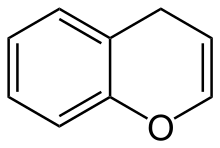
Benzopyran
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
ChemSpider |
|
PubChem CID |
|
UNII |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula | C9H8O |
Molar mass | 132.16 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Infobox references | |
Benzopyran is a polycyclic organic compound that results from the fusion of a benzene ring to a heterocyclic pyran ring.
According to current IUPAC nomenclature, the name chromene used in previous recommendations is retained; however, systematic ‘benzo’ names, for example 2H-1-benzopyran, are preferred IUPAC names for chromene, isochromene, chromane, isochromane, and their chalcogen analogues.[1] There are two isomers of benzopyran that vary by the orientation of the fusion of the two rings compared to the oxygen, resulting in 1-benzopyran (chromene) and 2-benzopyran (isochromene)—the number denotes where the oxygen atom is located by standard naphthalene-like nomenclature.
Some benzopyrans have shown anticancerous activity in vitro.[2]
The radical form of benzopyran is paramagnetic. The unpaired electron is delocalized over the whole benzopyran molecule, rendering it less reactive than one would expect otherwise, a similar example is the cyclopentadienyl radical. Commonly, benzopyran is encountered in the reduced state, in which it is partially saturated with one hydrogen atom, introducing a tetrahedral CH2 group in the pyran ring. Therefore, there are many structural isomers owing to the multiple possible positions of the oxygen atom and the tetrahedral carbon atom:
 2H-chromene (2H-1-benzopyran) |  4H-chromene (4H-1-benzopyran) |
5H-chromene | 7H-chromene |
8aH-chromene |
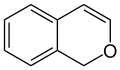 1H-isochromene (1H-2-benzopyran) |  3H-isochromene (3H-2-benzopyran) |
See also
- Benzofuran
- Benzopyrone
References
^ "Front Matter". Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. pp. P001–P004. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4..mw-parser-output cite.citationfont-style:inherit.mw-parser-output .citation qquotes:"""""""'""'".mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registrationcolor:#555.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration spanborder-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output code.cs1-codecolor:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-errordisplay:none;font-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-errorfont-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-maintdisplay:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-formatfont-size:95%.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-leftpadding-left:0.2em.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-rightpadding-right:0.2em
^ Stevenson, Alexander J; Ager, Eleanor I; Proctor, Martina A; Škalamera, Dubravka; Heaton, Andrew; Brown, David; Gabrielli, Brian G (2018). "Mechanism of action of the third generation benzopyrans and evaluation of their broad anti-cancer activity in vitro and in vivo". Scientific Reports. 8 (1): 5144. doi:10.1038/s41598-018-22882-w. PMC 5865165. PMID 29572477.
This article about an organic compound is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |