) | 26.4 (79.5) | 24.9 (76.8) | 22.6 (72.7) | 20.7 (69.3) | 22.6 (72.7) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 16.7 (62.1) | 16.6 (61.9) | 17.2 (63.0) | 17.5 (63.5) | 18.6 (65.5) | 20.6 (69.1) | 22.2 (72.0) | 23.2 (73.8) | 23.2 (73.8) | 21.8 (71.2) | 19.6 (67.3) | 17.9 (64.2) | 19.6 (67.3) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 13.7 (56.7) | 13.4 (56.1) | 13.9 (57.0) | 14.4 (57.9) | 15.6 (60.1) | 17.7 (63.9) | 19.2 (66.6) | 20.0 (68.0) | 20.0 (68.0) | 18.6 (65.5) | 16.6 (61.9) | 15.0 (59.0) | 16.5 (61.7) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 8.2 (46.8) | 7.4 (45.3) | 8.1 (46.6) | 9.8 (49.6) | 9.7 (49.5) | 13.2 (55.8) | 14.6 (58.3) | 16.4 (61.5) | 16.6 (61.9) | 13.4 (56.1) | 9.8 (49.6) | 6.4 (43.5) | 6.4 (43.5) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 74.1 (2.92) | 83.0 (3.27) | 60.2 (2.37) | 44.0 (1.73) | 28.9 (1.14) | 7.2 (0.28) | 1.6 (0.06) | 2.0 (0.08) | 32.9 (1.30) | 89.5 (3.52) | 88.8 (3.50) | 115.0 (4.53) | 627.2 (24.7) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 12 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 6 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 6 | 9 | 10 | 13 | 87 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 167.4 | 171.1 | 204.6 | 225.0 | 213.9 | 198.0 | 244.9 | 260.4 | 225.0 | 204.6 | 168.0 | 164.3 | 2,447.2 |
| Source: Instituto de Meteorologia,[60]ClimaTemps.com[61]for Sunshine hours data | |||||||||||||
Flora and fauna
In the south, there is very little left of the indigenous subtropical rainforest which once covered the whole island[citation needed] (the original settlers set fire to the island to clear the land for farming) and gave it the name it now bears (Madeira means "wood" in Portuguese). However, in the north, the valleys contain native trees of fine growth. These "laurisilva" forests, called lauraceas madeirense, notably the forests on the northern slopes of Madeira Island, are designated as a World Heritage Site by UNESCO.The paleobotanical record of Madeira reveals that laurisilva forest has existed in this island for at least 1.8 million years.[62] Critically endangered species such as the vine Jasminum azoricum[63] and the rowan Sorbus maderensis are endemic to Madeira.
Native flora gallery
Native birds gallery
Madeiran wall lizard

Madeiran wall lizard (Lacerta dugesii) captured in Levada do Norte, Madeira
The Madeiran wall lizard (Lacerta dugesii) is a species of lizard in the Lacertidae family. The species is endemic to the Island where it is very common, and is the only small lizard, ranging from sea coasts to altitudes of 1,850 metres (6,070 ft). It is usually found in rocky places or among scrub and may climb into trees. It is also found in gardens and on the walls of buildings. It feeds on small invertebrates such as ants and also eats some vegetable matter. The tail is easily shed and the stump regenerates slowly. The colouring is variable and tends to match the colour of the animal's surroundings, being some shade of brown or grey with occasionally a greenish tinge. Most animals are finely flecked with darker markings. The underparts are white or cream, sometimes with dark spots, with some males having orange or red underparts and blue throats, but these bright colours may fade if the animal is disturbed.[64] The Madeiran wall lizard grows to a snout-to-vent length of about 8 cm (3.1 in) with a tail about 1.7 times the length of its body. Females lay two to three clutches of eggs in a year with the juveniles being about 3 cm (1.2 in) when they hatch.[64]
Levadas

A levada
The island of Madeira is wet in the northwest, but dry in the southeast. In the 16th century the Portuguese started building levadas or aqueducts to carry water to the agricultural regions in the south. Madeira is very mountainous, and building the levadas was difficult and often convicts or slaves were used.[65] Many are cut into the sides of mountains, and it was also necessary to dig 25 miles (40 km) of tunnels, some of which are still accessible.
Today the levadas not only supply water to the southern parts of the island, but provide hydro-electric power.[66] There are over 1,350 miles (2,170 km) of levadas and they provide a network of walking paths. Some provide easy and relaxing walks through the countryside, but others are narrow, crumbling ledges where a slip could result in serious injury or death.
Two of the most popular levadas to hike are the Levada do Caldeirão Verde and the Levada do Caldeirão do Inferno, which should not be attempted by hikers prone to vertigo or without torches and helmets. The Levada do Caniçal is a much easier walk, running 7.1 miles (11.4 km) from Maroços to the Caniçal Tunnel. It is known as the mimosa levada, because "mimosa" trees, (the colloquial name for invasive acacia) are found all along the route.
Governance
Administratively, Madeira (with a population of 267,302 inhabitants in 2011[67]) and covering an area of 768.0 km2 (296.5 sq mi) is organised into eleven municipalities:[68]
| Municipality | Population (2011)[67] | Area | Main settlement | Parishes |
Funchal[69] | 111,892 | 7007757000000000000♠75.7 km2 (29.2 sq mi) | Funchal | 10 |
Santa Cruz[70] | 43,005 | 7007680000000000000♠68.0 km2 (26.3 sq mi) | Santa Cruz | 5 |
| Câmara de Lobos | 35,666 | 7007526000000000000♠52.6 km2 (20.3 sq mi) | Câmara de Lobos | 5 |
| Machico | 21,828 | 7007676000000000000♠67.6 km2 (26.1 sq mi) | Machico | 5 |
| Ribeira Brava | 13,375 | 7007649000000000000♠64.9 km2 (25.1 sq mi) | Ribeira Brava | 4 |
| Calheta | 11,521 | 7008110300000000000♠110.3 km2 (42.6 sq mi) | Calheta | 8 |
| Ponta do Sol | 8,862 | 7007468000000000000♠46.8 km2 (18.1 sq mi) | Ponta do Sol | 3 |
| Santana | 7,719 | 7007931000000000000♠93.1 km2 (35.9 sq mi) | Santana | 6 |
| São Vicente | 5,723 | 7007808000000000000♠80.8 km2 (31.2 sq mi) | São Vicente | 3 |
Porto Santo[71] | 5,483 | 7007424000000000000♠42.4 km2 (16.4 sq mi) | Vila Baleira | 1 |
| Porto Moniz | 2,711 | 7007826000000000000♠82.6 km2 (31.9 sq mi) | Porto Moniz | 4 |
Funchal

Partial view of the capital as seen from the mountains above it
Funchal is the capital and principal city of the Autonomous Region of Madeira, located along the southern coast of the island of Madeira. It is a modern city, located within a natural geological "amphitheatre" composed of vulcanological structure and fluvial hydrological forces. Beginning at the harbour (Porto de Funchal), the neighbourhoods and streets rise almost 1,200 metres (3,900 ft), along gentle slopes that helped to provide a natural shelter to the early settlers.
Population
Demographics
The island was settled by Portuguese people, especially farmers from the Minho region,[72] meaning that Madeirans (Portuguese: Madeirenses), as they are called, are ethnically Portuguese, though they have developed their own distinct regional identity and cultural traits.
The region has a total population of just under 270,000, the majority of whom live on the main island of Madeira where the population density is 6996337000000000000♠337/km2; meanwhile only around 5,000 live on the Porto Santo island where the population density is 6996112000000000000♠112/km2.
About 247,000 (96%) of the population are Catholic and Funchal is the location of the Catholic cathedral.[73]
Diaspora
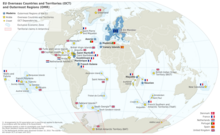
Map of the European Union in the world, with overseas countries and territories (OCT) and outermost regions (OMR) for which Madeira is included
Madeirans migrated to the United States, Venezuela, Brazil, British Guiana, St. Vincent and Trinidad.[74][75] Madeiran immigrants in North America mostly clustered in the New England and mid-Atlantic states, Toronto, Northern California, and Hawaii. The city of New Bedford is especially rich in Madeirans, hosting the Museum of Madeira Heritage, as well as the annual Madeiran and Luso-American celebration, the Feast of the Blessed Sacrament, the world's largest celebration of Madeiran heritage, regularly drawing crowds of tens of thousands to the city's Madeira Field.
In 1846, when a famine struck Madeira over 6,000 of the inhabitants migrated to British Guiana. In 1891 they numbered 4.3% of the population.[76] In 1902 in Honolulu, Hawaii there were 5,000 Portuguese people, mostly Madeirans. In 1910 this grew to 21,000.[77]
1849 saw an emigration of Protestant religious exiles from Madeira to the United States, by way of Trinidad and other locations in the West Indies. Most of them settled in Illinois[78] with financial and physical aid of the American Protestant Society, headquartered in New York City. In the late 1830s the Reverend Robert Reid Kalley, from Scotland, a Presbyterian minister as well as a physician, made a stop at Funchal, Madeira on his way to a mission in China, with his wife, so that she could recover from an illness. The Rev. Kalley and his wife stayed on Madeira where he began preaching the Protestant gospel and converting islanders from Catholicism.[79] Eventually, the Rev. Kalley was arrested for his religious conversion activities and imprisoned. Another missionary from Scotland, William Hepburn Hewitson, took on Protestant ministerial activities in Madeira. By 1846, about 1,000 Protestant Madeirenses, who were discriminated against and the subjects of mob violence because of their religious conversions, chose to immigrate to Trinidad and other locations in the West Indies in answer for a call for sugar plantation workers.[80] The Madeirenses exiles did not fare well in the West Indies. The tropical climate was unfamiliar and they found themselves in serious economic difficulties. By 1848, the American Protestant Society raised money and sent the Rev. Manuel J. Gonsalves, a Baptist minister and a naturalized U.S. citizen from Madeira, to work with the Rev. Arsenio da Silva, who had emigrated with the exiles from Madeira, to arrange to resettle those who wanted to come to the United States. The Rev. da Silva died in early 1849. Later in 1849, the Rev. Gonsalves was then charged with escorting the exiles from Trinidad to be settled in Sangamon and Morgan counties in Illinois on land purchased with funds raised by the American Protestant Society. Accounts state that anywhere from 700 to 1,000 exiles came to the United States at this time.[81][82]
There are several large Madeiran communities around the world, such as the number in the UK, including Jersey,[83] the Portuguese British community mostly made up of Madeirans celebrate Madeira Day.
Immigration
Madeira is part of the Schengen Area.
The Venezuelan (14.4%), British (14.2%), Brazilian (12.1%) and German (7.0%) nationalities constituted the largest foreign communities residing in the Autonomous Region of Madeira in 2017. The Venezuelan community showed a sharp increase (38.0%). In terms of geographical distribution, it is in Funchal that the foreign population mainly concentrates (59.2% of the total of the Region), followed by Santa Cruz (13.8%), Calheta (7.3%) and Porto Santo (4.0%). The foreign population with resident status in the Autonomous Region of Madeira totaled 6,720 (up by 10.0% from 2016), distributed between residence permits (6,692) and long-stay visas (28).[84]
Economy
Free Trade Zone and Public Administration

Caniçal on the left and Madeira Free Trade Zone on the right
The setting-up of a free trade zone has led to the installation, under more favourable conditions, of infrastructure, production shops and essential services for small and medium-sized industrial enterprises. The International Business Centre of Madeira comprises presently three sectors of investment: the Industrial Free Trade Zone, the International Shipping Register – MAR and the International Services. Madeira's tax regime has been approved by the European Commission as legal State Aid and its deadline has recently been extended by the E.C. until the end of 2027. The International Business Centre of Madeira, also known as Madeira Free Trade Zone, was created formally in the 1980s as a tool of regional economic policy. It consists of a set of incentives, mainly of a tax nature, granted with the objective of attracting inward investment into Madeira, recognized as the most efficient mechanism to modernize, diversify and internationalize the regional economy. The decision to create the International Business Centre of Madeira was the result of a thorough process of analysis and study. Other small island economies, with similar geographical and economic restraints, had successfully implemented projects of attraction of foreign direct investment based on international services activities, becoming therefore examples of successful economic policies.
Since the beginning, favorable operational and fiscal conditions have been offered in the context of a preferential tax regime, fully recognized and approved by the European Commission in the framework of State aid for regional purposes and under the terms for the Ultra-peripheral Regions set in the Treaties, namely Article 299 of the Treaty on European Union. The IBC of Madeira has therefore been fully integrated in the Portuguese and EU legal systems and, as a consequence, it is regulated and supervised by the competent Portuguese and EU authorities in a transparent and stable business environment, marking a clear difference from the so-called "tax havens" and "offshore jurisdictions", since its inception. In 2015, the European Commission authorized the new state aid regime for new companies incorporated between 2015 and 2020 and the extension of the deadline of the tax reductions until the end of 2027. The present tax regime is outlined in Article 36°-A of the Portuguese Tax Incentives Statute. Available data clearly demonstrates the contribution that this development programme has brought to the local economy over its 20 years of existence: impact in the local labour market, through the creation of qualified jobs for the young population but also for madeiran professionals who have returned to Madeira thanks to the opportunities now created; an increase in productivity due to the transfer of know how and the implementation of new business practices and technologies; indirect influence on other sectors of activity: business tourism benefits from the visits of investors and their clients and suppliers, and other sectors such as real estate, telecommunications and other services benefit from the growth of their client base; impact on direct sources of revenue: the companies attracted by the IBC of Madeira represent over 40% of the revenue in terms of corporate income tax for the Government of Madeira and nearly 3.000 jobs, most of which qualified, amongst other benefits. Also there are above average salaries paid by the companies in the IBC of Madeira in comparison with the wages paid in the other sectors of activity in Madeira.[85]
Madeira has been a significant recipient of European Union funding, totalling up to €2 billion. In 2012, it was reported that despite a population of just 250,000, the local administration owes some €6 billion.[86] Furthermore, the Portuguese treasury (IGCP) assumed Madeira's debt management between 2012 and 2015. The region continues to work with the central government on a long-term plan to reduce its debt levels and commercial debt stock. Moody's notes that the region has made significant fiscal consolidation efforts and that its tax revenue collection has increased significantly in recent years due to tax rate hikes. Madeira's tax revenues increased by 41% between 2012 and 2016, helping the region to reduce its deficit to operating revenue ratio to 10% in 2016 from 77% in 2013.[87]
Tourism

The manufactured coastal beach of Calheta: replacing the dark rock/sand of the volcanic island with beach sand.
Tourism is an important sector in the region's economy, contributing 20%[88] to the region's GDP, providing support throughout the year for commercial, transport and other activities and constituting a significant market for local products. The share in Gross Value Added of hotels and restaurants (9%) also highlights this phenomenon. The island of Porto Santo, with its 9 km (5.6 mi) long beach and its climate, is entirely devoted to tourism.
Visitors are mainly from the European Union, with German, British, Scandinavian and Portuguese tourists providing the main contingents. The average annual occupancy rate was 60.3% in 2008,[89] reaching its maximum in March and April, when it exceeds 70%.
Whale watching
Whale watching has become very popular in recent years. Many species of dolphins, such as common dolphin, spotted dolphin, striped dolphin, bottlenose dolphin, short-finned pilot whale, and whales such as Bryde's whale, Sei whale,[90]fin whale, sperm whale, beaked whales can be spotted near the coast or offshore.[91]
Renewable energy
Electricity on Madeira is provided solely through EEM (Empresa de Electricidade da Madeira, SA, which holds a monopoly for the provision of electrical supply on the autonomous region) and consists largely of fossil fuels, but with a significant supply of seasonal hydroelectricity from the levada system, wind power and a small amount of solar. In 2011, renewable energy formed 26.5% of the electricity used in Madeira.
Transport

A ferry makes daily trips between Madeira and Porto Santo.
The Islands have two airports, Cristiano Ronaldo International Airport and Porto Santo Airport, on the islands of Madeira and Porto Santo respectively. From Cristiano Ronaldo International Airport the most frequent flights are to Lisbon. There are also direct flights to over 30 other airports in Europe and nearby islands.[92]
Transport between the two main islands is by plane, or ferries from the Porto Santo Line,[93] the latter also carrying vehicles. Visiting the interior of the islands is now easy thanks to construction of the Vias Rápidas, major roads that cross the island. Modern roads reach all points of interest on the islands.
Funchal has an extensive public transportation system. Bus companies, including Horários do Funchal which has been operating for over a hundred years, have regularly scheduled routes to all points of interest on the island.
Culture
Music

Bailinho da Madeira
Folklore music in Madeira is widespread and mainly uses local musical instruments such as the machete, rajao, brinquinho and cavaquinho, which are used in traditional folkloric dances like the bailinho da Madeira.
Emigrants from Madeira also influenced the creation of new musical instruments. In the 1880s, the ukulele was created, based on two small guitar-like instruments of Madeiran origin, the cavaquinho and the rajao. The ukulele was introduced to the Hawaiian Islands by Portuguese immigrants from Madeira and Cape Verde.[94] Three immigrants in particular, Madeiran cabinet makers Manuel Nunes, José do Espírito Santo, and Augusto Dias, are generally credited as the first ukulele makers.[95] Two weeks after they disembarked from the SS Ravenscrag in late August 1879, the Hawaiian Gazette reported that "Madeira Islanders recently arrived here, have been delighting the people with nightly street concerts."[96]
Cuisine

"Lapas", the true limpet species Patella vulgata
Because of the geographic situation of Madeira in the Atlantic Ocean, the island has an abundance of fish of various kinds. The species that are consumed the most are espada (black scabbardfish), blue fin tuna, white marlin, blue marlin, albacore, bigeye tuna, wahoo, spearfish, skipjack tuna and many others are found in the local dishes as they are found up and down the coast of Madeira.[97] Espada is often served with banana. Bacalhau is also popular, as it is in Portugal.
There are many meat dishes on Madeira, one of the most popular being espetada.[98] Espetada is traditionally made of large chunks of beef rubbed in garlic, salt and bay leaf and marinated for 4 to 6 hours in Madeira wine, red wine vinegar and olive oil then skewered onto a bay laurel stick and left to grill over smouldering wood chips. These are so integral a part of traditional eating habits that a special iron stand is available with a T-shaped end, each branch of the "T" having a slot in the middle to hold a brochette (espeto in Portuguese); a small plate is then placed underneath to collect the juices. The brochettes are very long and have a V-shaped blade in order to pierce the meat more easily. It is usually accompanied with the local bread called bolo do caco.
Other popular dishes in Madeira include açorda, feijoada, carne de vinha d'alhos.
Traditional pastries in Madeira usually contain local ingredients, one of the most common being mel de cana, literally "sugarcane honey" (molasses). The traditional cake of Madeira is called Bolo de Mel, which translates as (Sugarcane) "Honey Cake" and according to custom, is never cut with a knife, but broken into pieces by hand. It is a rich and heavy cake. The cake commonly well known as "Madeira Cake" in England also finds its naming roots in the Island of Madeira.
Malasadas are a Madeiran creation which were taken around the world by emigrants to places such as Hawaii. In Madeira, Malasadas are mainly consumed during the Carnival of Madeira. Pastéis de nata, as in the rest of Portugal, are also very popular.
Milho frito is a very popular dish in Madeira which is very similar to the Italian dish polenta. Açorda Madeirense is another popular local dish.
Beverages

Bottles of Madeira labelled by the different grape varieties used to produce the many styles of wine

Coral Beer, produced since 1872[99] in the Island's main brewery, has achieved several Monde Selection medals
Madeira is a fortified wine, produced in the Madeira Islands; varieties may be sweet or dry. It has a history dating back to the Age of Exploration when Madeira was a standard port of call for ships heading to the New World or East Indies. To prevent the wine from spoiling, neutral grape spirits were added. However, wine producers of Madeira discovered, when an unsold shipment of wine returned to the islands after a round trip, that the flavour of the wine had been transformed by exposure to heat and movement. Today, Madeira is noted for its unique winemaking process which involves heating the wine and deliberately exposing the wine to some levels of oxidation.[100] Most countries limit the use of the term Madeira to those wines that come from the Madeira Islands, to which the European Union grants Protected Designation of Origin (PDO) status.[101]
A local beer called Coral is produced by the Madeira Brewery, which dates from 1872. It has achieved 2 Monde Selection Grand Gold Medals, 24 Monde Selection Gold Medals and 2 Monde Selection Silver Medals.[99] Other alcoholic drinks are also popular in Madeira, such as the locally created Poncha, Niquita, Pé de Cabra, Aniz, as well as Portuguese drinks such as Macieira Brandy, Licor Beirão.
Laranjada is a type of carbonated soft drink with an orange flavour, its name being derived from the Portuguese word laranja ("orange"). Launched in 1872 it was the first soft drink to be produced in Portugal, and remains very popular to the present day. Brisa drinks, a brand name, are also very popular and come in a range of flavours.
There is also a huge coffee culture in Madeira. Like in mainland Portugal, popular coffee-based drinks include Garoto, Galão, Bica, Café com Cheirinho, Mazagran, Chinesa and many more.
Sports
Sister provinces
Madeira Island has the following sister provinces:
 Italy: Autonomous Region of Aosta Valley (1987)
Italy: Autonomous Region of Aosta Valley (1987) Jersey: Bailiwick of Jersey (1998)
Jersey: Bailiwick of Jersey (1998) South Africa: Eastern Cape Province
South Africa: Eastern Cape Province South Korea: Jeju Province (2007)
South Korea: Jeju Province (2007) Gibraltar: Gibraltar (2009) [102]
Gibraltar: Gibraltar (2009) [102]
Postage stamps
Portugal has issued postage stamps for Madeira during several periods, beginning in 1868.
Notable people

Cristiano Ronaldo, born in Madeira, was the 2008, 2013, 2014, 2016 and 2017 FIFA World Player of the Year

Joe Berardo is a businessman, stock investor, speculator and art collector. He is also one of the wealthiest people in Portugal.
The following people were either born or have lived part of their lives in Madeira:
Charles I of Austria, last Emperor of Austria and last King of Hungary, deposed monarch, died in exile on Madeira in 1922
Joe Berardo, Portuguese millionaire, and art collector
Rubina Berardo, Portuguese politician
António de Abreu, naval officer and navigator
Nadia Almada, a winner of the British reality show Big Brother
Menasseh Ben Israel, Jewish rabbi.
Catarina Fagundes, Olympic athlete for windsurf
Vânia Fernandes, Portuguese singer who represented Portugal in Eurovision 2008
José Vicente de Freitas, military general and politician
Vasco da Gama Rodrigues, poet, born in Paul do Mar
Teodósio Clemente de Gouveia, Cardinal of the Roman Catholic Church
George Walter Grabham, geologist
Herberto Hélder, poet
Moisés Henriques, former Australian Under-19 Captain and current NSW Blues and Australian international Twenty20 cricketer
Alberto João Jardim, second President of the Regional Government
Luís Jardim, producer of music
Paul Langerhans, German pathologist and biologist
Fátima Lopes, fashion designer
Jaime Ornelas Camacho, first and former President of the Regional Government
Aires de Ornelas e Vasconcelos, former Archbishop of the former Portuguese colonial enclave Goa (in India)
Lloyd Mathews, British naval officer, politician and abolitionist
Dionísio Pestana, president of the Pestana Group
Rigo 23, artist
João Rodrigues, Olympic windsurfer
Cristiano Ronaldo, Juventus F.C., Portugal and former Sporting, Manchester United and Real Madrid footballer
John Santos, photographer
Ana da Silva, founding member of post-punk band The Raincoats
Pedro Macedo Camacho, composer- Flávia Brito, Miss Universo Portugal 2016, beauty pageant
- Manoel Dias Soeyro or Menasseh Ben Israel (1604–1657), Sephardi rabbi and publisher
Artur de Sousa Pinga, former CS Marítimo and FC Porto football player
Maximiano de Sousa (Max), popular singer, born in Funchal
Virgílio Teixeira, actor
José Travassos Valdez, 1st Count of Bonfim, governor during 1827–1828
Miguel Albuquerque, third and current President of the Regional Government
Bernardo Sousa, rally driver in the WRC
José Tolentino Mendonça, priest, theologian, poet, archbishop, Archivist and Librarian of the Holy Roman Church
See also
- "Have Some Madeira M'Dear"
- List of birds of Madeira
Madeira Islands Open, an annual European Tour golf tournament- Surfing in Madeira
Ribeiro Frio, a village on the island of Madeira
References
^ "Sub-national HDI - Area Database - Global Data Lab". hdi.globaldatalab.org. Retrieved 2018-09-13..mw-parser-output cite.citationfont-style:inherit.mw-parser-output qquotes:"""""""'""'".mw-parser-output code.cs1-codecolor:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registrationcolor:#555.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration spanborder-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-errordisplay:none;font-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-errorfont-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-formatfont-size:95%.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-leftpadding-left:0.2em.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-rightpadding-right:0.2em
^ Until 2002, the Portuguese escudo was used in financial transactions, and until 1910 the Portuguese real was the currency used by the monarchy of Portugal.
^ IGP, ed. (2010), Carta Administrativa Oficial de Portugal (in Portuguese), Lisbon, Portugal: Instituto Geográfico Português, archived from the original on 3 July 2014, retrieved 1 July 2011
^ "EUR-Lex – 12002E299 – EN". eur-lex.europa.eu.
^ Madeira beats its previous tourism record in 2017, RTP Madeira, in Portuguese, 21.05.2018
^ "Madeira welcomes most cruisers". The Portugal News. Retrieved 12 March 2013.
^ Madeira’s hotel industry registered new records in overnight stays and revenue, Regional Directorate of Statistics of Madeira (DREM), 21.05.2018
^ "About IBC". www.ibc-madeira.com.
^ Plutarch, The Parallel Lives: Sertorius, ch. 8
^ World Archaeology, Issue 66, August/September 2014, Volume 6, No. 6, p. 64.
^ Nicholas Cayetano de Bettencourt Pitta, 1812, pp. 11–17
^ Fernández-Armesto, Felipe (2004). "Machim (supp. fl. 14th cent.)". Oxford Dictionary of National Biography. 1. Oxford: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/ref:odnb/17535. Retrieved 2 September 2009.
^ Nicholas Cayetano de Bettencourt Pitta, 1812, p.20
^ The discoveries of Porto Santo and Madeira were first described by Gomes Eanes de Zurara in Chronica da Descoberta e Conquista da Guiné. (Eng. version by Edgar Prestage in 2 vols. issued by the Hakluyt Society, London, 1896–1899: The Chronicle of Discovery and Conquest of Guinea.) French author Arkan Simaan refers to these discoveries in his historical novel based on Azurara's Chronicle: L'Écuyer d'Henri le Navigateur (2007), published by Éditions l'Harmattan, Paris.
^ Dervenn, Claude (1957). Madeira. Translated by Hogarth-Gaute, Frances. London, UK: George G. Harrap and Co. p. 20. OCLC 645870163. Retrieved 2016-06-07.And when he returned in May 1420 to take possession of "his" island, it was with his wife and the sons and daughters that the virtuous Constanga had given him.
^ Alfred W. Crosby (2015). Ecological Imperialism, The Biological Expansion of Europe, 900–1900 (2 ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 77. ISBN 978-1-107-56987-4.
^ Ponting, Clive (2000). World history: a new perspective. London: Chatto & Windus. p. 482. ISBN 0-7011-6834-X.
^ Godinho, V. M. Os Descobrimentos e a Economia Mundial, Arcádia, 1965, Vol 1 and 2, Lisboa
^ Fernando Augusto da Silva & Carlos Azevedo de Menezes, "Porto Santo", Elucidário Madeirense, vol. 3 (O-Z), Funchal, DRAC, p. 124.
^ Christian Slaves, Muslim Masters: White Slavery in the Mediterranean, the Barbary Coast and Italy, 1500–1800. Robert Davis (2004). p. 7.
ISBN 1-4039-4551-9.
^ "Officer's presentation sword given to Brigadier General William Henry Clinton from the British Consul and Factory in Madeira, 1802". National Army Museum. Retrieved 15 August 2016.
^ "Gordon, Sir James Willoughby, 1st bt. (1772–1851), of Niton, I.o.W". UK Parliament. Retrieved 15 August 2016.
^ "The Map Room: Africa: Madeira". British Empire. Retrieved 30 July 2010.
^ "Cable ship Dacia". Ships hit by U-boats – German and Austrian U-boats of World War One – Kaiserliche Marine. uboat.net. 13 November 2010. Retrieved 13 November 2010.
^ Glover, Bill (10 July 2015). "CS Dacia". History of the Atlantic Cable & Undersea Communications. Retrieved 7 June 2016.
^ "Submarine carrier Kanguroo". Ships hit by U-boats – German and Austrian U-boats of World War One – Kaiserliche Marine. uboat.net. 13 November 2010. Retrieved 13 November 2010.
^ "Gunboat Surprise". Ships hit by U-boats - German and Austrian U-boats of World War One - Kaiserliche Marine. uboat.net. 13 November 2010. Retrieved 13 November 2010.
^
"A bit of History". Retrieved 2016-10-16.
^ Valentiner, Max (1917). 300000 tonnen versenkt! Meine U-boots-fahrten (50. bis 100. tausend. ed.). Berlin: Ullstein & co. p. 118. Retrieved 27 January 2017.
^ The New York Times, 6 November 1921 (accessed 4 May 2009)
^ "Madeira: Número de mortos aumentou para 42", Público (in Portuguese), 26 February 2010, archived from the original on 11 June 2010
^ "Sobe para 43 o número de mortos, já se contam mais de 100 feridos", Público (in Portuguese), 21 February 2010, archived from the original on 19 September 2011
^ Riebeek, Holli. "Fires in Madeira, Portugal". Earth Observatory. NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. Retrieved 8 September 2013.
^ Sapa-DPA (16 August 2010). "Wildfires ravage Portuguese nature parks". IOL News. Retrieved 8 September 2013.Fires that had raged there in the recent days had devastated 95 percent of Funchal Ecological Park, destroying a decade of efforts to replant indigenous species in the area measuring 1 000 hectares, the daily Publico quoted environmentalists as saying.
^ "Fires ravage Madeira islands and mainland Portugal". Reuters. 19 July 2012. Retrieved 8 September 2013.
^ Scott, Michon. "Madeira Wildfires". Earth Observatory. NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. Retrieved 8 September 2013.
^ Miller, Shari (20 July 2012). "Holiday resorts under threat as towering walls of flame ravage Madeira islands". Daily Mail. Retrieved 8 September 2013.
^ "Portugal's Madeira hit by forest fires". BBC News. 20 July 2012. Retrieved 8 September 2013.
^ "Denguekuume leviää Madeiralla ('Dengue Fever Spreads In Madeira')". YLE.fi. 10 October 2012. Retrieved 20 October 2012.
^ "Dengue Fever in Madeira, Portugal". WHO. 17 October 2012. Retrieved 20 October 2012.
^
"Dengue outbreak in Madeira controlled". Retrieved 11 April 2013.
^ Porter, Tom (17 August 2013). "Hospital Evacuated as Fire Rages on Madeira". IBTimes UK. Retrieved 8 September 2013.
^ "Wildfire inferno forces hospital and homes to be evacuated on Portuguese island Madeira". euronews. 17 August 2013. Retrieved 8 September 2013.
^ "Wildfires kills three on holiday island". 10 August 2016 – via www.bbc.co.uk.
^ Badcock, James; Rothwell, James (10 August 2016). "Three dead including elderly woman as wildfire hits island of Madeira" – via www.telegraph.co.uk.
^ Minder, Raphael (August 11, 2016). "Deadly Wildfires on Portuguese Island of Madeira Reach Its Largest City". nytimes.com. Retrieved August 11, 2016.
^ "Falling tree kills 13 on Madeira". 15 August 2017 – via www.bbc.com.
^ Official website of the Celebrations of the 600 years of the Discovery of Madeira and Porto Santo Islands, 17.07.2018
^ Portugal's President addresses Madeira 600th anniversary, Madeira Tourism official channel on Youtube, 17.07.2018
^ "Madeira Islands Tourism". Madeiraislands.travel. Archived from the original on 30 May 2010. Retrieved 30 July 2010.
^ Ribeiro et al., 1996
^ Kullberg & Kullberg, 2000
^ Geldemacher et al., 2000
^ Ribeiro, 2001
^ ab "Madeira". Global Volcanism Program. Smithsonian Institution.
^ "MadeiraHelp.com". MadeiraHelp.com. 22 February 1999. Archived from the original on 31 July 2010. Retrieved 30 July 2010.
^ Robert White, 1851, p. 4
^ "World Map of Köppen−Geiger Climate Classification". Archived from the original on 6 September 2010.
^ "Lava Pools". tripadvisor.com.
^ "Weather Information for Funchal".
^ "Funchal, Madeira Climate, Temperature, Average Weather History, Rainfall/Precipitation, Sunshine".
^ Góis-Marques, Carlos A.; Madeira, José; Menezes de Sequeira, Miguel (7 February 2017). "Inventory and review of the Mio–Pleistocene São Jorge flora (Madeira Island, Portugal): palaeoecological and biogeographical implications". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 16 (2): 1–19. doi:10.1080/14772019.2017.1282991.
^ Fernandes, F. (2011). "Jasminum azoricum". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2012.2. Retrieved 8 January 2013.
^ ab Arnold, E. Nicholas; Ovenden, Denys W. (2002). Field Guide: Reptiles & Amphibians of Britain & Europe. London: Collins & Co. pp. 154–155. ISBN 9780002199643.
^ Hancock, Matthew (13 November 2000). "Madeira: Walking a heavenly tightrope". Telegraph Travel. Telegraph Media Group. Retrieved 20 May 2018.
^ Centre, UNESCO World Heritage. "Levadas of Madeira Island — UNESCO World Heritage Centre". whc.unesco.org. Retrieved 2017-10-19.
^ ab "Censos 2011 Resultados Preliminares 2011". INE.
^ Map of municipalities at FreguesiasDePortugas l.com
^ Statistics include Savage Islands, which are administered by the parish of Sé
^ Statistics include the mainland parish of Santa Cruz and the islands of the Desertas
^ Statistics represent island population; Porto Santo is the second largest island in the archipelago of Madeira
^ "Alberto Vieira, ''O Infante e a Madeira: dúvidas e certezas, Centro Estudos História Atlântico". Ceha-madeira.net. Archived from the original on 31 May 2010. Retrieved 30 July 2010.
^ "Diocese of Funchal". Catholic Hierarchy. Retrieved 16 January 2018.
^ "Madeiran Portuguese Migration to Guyana, St. Vincent, Antigua and Trinidad: A Comparative Overview" (PDF). Jo-Anne S. Ferreira, University of the West Indies, St. Augustine
^ "Madeira and Emigration"
^ "Portuguese emigration from Madeira to British Guiana"
^ "Portuguese Immigrants in the United States: Chronology, 1900-1919". Library of Congress. Retrieved August 26, 2017.
^ "Protestant Exiles from Madeira in Illinois". loc.gov.
^ "Portuguese Immigration To Jacksonville In 1849". orgsites.com. Archived from the original on 16 January 2015. Retrieved 15 January 2015.
^ "History of Sangamon County, Illinois". google.com.
^ "Historical Encyclopedia of Illinois". google.com.
^ "The Christian World". google.com.
^ "BBC – Jersey Voices"
^ In 2017 the return of emigrants in Venezuela contributed to the 10.0% increase in the foreign population residing in the Autonomous Region of Madeira, Regional Directorate of Statistics of Madeira (DREM), 04.07.2018
^ "International Business Centre of Madeira – About IBC". ibc-madeira.com.
^ "Billions of euros of EU money yet Madeira has built up massive debts". Retrieved 10 July 2016.
^ "Moody's changes outlook to positive on the ratings of Azores and Madeira; ratings affirmed". Moody's. 5 September 2017.
^ "Telegraph article". www.telegraph.co.uk. 23 February 2010. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
^ "Statistics from DRE of Madeira tourism (2008)" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 August 2010. Retrieved 30 July 2010.
^ Sei Whale, Balaenoptera borealis off Madeira, Portugal. YouTube. 3 January 2013.
^ "Madeira whale and Dolphin watching". www.madeirawindbirds.com. 30 August 2010. Retrieved 10 December 2010.
^ "Madeira > Departures > Destinations and Airlines > Destinations and Airlines". Retrieved 10 July 2016.
^ Administrator. "Porto Santo Line". Retrieved 10 July 2016.
^ Nidel, Richard (2004). World Music: The Basics. Routledge. p. 312. ISBN 978-0-415-96800-3.
^ Roberts, Helen (1926). Ancient Hawaiian Music. Bernice P. Bishop Museum. pp. 9–10.
^ King, John (2000). "Prolegomena to a History of the 'Ukulele". Ukulele Guild of Hawai'i. Archived from the original on 3 August 2004. Retrieved February 2, 2016.
^ "Fish that can be found in Madeira Archipelago undersea". Madeira Birdwatching. Retrieved 20 January 2018.
^
"Madeira Espetada". theworldwidegourmet.com. Retrieved 30 August 2010.
^ ab "Coral Branca - Empresa de Cervejas da Madeira".
^ T. Stevenson "The Sotheby's Wine Encyclopedia" pg 340–341 Dorling Kindersley 2005
ISBN 0-7566-1324-8
^ "Labelling of wine and certain other wine sector products". Europa.eu. Retrieved 12 March 2013.
^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2 March 2016. Retrieved 21 February 2016.CS1 maint: Archived copy as title (link)
Bibliography
Pitta, Nicholas Cayetano de Bettencourt (1812). Account of the Island of Madeira. London: C. Stewart Printer.
Koebel, William Henry (1909). Madeira: old and new. London: Francis Griffiths.
Dervenn, Claude (1957). Madeira. Translated by Hogarth-Gaute, Frances. London: George G. Harrap and Co.
Walvin, James (2000). Making the Black Atlantic: Britain and the African Diaspora. London: Cassell.
External links
 Wikimedia Atlas of Madeira
Wikimedia Atlas of Madeira- Madeira's Government Website
Madeira at Curlie