West German federal election, 1949
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 402 seats in the Bundestag, as well as 8 nonvoting delegates elected by the West Berlin Legislature 206 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 78.5% (voting eligible)[2] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
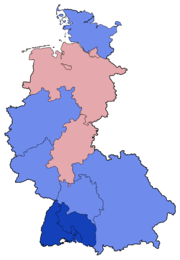 Election results by state: the lighter blue denotes states where CDU/CSU had the plurality of votes; darker blue denotes states where CDU had the absolute majority of the votes; and pink denotes states where the SPD had the plurality of votes | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Federal elections were held in West Germany on 14 August 1949 to elect the first Bundestag,[3] with a further eight seats elected in West Berlin between 1949 and January 1952 and another eleven between February 1952 and 1953.[4] They were the first contested elections since 1933 and the first after the division of the country.
Contents
1 Campaign
2 Results
3 Post-election
4 References
5 Further reading
Campaign
After World War II, the German Instrument of Surrender and the country's division into four Allied occupation zones, the elections were held in the Federal Republic of Germany, established under occupation statute in the three Western zones with the proclamation of its Basic Law by the Parlamentarischer Rat assembly of the West German states on 23 May 1949. Most West German parties at the time of the 1949 Bundestag election were committed to democracy, but they disagreed on what kind of democracy West Germany should become.

CDU election poster
The Christian Democratic (CDU) leader, 73-year-old Konrad Adenauer, former mayor of Cologne and party chairman in the British Zone since March 1946, believed in moderate, non-denominational and humanist Christian democracy,[5][6]social market economy and integration with the West. In 1948 he had become president of the Parlamentarischer Rat, an office that added to his popularity as protagonist of a "state-to-be".

SPD election poster
The Social Democratic (SPD) leader, Kurt Schumacher, wanted a united, democratic and socialist Germany. Schumacher had heavily agitated against the forced merger of the Communist Party (KPD) and SPD (both in the Soviet occupation zone) into the Socialist Unity Party of Germany and he had also turned the party's course away from the working class advocacy group of the Weimar Republic towards a left-wing big tent party with distinct patriotic features. He constantly accused Adenauer of betraying national interests (see, for example, Bjöl, Grimberg's History of the Nations), culminating in his heckle at the Bundestag session of 25 September 1949: "The Chancellor of the Allies!".
Results
In the end and to the great disappointment of the Social Democrats, the CDU/CSU outnumbered them by 31.0% to 29.2% of the votes cast. Enough participating West Germans favoured Adenauer's and his coalition partners' – the liberal Free Democrats' (FDP) and the conservative German Party's (DP) – policies and promises over Schumacher's and the other left-wingers' policies to give the centre-right parties a slight majority of deputies.
To enter the Bundestag, a party had to surmount a threshold of 5% at least in one of the states or to win at least one electoral district; ten parties succeeded. A number of non-voting members (elected in 1949:2 CDU, 5 SPD, 1 FDP; joined in February 1952 by: 3 CDU, 4 SPD, 4 FDP) indirectly elected by the West Berlin legislature (Stadtverordnetenversammlung) are included below in parentheses. The French Saar Protectorate did not participate in this election.
| Parties | Votes | % | Con. seats | PL seats | Total seats | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Social Democratic Party (SPD) | 6,934,975 | 29.2 | 96 | 35 | 131 (9) | 32.6 | |
Christian Democratic Union (CDU) | 5,978,636 | 25.2 | 91 | 24 | 115 (5) | 28.6 | |
Free Democratic Party (FDP) | 2,829,920 | 11.9 | 12 | 40 | 52 (5) | 12.9 | |
Christian Social Union (CSU) | 1,380,448 | 5.8 | 24 | 0 | 24 | 6.0 | |
Communist Party of Germany (KPD) | 1,361,706 | 5.7 | 0 | 15 | 15 | 3.7 | |
Bavaria Party (BP) | 986,478 | 4.2 | 11 | 6 | 17 | 4.2 | |
German Party (DP) | 939,934 | 4.0 | 5 | 12 | 17 | 4.2 | |
Centre Party (DZP) | 727,505 | 3.1 | 0 | 10 | 10 | 2.5 | |
Economic Reconstruction League (WAV) | 681,888 | 2.9 | 0 | 12 | 12 | 3.0 | |
German Conservative Party – German Right Party (DKP-DRP) | 429,031 | 1.8 | 0 | 5 | 5 | 1.2 | |
South Schleswig Voter Federation (SSW) | 75,388 | 0.3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0.2 | |
Independents | 1,141,647 | 4.8 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 0.7 | |
| Radical Social Freedom Party (RSF) | 216,749 | 0.9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| European People's Movement of Germany (EVD) | 26,162 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Rheinish-Westfalian People's Party (RWVP) | 21,931 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Invalid/blank votes | 763,216 | — | — | — | — | — | |
| Totals | 24,495,614 | 100 | 242 | 160 | 402 (19) | 100 | |
| Registered voters/turnout | 31,207,620 | 78.5 | — | — | — | — | |
Source: Federal Returning Officer, Nohlen & Stöver | |||||||
139 | 52 | 17 | 131 | 17 | 15 | 12 | ||||
CDU/CSU | FDP | DP | SPD | BP | KPD | WAV |
Post-election
Schumacher had explicitly refused a grand coalition and led his party into opposition, where it would remain until December 1966, assuming the chair of the SPD parliamentary group as minority leader. On 12 September 1949, he lost the German presidential election, defeated by FDP chairman Theodor Heuss in the second ballot. Schumacher died on 20 August 1952 of the long-term consequences of his concentration camp imprisonment during the Nazi years.
Adenauer had favoured the formation of a smaller centre-right coalition from the beginning. Nominated by the CDU/CSU faction, he was elected the first Chancellor of the Federal Republic of Germany on 15 September 1949 by an absolute majority of 202 of 402 votes. Adenauer had ensured that the votes of the predominantly Social Democrat West Berlin deputies did not count and later stated that he "naturally" had voted for himself.[7] On 20 September, he formed the Cabinet Adenauer I of CDU/CSU, FDP, and DP ministers. Chosen as an interim Chancellor, he held the office until 1963, being re-elected three times (in 1953, in 1957 and in 1961).
References
^ "Wahl zum 1. Deutschen Bundestag am 14. August 1949" (in German). Bundeswahlleiter. Archived from the original on 6 May 2012. Retrieved 5 May 2012..mw-parser-output cite.citationfont-style:inherit.mw-parser-output qquotes:"""""""'""'".mw-parser-output code.cs1-codecolor:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registrationcolor:#555.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration spanborder-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-errordisplay:none;font-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-errorfont-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-formatfont-size:95%.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-leftpadding-left:0.2em.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-rightpadding-right:0.2em
^ "Voter turnout by election year". Website of the Federal Returning Officer's Office. The Federal Returning Officer. Archived from the original on 8 September 2013. Retrieved 7 November 2014.
^ Nohlen, Dieter; Stöver, Philip (31 May 2010). Elections in Europe: A data handbook. Nomos. p. 762. ISBN 978-3832956097.
^ Nohlen, Dieter; Stöver, Philip (31 May 2010). Elections in Europe: A data handbook. Nomos. p. 793. ISBN 978-3832956097.
^ Dennis L. Bark and David R. Gress, A History of West Germany, volume 1: 1945–1963: From Shadow to Substance, London, UK: Basil Blackwell, 1989
^ Erling Bjöl, Grimberg's History of the Nations, volume 23: The Rich West, "The Giant Dwarf: West Germany," Helsinki: WSOY, 1985
^ David Reynolds (2015) One World Divisible: A Global History Since 1945, Penguin UK
Further reading
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to 1949 Germany Bundestagswahl. |
Kirchheimer, Otto (1950). "The Composition of the German Bundestag, 1950". Western Political Quarterly. 3 (4): 590–601. doi:10.2307/442516.


