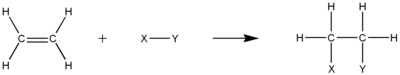Alkene

A 3D model of ethylene, the simplest alkene.
In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond.[1] The words alkene and olefin are often used interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n.[2] Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms fewer than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), with the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene, is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially.[3]Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.[2]
Contents
1 Structure
1.1 Bonding
1.2 Shape
2 Physical properties
3 Reactions
3.1 Addition reactions
3.1.1 Hydrogenation
3.1.2 Hydration
3.1.3 Halogenation
3.1.4 Hydrohalogenation
3.1.5 Halohydrin formation
3.1.6 Oxidation
3.1.7 Photooxygenation
3.2 Polymerization
3.3 Metal complexation
3.4 Reaction overview
4 Synthesis
4.1 Industrial methods
4.2 Elimination reactions
4.3 Synthesis from carbonyl compounds
4.4 Synthesis from alkenes: olefin metathesis and hydrovinylation
4.5 From alkynes
4.6 Rearrangements and related reactions
5 Nomenclature
5.1 IUPAC names
5.2 Cis–trans notation
5.3 E–Z notation
5.4 Groups containing C=C double bonds
6 See also
7 Nomenclature links
8 References
Structure
Bonding

Ethylene (ethene), showing the pi bond in green.
Like a single covalent bond, double bonds can be described in terms of overlapping atomic orbitals, except that, unlike a single bond (which consists of a single sigma bond), a carbon–carbon double bond consists of one sigma bond and one pi bond. This double bond is stronger than a single covalent bond (611 kJ/mol for C=C vs. 347 kJ/mol for C–C)[1] and also shorter, with an average bond length of 1.33 ångströms (133 pm).
Each carbon of the double bond uses its three sp2hybrid orbitals to form sigma bonds to three atoms (the other carbon and two hydrogen atoms). The unhybridized 2p atomic orbitals, which lie perpendicular to the plane created by the axes of the three sp² hybrid orbitals, combine to form the pi bond. This bond lies outside the main C–C axis, with half of the bond on one side of the molecule and half on the other. With a strength of 65 kcal/mol, the pi bond is significantly weaker than the sigma bond.
Rotation about the carbon–carbon double bond is restricted because it incurs an energetic cost to break the alignment of the p orbitals on the two carbon atoms. As a consequence, substituted alkenes may exist as one of two isomers, called cis or trans isomers. More complex alkenes may be named with the E–Z notation for molecules with three or four different substituents (side groups). For example, of the isomers of butene, the two methyl groups of (Z)-but-2-ene (a.k.a. cis-2-butene) appear on the same side of the double bond, and in (E)-but-2-ene (a.k.a. trans-2-butene) the methyl groups appear on opposite sides. These two isomers of butene are slightly different in their chemical and physical properties.
Twisting to a 90° dihedral angle between two of the groups on the carbons requires less energy than the strength of a pi bond, and the bond still holds. The carbons of the double bond become pyramidal, which allows preserving some p orbital alignment—and hence pi bonding. The other two attached groups remain at a larger dihedral angle. This contradicts a common textbook assertion that the two carbons retain their planar nature when twisting, in which case the p orbitals would rotate enough away from each other to be unable to sustain a pi bond. In a 90°-twisted alkene, the p orbitals are only misaligned by 42° and the strain energy is only around 40 kcal/mol. In contrast, a fully broken pi bond has an energetic cost of around 65 kcal/mol.[4]
Some pyramidal alkenes are stable. For example, trans-cyclooctene is a stable strained alkene and the orbital misalignment is only 19°, despite having a significant dihedral angle of 137° (a planar system has a dihedral angle of 180°) and a degree of pyramidalization of 18°. Even trans-cycloheptene is stable at low temperatures.[4]
Shape
As predicted by the VSEPR model of electron pair repulsion, the molecular geometry of alkenes includes bond angles about each carbon in a double bond of about 120°. The angle may vary because of steric strain introduced by nonbonded interactions between functional groups attached to the carbons of the double bond. For example, the C–C–C bond angle in propylene is 123.9°.
For bridged alkenes, Bredt's rule states that a double bond cannot occur at the bridgehead of a bridged ring system unless the rings are large enough.[5] Following Fawcett and defining S as the total number of non-bridgehead atoms in the rings,[6] bicyclic systems require S ≥ 7 for stability[5] and tricyclic systems require S ≥ 11.[7]
Physical properties
Many of the physical properties of alkenes and alkanes are similar: they are colourless, nonpolar, and combustable. The physical state depends on molecular mass: like the corresponding saturated hydrocarbons, the simplest alkenes, ethene, propene, and butene are gases at room temperature. Linear alkenes of approximately five to sixteen carbons are liquids, and higher alkenes are waxy solids. The melting point of the solids also increases with increase in molecular mass.
Alkenes generally have stronger smells than the corresponding alkane. Ethylene is described to have a "sweet" odor,[8] while ethane is odorless, for example. The binding of cupric ion to the olefin in the mammalian olfactory receptor MOR244-3 is implicated in the smell of alkenes (as well as thiols). Strained alkenes, in particular, like norbornene and trans-cyclooctene are known to have strong, unpleasant odors, a fact consistent with the stronger π complexes they form with metal ions including copper.[9]
Reactions
Alkenes are relatively stable compounds, but are more reactive than alkanes, either because of the reactivity of the carbon–carbon pi-bond or the presence of allylic CH centers. Most reactions of alkenes involve additions to this pi bond, forming new single bonds. Alkenes serve as a feedstock for the petrochemical industry because they can participate in a wide variety of reactions, prominently polymerization and alkylation.
Addition reactions
Alkenes react in many addition reactions, which occur by opening up the double-bond. Most of these addition reactions follow the mechanism of electrophilic addition. Examples are hydrohalogenation, halogenation, halohydrin formation, oxymercuration, hydroboration, dichlorocarbene addition, Simmons–Smith reaction, catalytic hydrogenation, epoxidation, radical polymerization and hydroxylation.
Hydrogenation
Hydrogenation of alkenes produces the corresponding alkanes. The reaction is carried out under pressure at a temperature of 200 °C in the presence of a metallic catalyst. Common industrial catalysts are based on platinum, nickel or palladium. For laboratory syntheses, Raney nickel (an alloy of nickel and aluminium) is often employed. The simplest example of this reaction is the catalytic hydrogenation of ethylene to yield ethane:
- CH2=CH2 + H2 → CH3–CH3
Hydration
Hydration, the addition of water across the double bond of alkenes, yields alcohols. The reaction is catalyzed by strong acids such as sulfuric acid. This reaction is carried out on an industrial scale to produce ethanol.
- CH2=CH2 + H2O → CH3–CH2OH
Alkenes can also be converted into alcohols via the oxymercuration–demercuration reaction , the hydroboration–oxidation reaction or by Mukaiyama hydration.
Halogenation
In electrophilic halogenation the addition of elemental bromine or chlorine to alkenes yields vicinal dibromo- and dichloroalkanes (1,2-dihalides or ethylene dihalides), respectively. The decoloration of a solution of bromine in water is an analytical test for the presence of alkenes:
- CH2=CH2 + Br2 → BrCH2–CH2Br
Related reactions are also used as quantitative measures of unsaturation, expressed as the bromine number and iodine number of a compound or mixture.
Hydrohalogenation
Hydrohalogenation is the addition of hydrogen halides such as HCl or HI to alkenes to yield the corresponding haloalkanes:
CH3–CH=CH
2 + HI → CH3–CHI−CH
2–H
If the two carbon atoms at the double bond are linked to a different number of hydrogen atoms, the halogen is found preferentially at the carbon with fewer hydrogen substituents. This patterns is known as Markovnikov's rule. The use of radical initiators or other compounds can lead to the opposite product result. Hydrobromic acid in particular is prone to forming radicals in the presence of various impurities or even atmospheric oxygen, leading to the reversal of the Markovnikov result:[10]
CH3–CH=CH
2 + HBr → CH3–CHH–CH
2–Br
Halohydrin formation
Alkenes react with water and halogens to form halohydrins by an addition reaction. Markovnikov regiochemistry and anti stereochemistry occur.
- CH2=CH2 + X2 + H2O → XCH2–CH2OH + HX
Oxidation
Alkenes are oxidized with a large number of oxidizing agents. In the presence of oxygen, alkenes burn with a bright flame to produce carbon dioxide and water. Catalytic oxidation with oxygen or the reaction with percarboxylic acids yields epoxides. Reaction with ozone in ozonolysis leads to the breaking of the double bond, yielding two aldehydes or ketones. Reaction with concentrated, hot KMnO4 (or other oxidizing salts) in an acidic solution will yield ketones or carboxylic acids.
- R1–CH=CH–R2 + O3 → R1–CHO + R2–CHO + H2O
This reaction can be used to determine the position of a double bond in an unknown alkene.
The oxidation can be stopped at the vicinal diol rather than full cleavage of the alkene by using milder (dilute,lower temperature) KMnO4 or with osmium tetroxide or other oxidants.
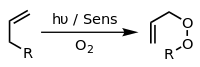
Photooxygenation
In the presence of an appropriate photosensitiser, such as methylene blue and light, alkenes can undergo reaction with reactive oxygen species generated by the photosensitiser, such as hydroxyl radicals, singlet oxygen or superoxide ion. These reactive photochemical intermediates are generated in what are known as Type I, Type II, and Type III processes, respectively.[citation needed] These various alternative processes and reactions can be controlled by choice of specific reaction conditions, leading to a wide range of different products. A common example is the [4+2]-cycloaddition of singlet oxygen with a diene such as cyclopentadiene to yield an endoperoxide:
![Generation of singlet oxygen and its [4+2]-cycloaddition with cyclopentadiene](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/1/12/4%2B2_cycloaddition_cyclopentadiene_O2.svg/350px-4%2B2_cycloaddition_cyclopentadiene_O2.svg.png)
Another example is the Schenck ene reaction, in which singlet oxygen reacts with an allylic structure to give a transposed allyl peroxide:
Polymerization
Polymerization of alkenes is a reaction that yields polymers of high industrial value at great economy, such as the plastics polyethylene and polypropylene. Polymers from alkene monomers are referred to in a general way as polyolefins or in rare instances as polyalkenes. A polymer from alpha-olefins is called a polyalphaolefin (PAO). Polymerization can proceed via either a free-radical or an ionic mechanism, converting the double to a single bond and forming single bonds to join the other monomers. Polymerization of conjugated dienes such as buta-1,3-diene or isoprene (2-methylbuta-1,3-diene) results in largely 1,4-addition with possibly some 1,2-addition of the diene monomer to a growing polymer chain.
Metal complexation

Structure of bis(cyclooctadiene)nickel(0), a metal–alkene complex
Alkenes are ligands in transition metal alkene complexes. The two carbon centres bond to the metal using the C–C pi- and pi*-orbitals. Mono- and diolefins are often used as ligands in stable complexes. Cyclooctadiene and norbornadiene are popular chelating agents, and even ethylene itself is sometimes used as a ligand, for example, in Zeise's salt. In addition, metal–alkene complexes are intermediates in many metal-catalyzed reactions including hydrogenation, hydroformylation, and polymerization.
Reaction overview
| Reaction name | Product | Comment |
|---|---|---|
Hydrogenation | alkanes | addition of hydrogen |
Hydroalkenylation | alkenes | hydrometalation / insertion / beta-elimination by metal catalyst |
Halogen addition reaction | 1,2-dihalide | electrophilic addition of halogens |
Hydrohalogenation (Markovnikov) | haloalkanes | addition of hydrohalic acids |
| Anti-Markovnikov hydrohalogenation | haloalkanes | free radicals mediated addition of hydrohalic acids |
Hydroamination | amines | addition of N–H bond across C–C double bond |
Hydroformylation | aldehydes | industrial process, addition of CO and H2 |
Sharpless bishydroxylation | diols | oxidation, reagent: osmium tetroxide, chiral ligand |
Woodward cis-hydroxylation | diols | oxidation, reagents: iodine, silver acetate |
Ozonolysis | aldehydes or ketones | reagent: ozone |
Olefin metathesis | alkenes | two alkenes rearrange to form two new alkenes |
Diels–Alder reaction | cyclohexenes | cycloaddition with a diene |
Pauson–Khand reaction | cyclopentenones | cycloaddition with an alkyne and CO |
Hydroboration–oxidation | alcohols | reagents: borane, then a peroxide |
Oxymercuration-reduction | alcohols | electrophilic addition of mercuric acetate, then reduction |
Prins reaction | 1,3-diols | electrophilic addition with aldehyde or ketone |
Paterno–Büchi reaction | oxetanes | photochemical reaction with aldehyde or ketone |
Epoxidation | epoxide | electrophilic addition of a peroxide |
Cyclopropanation | cyclopropanes | addition of carbenes or carbenoids |
Hydroacylation | ketones | oxidative addition / reductive elimination by metal catalyst |
Hydrophosphination | phosphines |
Synthesis
Industrial methods
Alkenes are produced by hydrocarbon cracking. Raw materials are mostly natural gas condensate components (principally ethane and propane) in the US and Mideast and naphtha in Europe and Asia. Alkanes are broken apart at high temperatures, often in the presence of a zeolite catalyst, to produce a mixture of primarily aliphatic alkenes and lower molecular weight alkanes. The mixture is feedstock and temperature dependent, and separated by fractional distillation. This is mainly used for the manufacture of small alkenes (up to six carbons).[11]
Related to this is catalytic dehydrogenation, where an alkane loses hydrogen at high temperatures to produce a corresponding alkene.[1] This is the reverse of the catalytic hydrogenation of alkenes.

This process is also known as reforming. Both processes are endothermic and are driven towards the alkene at high temperatures by entropy.
Catalytic synthesis of higher α-alkenes (of the type RCH=CH2) can also be achieved by a reaction of ethylene with the organometallic compound triethylaluminium in the presence of nickel, cobalt, or platinum.
Elimination reactions
One of the principal methods for alkene synthesis in the laboratory is the room elimination of alkyl halides, alcohols, and similar compounds. Most common is the β-elimination via the E2 or E1 mechanism,[12] but α-eliminations are also known.
The E2 mechanism provides a more reliable β-elimination method than E1 for most alkene syntheses. Most E2 eliminations start with an alkyl halide or alkyl sulfonate ester (such as a tosylate or triflate). When an alkyl halide is used, the reaction is called a dehydrohalogenation. For unsymmetrical products, the more substituted alkenes (those with fewer hydrogens attached to the C=C) tend to predominate (see Zaitsev's rule). Two common methods of elimination reactions are dehydrohalogenation of alkyl halides and dehydration of alcohols. A typical example is shown below; note that if possible, the H is anti to the leaving group, even though this leads to the less stable Z-isomer.[13]

Alkenes can be synthesized from alcohols via dehydration, in which case water is lost via the E1 mechanism. For example, the dehydration of ethanol produces ethene:
CH3CH2OH + H2SO4 → H2C=CH2 + H3O+ + HSO−
4
An alcohol may also be converted to a better leaving group (e.g., xanthate), so as to allow a milder syn-elimination such as the Chugaev elimination and the Grieco elimination. Related reactions include eliminations by β-haloethers (the Boord olefin synthesis) and esters (ester pyrolysis).
Alkenes can be prepared indirectly from alkyl amines. The amine or ammonia is not a suitable leaving group, so the amine is first either alkylated (as in the Hofmann elimination) or oxidized to an amine oxide (the Cope reaction) to render a smooth elimination possible. The Cope reaction is a syn-elimination that occurs at or below 150 °C, for example:[14]

The Hofmann elimination is unusual in that the less substituted (non-Saytseff) alkene is usually the major product.
Alkenes are generated from α-halosulfones in the Ramberg–Bäcklund reaction, via a three-membered ring sulfone intermediate.
Synthesis from carbonyl compounds
Another important method for alkene synthesis involves construction of a new carbon–carbon double bond by coupling of a carbonyl compound (such as an aldehyde or ketone) to a carbanion equivalent. Such reactions are sometimes called olefinations. The most well-known of these methods is the Wittig reaction, but other related methods are known.
The Wittig reaction involves reaction of an aldehyde or ketone with a Wittig reagent (or phosphorane) of the type Ph3P=CHR to produce an alkene and Ph3P=O. The Wittig reagent is itself prepared easily from triphenylphosphine and an alkyl halide. The reaction is quite general and many functional groups are tolerated, even esters, as in this example:[15]

Related to the Wittig reaction is the Peterson olefination. This uses a less accessible silicon-based reagent in place of the phosphorane, but it allows for the selection of E- or Z-products. If an E-product is desired, another alternative is the Julia olefination, which uses the carbanion generated from a phenyl sulfone. The Takai olefination based on an organochromium intermediate also delivers E-products. A titanium compound, Tebbe's reagent, is useful for the synthesis of methylene compounds; in this case, even esters and amides react.
A pair of carbonyl compounds can also be reductively coupled together (with reduction) to generate an alkene. Symmetrical alkenes can be prepared from a single aldehyde or ketone coupling with itself, using titanium metal reduction (the McMurry reaction). If two different ketones are to be coupled, a more complex, indirect method such as the Barton–Kellogg reaction may be used.
A single ketone can also be converted to the corresponding alkene via its tosylhydrazone, using sodium methoxide (the Bamford–Stevens reaction) or an alkyllithium (the Shapiro reaction).
Synthesis from alkenes: olefin metathesis and hydrovinylation
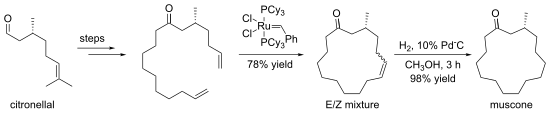
Alkenes can be prepared by exchange with other alkenes, in a reaction known as olefin metathesis. Frequently, loss of ethene gas is used to drive the reaction towards a desired product. In many cases, a mixture of geometric isomers is obtained, but the reaction tolerates many functional groups. The method is particularly effective for the preparation of cyclic alkenes, as in this synthesis of muscone:
Transition metal catalyzed hydrovinylation is another important alkene synthesis process starting from alkene itself.[16] In general, it involves the addition of a hydrogen and a vinyl group (or an alkenyl group) across a double bond. The hydrovinylation reaction was first reported by Alderson, Jenner, and Lindsey by using rhodium and ruthenium salts, other metal catalysts commonly employed nowadays included iron, cobalt, nickel, and palladium. The addition can be done highly regio- and stereoselectively, the choices of metal centers, ligands, substrates and counterions often play very important role.[17][18][19] Recent studies showed that the use of N-heterocyclic carbene with Ni can be useful for the selective preparations of functionalized geminal olefins or 1,1-disubstituted alkenes.[20][21]
From alkynes
Reduction of alkynes is a useful method for the stereoselective synthesis of disubstituted alkenes. If the cis-alkene is desired, hydrogenation in the presence of Lindlar's catalyst (a heterogeneous catalyst that consists of palladium deposited on calcium carbonate and treated with various forms of lead) is commonly used, though hydroboration followed by hydrolysis provides an alternative approach. Reduction of the alkyne by sodium metal in liquid ammonia gives the trans-alkene.[22]
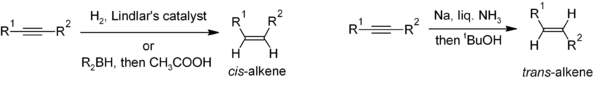
For the preparation multisubstituted alkenes, carbometalation of alkynes can give rise to a large variety of alkene derivatives.
Alkenes can be synthesized from other alkenes via rearrangement reactions. Besides olefin metathesis (described above), a large number of pericyclic reactions can be used such as the ene reaction and the Cope rearrangement.

In the Diels–Alder reaction, a cyclohexene derivative is prepared from a diene and a reactive or electron-deficient alkene.
Nomenclature
Although the nomenclature is not followed widely, according to IUPAC, alkenes are acyclic hydrocarbons with one double bond between carbon centers. Olefins comprise a larger collection of cyclic and acyclic alkenes as well as dienes and polyenes.[23]
IUPAC names
To form the root of the IUPAC names for alkenes, simply change the -an- infix of the parent to -en-. For example, CH3-CH3 is the alkane ethANe. The name of CH2=CH2 is therefore ethENe.
In higher alkenes, where isomers exist that differ in location of the double bond, the following numbering system is used:
- Number the longest carbon chain that contains the double bond in the direction that gives the carbon atoms of the double bond the lowest possible numbers.
- Indicate the location of the double bond by the location of its first carbon.
- Name branched or substituted alkenes in a manner similar to alkanes.
- Number the carbon atoms, locate and name substituent groups, locate the double bond, and name the main chain.

Naming substituted hex-1-enes
Cis–trans notation
In the specific case of disubstituted alkenes where the two carbons have one substituent each, cis–trans notation may be used. If both substituents are on the same side of the bond, it is defined as cis-. If the substituents are on either side of the bond, it is defined as trans-.

The difference between cis- and trans- isomers
E–Z notation
When an alkene has more than one substituent (especially necessary with 3 or 4 substituents), the double bond geometry is described using the labels E and Z. These labels come from the German words entgegen, meaning "opposite", and zusammen, meaning "together". Alkenes with the higher priority groups (as determined by CIP rules) on the same side of the double bond have these groups together and are designated Z. Alkenes with the higher priority groups on opposite sides are designated E. A mnemonic to remember this: Z notation has the higher priority groups on "ze zame zide."

The difference between E and Z isomers
Groups containing C=C double bonds
IUPAC recognizes two names for hydrocarbon groups containing carbon–carbon double bonds, the vinyl group and the allyl group.[2]

See also
| Look up alkene in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
| Wikiquote has quotations related to: Alkene |
- Alpha-olefin
- Cycloalkene
- Arenes
- Diene
- Dendralene
- Radialene
- Annulene
- Polyene
- Nitroalkene
Nomenclature links
- Rule A-3. Unsaturated Compounds and Univalent Radicals [1] IUPAC Blue Book.
- Rule A-4. Bivalent and Multivalent Radicals [2] IUPAC Blue Book.
- Rules A-11.3, A-11.4, A-11.5 Unsaturated monocyclic hydrocarbons and substituents [3] IUPAC Blue Book.
- Rule A-23. Hydrogenated Compounds of Fused Polycyclic Hydrocarbons [4] IUPAC Blue Book.
References
^ abc Wade, L.G. (2006). Organic Chemistry (6th ed.). Pearson Prentice Hall. p. 279. ISBN 978-1-4058-5345-3..mw-parser-output cite.citationfont-style:inherit.mw-parser-output qquotes:"""""""'""'".mw-parser-output code.cs1-codecolor:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registrationcolor:#555.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration spanborder-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-errordisplay:none;font-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-errorfont-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-formatfont-size:95%.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-leftpadding-left:0.2em.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-rightpadding-right:0.2em
^ abc Moss, G. P.; Smith, P. A. S.; Tavernier, D. (1995). "Glossary of Class Names of Organic Compounds and Reactive Intermediates Based on Structure (IUPAC Recommendations 1995)". Pure and Applied Chemistry. 67 (8–9): 1307–1375. doi:10.1351/pac199567081307.
^ "Production: Growth is the Norm". Chemical and Engineering News. 84 (28): 59–236. July 10, 2006. doi:10.1021/cen-v084n034.p059.
^ ab Barrows, Susan E.; Eberlein, Thomas H. (2005). "Understanding Rotation about a C=C Double Bond". J. Chem. Educ. 82 (9): 1329. Bibcode:2005JChEd..82.1329B. doi:10.1021/ed082p1329.
^ ab Bansal, Raj K. (1998). "Bredt's Rule". Organic Reaction Mechanisms (3rd ed.). McGraw-Hill Education. pp. 14–16. ISBN 9780074620830.
^ Fawcett, Frank S. (1950). "Bredt's Rule of Double Bonds in Atomic-Bridged-Ring Structures". Chem. Rev. 47 (2): 219–274. doi:10.1021/cr60147a003.
^ Bredt's Rule. Comprehensive Organic Name Reactions and Reagents. 116. 2010. pp. 525–528. doi:10.1002/9780470638859.conrr116. ISBN 9780470638859.
^ "New evidence of the geological origins of the ancient Delphic oracle (Greece)". Nature News. 2001-07-17. doi:10.1038/news010719-10.
^ Duan, Xufang; Block, Eric; Li, Zhen; Connelly, Timothy; Zhang, Jian; Huang, Zhimin; Su, Xubo; Pan, Yi; Wu, Lifang (2012-02-28). "Crucial role of copper in detection of metal-coordinating odorants". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 109 (9): 3492–3497. Bibcode:2012PNAS..109.3492D. doi:10.1073/pnas.1111297109. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 3295281. PMID 22328155.
^ Streiwieser, A.; Heathcock, C.H.; Kosower, E.M. (1992). "11.6.G. Alkenes: Reactions: Free Radical Additions". Introduction to Organic Chemistry (4th ed.). New York: Macmillan. p. 288.
^ Wade, L.G. (2006). Organic Chemistry (6th ed.). Pearson Prentice Hall. p. 309. ISBN 978-1-4058-5345-3.
^ Saunders, W. H. (1964). Patai, Saul, ed. The Chemistry of Alkenes. Wiley Interscience. pp. 149–150.
^ Cram, D.J.; Greene, Frederick D.; Depuy, C. H. (1956). "Studies in Stereochemistry. XXV. Eclipsing Effects in the E2 Reaction1". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 78 (4): 790–796. doi:10.1021/ja01585a024.
^ Bach, R.D.; Andrzejewski, Denis; Dusold, Laurence R. (1973). "Mechanism of the Cope elimination". J. Org. Chem. 38 (9): 1742–3. doi:10.1021/jo00949a029.
^ Snider, Barry B.; Matsuo, Y; Snider, BB (2006). "Synthesis of ent-Thallusin". Org. Lett. 8 (10): 2123–6. doi:10.1021/ol0605777. PMC 2518398. PMID 16671797.
^ Vogt, D. (2010). "Cobalt-Catalyzed Asymmetric Hydrovinylation". Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 49 (40): 7166–8. doi:10.1002/anie.201003133. PMID 20672269.
^ Grutters, M. M. P.; Muller, C.; Vogt, D. (2006). "Highly Selective Cobalt-Catalyzed Hydrovinylation of Styrene". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128 (23): 7414–5. doi:10.1021/ja058095y. PMID 16756275.
^ Hilt, G.; Danz, M.; Treutwein, J. (2009). "Cobalt-Catalyzed 1,4-Hydrovinylation of Styrenes and 1-Aryl-1,3-butadienes". Org. Lett. 11 (15): 3322–5. doi:10.1021/ol901064p. PMID 19583205.
^ Sharma, R. K.; RajanBabu, T. V. (2010). "Asymmetric Hydrovinylation of Unactivated Linear 1,3-Dienes". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132 (10): 3295–7. doi:10.1021/ja1004703. PMC 2836389. PMID 20163120.
^ Ho, C.-Y.; He, L. (2010). "Catalytic Intermolecular Tail-to-Tail Hydroalkenylation of Styrenes with alpha-Olefins: Regioselective Migratory Insertion Controlled by a Nickel/N-Heterocyclic Carbene". Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 49 (48): 9182–9186. doi:10.1002/anie.201001849. PMID 20853303.
^ Ho, C.-Y.; He, L. (2012). "Shuffle Off the Classic Beta-Si Elimination by Ni-NHC Cooperation: Implication for C–C Forming Reactions Involving Ni-Alkyl-Beta-Silanes". Chem. Commun. 48 (10): 1481–1483. doi:10.1039/c1cc14593b. PMID 22116100.
^ Zweifel, George S.; Nantz, Michael H. (2007). Modern Organic Synthesis: An Introduction. New York: W. H. Freeman & Co. p. 366. ISBN 978-0-7167-7266-8.
^ http://goldbook.iupac.org/O04281.html