Rotation around a fixed axis
| Part of a series of articles about |
| Classical mechanics |
|---|
F→=ma→displaystyle vec F=mvec a  Second law of motion |
|
Branches
|
Fundamentals
|
Formulations
|
Core topics
|
Rotation
|
Scientists
|

Sphere rotating around one of its diameters
Rotation around a fixed axis or about a fixed axis of revolution or motion with respect to a fixed axis of rotation is a special case of rotational motion. The fixed axis hypothesis excludes the possibility of an axis changing its orientation, and cannot describe such phenomena as wobbling or precession. According to Euler's rotation theorem, simultaneous rotation along a number of stationary axes at the same time is impossible. If two rotations are forced at the same time, a new axis of rotation will appear.
This article assumes that the rotation is also stable, such that no torque is required to keep it going. The kinematics and dynamics of rotation around a fixed axis of a rigid body are mathematically much simpler than those for free rotation of a rigid body; they are entirely analogous to those of linear motion along a single fixed direction, which is not true for free rotation of a rigid body. The expressions for the kinetic energy of the object, and for the forces on the parts of the object, are also simpler for rotation around a fixed axis, than for general rotational motion. For these reasons, rotation around a fixed axis is typically taught in introductory physics courses after students have mastered linear motion; the full generality of rotational motion is not usually taught in introductory physics classes.
Contents
1 Translation and rotation
2 Kinematics
2.1 Angular displacement
2.2 Angular speed and angular velocity
2.3 Angular acceleration
2.4 Equations of kinematics
3 Dynamics
3.1 Moment of inertia
3.2 Torque
3.3 Angular momentum
3.4 Kinetic energy
4 Vector expression
5 Examples and applications
5.1 Constant angular speed
5.2 Centripetal force
6 See also
7 References
Translation and rotation
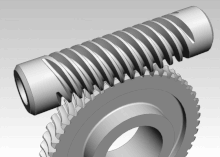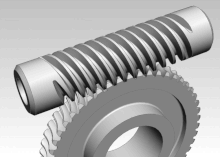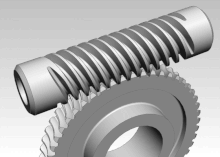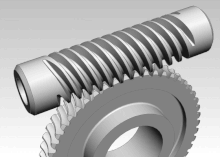
An example of rotation. Each part of the worm drive—both the worm and the worm gear—is rotating on its own axis.
A rigid body is an object of finite extent in which all the distances between the component particles are constant. No truly rigid body exists; external forces can deform any solid. For our purposes, then, a rigid body is a solid which requires large forces to deform it appreciably.
A change in the position of a particle in three-dimensional space can be completely specified by three coordinates. A change in the position of a rigid body is more complicated to describe. It can be regarded as a combination of two distinct types of motion: translational motion and circular motion.
Purely translational motion occurs when every particle of the body has the same instantaneous velocity as every other particle; then the path traced out by any particle is exactly parallel to the path traced out by every other particle in the body. Under translational motion, the change in the position of a rigid body is specified completely by three coordinates such as x, y, and z giving the displacement of any point, such as the center of mass, fixed to the rigid body.
Purely rotational motion occurs if every particle in the body moves in a circle about a single line. This line is called the axis of rotation. Then the radius vectors from the axis to all particles undergo the same angular displacement at the same time. The axis of rotation need not go through the body. In general, any rotation can be specified completely by the three angular displacements with respect to the rectangular-coordinate axes x, y, and z. Any change in the position of the rigid body is thus completely described by three translational and three rotational coordinates.
Any displacement of a rigid body may be arrived at by first subjecting the body to a displacement followed by a rotation, or conversely, to a rotation followed by a displacement. We already know that for any collection of particles—whether at rest with respect to one another, as in a rigid body, or in relative motion, like the exploding fragments of a shell, the acceleration of the center of mass is given by
- Fnet=Macmdisplaystyle F_mathrm net =Ma_mathrm cm ;!
where M is the total mass of the system and acm is the acceleration of the center of mass. There remains the matter of describing the rotation of the body about the center of mass and relating it to the external forces acting on the body. The kinematics and dynamics of rotational motion around a single axis resemble the kinematics and dynamics of translational motion; rotational motion around a single axis even has a work-energy theorem analogous to that of particle dynamics.
Kinematics
Angular displacement
A particle moves in a circle of radius rdisplaystyle r



In mathematics and physics it is usual to use the natural unit radians rather than degrees or revolutions. Units are converted as follows:
- 1 revolution =360∘=2π radians, and1 rad=180∘π≈57.27∘.displaystyle beginaligned1text revolution &=360^circ =2pi text radians, and\1text rad&=frac 180^circ pi approx 57.27^circ .endaligned
An angular displacement is a change in angular position:
- Δθ=θ2−θ1,displaystyle Delta theta =theta _2-theta _1,!
where Δθdisplaystyle Delta theta 


Angular speed and angular velocity
Change in angular displacement per unit time is called angular velocity with direction along the axis of rotation. The symbol for angular velocity is ωdisplaystyle omega 
- ω¯=ΔθΔt=θ2−θ1t2−t1.displaystyle overline omega =frac Delta theta Delta t=frac theta _2-theta _1t_2-t_1.
The instantaneous angular velocity is given by
- ω(t)=dθdt.displaystyle omega (t)=frac dtheta dt.
Using the formula for angular position and letting v=dsdtdisplaystyle v=frac dsdt
- ω=dθdt=vr,displaystyle omega =frac dtheta dt=frac vr,
where vdisplaystyle v
Angular velocity and frequency are related by
ω=2πfdisplaystyle omega =2pi f!.
Angular acceleration
A changing angular velocity indicates the presence of an angular acceleration in rigid body, typically measured in rad s−2. The average angular acceleration α¯displaystyle overline alpha 
- α¯=ΔωΔt=ω2−ω1t2−t1.displaystyle overline alpha =frac Delta omega Delta t=frac omega _2-omega _1t_2-t_1.
The instantaneous acceleration α(t) is given by
- α(t)=dωdt=d2θdt2.displaystyle alpha (t)=frac domega dt=frac d^2theta dt^2.
Thus, the angular acceleration is the rate of change of the angular velocity, just as acceleration is the rate of change of velocity.
The translational acceleration of a point on the object rotating is given by
- a=rα,displaystyle a=ralpha ,!
where r is the radius or distance from the axis of rotation. This is also the tangential component of acceleration: it is tangential to the direction of motion of the point. If this component is 0, the motion is uniform circular motion, and the velocity changes in direction only.
The radial acceleration (perpendicular to direction of motion) is given by
aR=v2r=ω2rdisplaystyle a_mathrm R =frac v^2r=omega ^2r!.
It is directed towards the center of the rotational motion, and is often called the centripetal acceleration.
The angular acceleration is caused by the torque, which can have a positive or negative value in accordance with the convention of positive and negative angular frequency. The ratio of torque and angular acceleration (how difficult it is to start, stop, or otherwise change rotation) is given by the moment of inertia: T=Iαdisplaystyle T=Ialpha 
Equations of kinematics
When the angular acceleration is constant, the five quantities angular displacement θdisplaystyle theta 




- ωf=ωi+αtθ=ωit+12αt2ωf2=ωi2+2αθθ=12(ωf+ωi)tdisplaystyle beginalignedomega _f&=omega _i+alpha t\theta &=omega _it+frac 12alpha t^2\omega _f^2&=omega _i^2+2alpha theta \theta &=frac 12left(omega _f+omega _iright)tendaligned
Dynamics
Moment of inertia
The moment of inertia of an object, symbolized by I, is a measure of the object's resistance to changes to its rotation. The moment of inertia is measured in kilogram metre² (kg m²). It depends on the object's mass: increasing the mass of an object increases the moment of inertia. It also depends on the distribution of the mass: distributing the mass further from the center of rotation increases the moment of inertia by a greater degree. For a single particle of mass mdisplaystyle m

- I=mr2.displaystyle I=mr^2.
Torque
Torque τdisplaystyle boldsymbol tau 
- τ=r×F,displaystyle boldsymbol tau =mathbf r times mathbf F ,
where × denotes the cross product. A net torque acting upon an object will produce an angular acceleration of the object according to
- τ=Iα,displaystyle boldsymbol tau =Iboldsymbol alpha ,
just as F = ma in linear dynamics.
The work done by a torque acting on an object equals the magnitude of the torque times the angle through which the torque is applied:
- W=τθ.displaystyle W=tau theta .!
The power of a torque is equal to the work done by the torque per unit time, hence:
- P=τω.displaystyle P=tau omega .!
Angular momentum
The angular momentum Ldisplaystyle mathbf L 
L=∑r×pdisplaystyle mathbf L =sum mathbf r times mathbf pfor all particles in the object.
Angular momentum is the product of moment of inertia and angular velocity:
- L=Iω,displaystyle mathbf L =Iboldsymbol omega ,
just as p = mv in linear dynamics.
The equivalent of linear momentum in rotational motion is angular momentum. The greater the angular momentum of the spinning object such as a top, the greater its tendency to continue to spin.
The Angular Momentum of a rotating body is proportional to its mass and to how rapidly it is turning. In addition, the angular momentum depends on how the mass is distributed relative to the axis of rotation: the further away the mass is located from the axis of rotation, the greater the angular momentum. A flat disk such as a record turntable has less angular momentum than a hollow cylinder of the same mass and velocity of rotation.
Like linear momentum, angular momentum is vector quantity, and its conservation implies that the direction of the spin axis tends to remain unchanged. For this reason, the spinning top remains upright whereas a stationary one falls over immediately.
The angular momentum equation can be used to relate the moment of the resultant force on a body about an axis (sometimes called torque), and the rate of rotation about that axis.
Torque and angular momentum are related according to
- τ=dLdt,displaystyle boldsymbol tau =frac dmathbf L dt,
just as F = dp/dt in linear dynamics. In the absence of an external torque, the angular momentum of a body remains constant. The conservation of angular momentum is notably demonstrated in figure skating: when pulling the arms closer to the body during a spin, the moment of inertia is decreased, and so the angular velocity is increased.
Kinetic energy
The kinetic energy Krot due to the rotation of the body is given by
- Krot=12Iω2,displaystyle K_textrot=frac 12Iomega ^2,
just as Ktrans = 1⁄2mv2 in linear dynamics.
Kinetic energy is the energy of motion. The amount of translational kinetic energy found in two variables: the mass of the object (m) and the speed of the object (v) as shown in the equation above. Kinetic energy must always be either zero or a positive value. While velocity can have either a positive or negative value, velocity squared will always be positive.[1]
Vector expression
The above development is a special case of general rotational motion. In the general case, angular displacement, angular velocity, angular acceleration, and torque are considered to be vectors.
An angular displacement is considered to be a vector, pointing along the axis, of magnitude equal to that of Δθdisplaystyle Delta theta 
The angular velocity vector also points along the axis of rotation in the same way as the angular displacements it causes. If a disk spins counterclockwise as seen from above, its angular velocity vector points upwards. Similarly, the angular acceleration vector points along the axis of rotation in the same direction that the angular velocity would point if the angular acceleration were maintained for a long time.
The torque vector points along the axis around which the torque tends to cause rotation. To maintain rotation around a fixed axis, the total torque vector has to be along the axis, so that it only changes the magnitude and not the direction of the angular velocity vector. In the case of a hinge, only the component of the torque vector along the axis has an effect on the rotation, other forces and torques are compensated by the structure.
Examples and applications
Constant angular speed
The simplest case of rotation around a fixed axis is that of constant angular speed. Then the total torque is zero. For the example of the Earth rotating around its axis, there is very little friction. For a fan, the motor applies a torque to compensate for friction. Similar to the fan, equipment found in the mass production manufacturing industry demonstrate rotation around a fixed axis effectively. For example, a multi-spindle lathe is used to rotate the material on its axis to effectively increase production of cutting, deformation and turning.[2] The angle of rotation is a linear function of time, which modulo 360° is a periodic function.
An example of this is the two-body problem with circular orbits.
Centripetal force
Internal tensile stress provides the centripetal force that keeps a spinning object together. A rigid body model neglects the accompanying strain. If the body is not rigid this strain will cause it to change shape. This is expressed as the object changing shape due to the "centrifugal force".
Celestial bodies rotating about each other often have elliptic orbits. The special case of circular orbits is an example of a rotation around a fixed axis: this axis is the line through the center of mass perpendicular to the plane of motion. The centripetal force is provided by gravity, see also two-body problem. This usually also applies for a spinning celestial body, so it need not be solid to keep together unless the angular speed is too high in relation to its density. (It will, however, tend to become oblate.) For example, a spinning celestial body of water must take at least 3 hours and 18 minutes to rotate, regardless of size, or the water will separate[citation needed]. If the density of the fluid is higher the time can be less. See orbital period.[3]
See also
- Anatomical terms of motion
- Artificial gravity by rotation
- Axle
- Axial precession
- Axial tilt
Carousel, Ferris wheel- Center pin
- Centrifugal force
- Centrifuge
- Centripetal force
- Circular motion
- Coriolis effect
- Fictitious force
- Flywheel
- Gyration
- Instant centre of rotation
- Linear-rotational analogs
- Revolutions per minute
- Revolving door
- Rigid body angular momentum
- Rotation matrix
- Rotational speed
- Rotational symmetry
- Run-out
- Spin
References
^ "Khan Academy". Khan Academy. Retrieved 2017-08-02..mw-parser-output cite.citationfont-style:inherit.mw-parser-output qquotes:"""""""'""'".mw-parser-output code.cs1-codecolor:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registrationcolor:#555.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration spanborder-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-errordisplay:none;font-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-errorfont-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-formatfont-size:95%.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-leftpadding-left:0.2em.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-rightpadding-right:0.2em
^ "Multi Spindle Machines - An In-Depth Overview". Davenport Machine. Retrieved 2017-08-02.
^ Mobberley, Martin (2009-03-01). Cataclysmic Cosmic Events and How to Observe Them. Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 9780387799469.
Fundamentals of Physics Extended 7th Edition by Halliday, Resnick and Walker.
ISBN 0-471-23231-9
Concepts of Physics Volume 1, by H. C. Verma, 1st edition,
ISBN 81-7709-187-5

















