Partitions of Poland
| Partitions of Poland | |
|---|---|
 The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth in 1772 | |
| Elimination | |
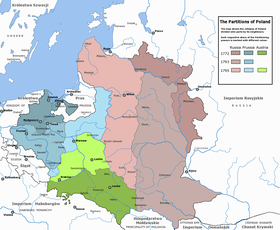 The three partitions of Poland (the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth). The Russian Partition (red), the Austrian Partition (green), and the Prussian Partition (blue) | |
The Partitions of Poland[nb 1] were three partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that took place toward the end of the 18th century and ended the existence of the state, resulting in the elimination of sovereign Poland and Lithuania for 123 years. The partitions were conducted by Habsburg Austria, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Russian Empire, which divided up the Commonwealth lands among themselves progressively in the process of territorial seizures and annexations.[1][2][3][4]
The First Partition of Poland was decided on August 5, 1772. Two decades later, Russian and Prussian troops entered the Commonwealth again and the Second Partition was signed on January 23, 1793. Austria did not participate in the Second Partition. The Third Partition of Poland took place on October 24, 1795, in reaction to the unsuccessful Polish Kościuszko Uprising the previous year. With this partition, the Commonwealth ceased to exist.[1]
In English, the term "Partitions of Poland" is sometimes used geographically as toponymy, to mean the three parts that the partitioning powers divided the Commonwealth into the Austrian Partition, the Prussian Partition and the Russian Partition. In Polish, there are two separate words for the two meanings. The consecutive acts of dividing and annexation of Poland are referred to as rozbiór (plural: rozbiory), while the term zabór (pl. zabory) means each part of the Commonwealth annexed in 1772–95 becoming part of Imperial Russia, Prussia, or Austria.
In Polish historiography, the term "Fourth Partition of Poland" has also been used, in reference to any subsequent annexation of Polish lands by foreign invaders. Depending on source and historical period, this could mean the events of 1815, or 1832 and 1846, or 1939 (see below), bringing the total number of Poland's names for the ceding of territory to neighboring empires to seven. The term "Fourth Partition" in a temporal sense can also mean the diaspora communities that played an important political role in re-establishing the Polish sovereign state after 1918.
Contents
1 History
1.1 First Partition
1.2 Second Partition
1.3 Third Partition
2 Summary
3 Aftermath
4 "Fourth Partition"
5 Historiography
6 Other countries
7 See also
8 Notes
9 References
10 Further reading
11 External links
History

Allegory of the 1st partition of Poland, showing Catherine the Great of Russia (left), Joseph II of Austria and Frederick the Great of Prussia (right) quarrelling over their territorial seizures

Włodzimierz Tetmajer, Allegory of Dead Poland, St. Nicholas Cathedral, Kalisz
During the reign of Władysław IV (1632–48), the liberum veto was developed, a policy of parliamentary procedure based on the assumption of the political equality of every "gentleman", with the corollary that unanimous consent was needed for all measures.[1] A single member of parliament's belief that a measure was injurious to his own constituency (usually simply his own estate), even after the act had been approved, became enough to strike the act. Thus it became increasingly difficult to undertake action. The liberum veto also provided openings for foreign diplomats to get their ways, through bribing nobles to exercise it.[1] Thus, one could characterise Poland–Lithuania in its final period (mid-18th century) before the partitions as already in a state of disorder and not a completely sovereign state, and almost as a vassal state,[5] or in modern terms, a Russian satellite state, with Russian tsars effectively choosing Polish kings. This applies particularly to the last Commonwealth King Stanisław August Poniatowski, who for some time had been a lover of Russian Empress Catherine the Great.
In 1730 the neighbors of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (Rzeczpospolita), namely Prussia, Austria and Russia, signed a secret agreement to maintain the status quo: specifically, to ensure that the Commonwealth laws would not change. Their alliance later became known in Poland as the "Alliance of the Three Black Eagles" (or Löwenwolde's Treaty), because all three states used a black eagle as a state symbol (in contrast to the white eagle, a symbol of Poland). The Commonwealth had been forced to rely on Russia for protection against the rising Kingdom of Prussia, which demanded a slice of the northwest in order to unite its Western and Eastern portions; this would leave the Commonwealth with a Baltic coast only in Latvia and Lithuania.[1] The Commonwealth could never be liquidated unless its long-time ally Austria allowed it,[citation needed] so Catherine had to use diplomacy to win Austria to her side.
The Commonwealth had remained neutral in the Seven Years' War (1756–1763), yet it sympathized with the alliance of France, Austria, and Russia, and allowed Russian troops access to its western lands as bases against Prussia. Frederick II retaliated by ordering enough Polish currency counterfeited to severely affect the Polish economy. Through the Polish nobles whom Russia controlled and the Russian Minister to Warsaw, ambassador and Prince Nicholas Repnin, Empress Catherine the Great forced a constitution on the Commonwealth at the so-called Repnin Sejm of 1767, named after ambassador Repnin, who effectively dictated the terms of that Sejm (and ordered the capture and exile to Kaluga of some vocal opponents of his policies,[5][6][7] including bishop Józef Andrzej Załuski[8] and others). This new constitution undid the reforms made in 1764 under Stanisław II. The liberum veto and all the old abuses of the last one and a half centuries were guaranteed as unalterable parts of this new constitution (in the so-called Cardinal Laws[7][9]). Repnin also demanded religious freedom for the Protestant and Orthodox Christians, and the resulting reaction among some of Poland's Roman Catholics, as well as the deep resentment of Russian intervention in the Commonwealth's domestic affairs, led to the War of the Confederation of Bar of 1768–1772, formed in Bar, where the Poles tried to expel Russian forces from Commonwealth territory.[5][7] The irregular and poorly commanded Polish forces had little chance in the face of the regular Russian army and suffered a major defeat. Adding to the chaos was a Ukrainian Cossack and peasant rebellion, the Koliyivshchyna, which erupted in 1768 and resulted in massacres of noblemen (szlachta), Jews, Uniates, and Catholic priests, before it was put down by Polish and Russian troops.
In 1769 Austria annexed a small territory of Spisz and in 1770 – Nowy Sącz and Nowy Targ. These territories had been a bone of contention between Poland and Hungary, which was a part of the Austrian crown lands.
First Partition
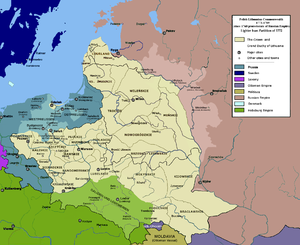
Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, after the First Partition, as a protectorate of the Russian Empire (1773–89)
In February 1772, the agreement of partition was signed in Vienna. Early in August, Russian, Prussian and Austrian troops simultaneously invaded the Commonwealth and occupied the provinces agreed upon among themselves. On August 5, 1772, the occupation manifesto was issued, much to the consternation of a country too exhausted by the endeavors of the Confederation of Bar to offer successful resistance;[1] nevertheless, several battles and sieges took place, as Commonwealth troops refused to lay down their arms (most notably, in Tyniec, Częstochowa and Kraków).
The partition treaty was ratified by its signatories on September 22, 1772. Frederick II of Prussia was elated with his success; Prussia took most of Royal Prussia (without Danzig) that stood between its possessions in the Kingdom of Prussia and the Margraviate of Brandenburg, as well as Ermland (Warmia), northern areas of Greater Poland along the Noteć River (the Netze District), and parts of Kuyavia (but not the city of Toruń).[1] Despite token criticism of the partition from Austrian Empress Maria Theresa, Austrian statesman Wenzel Anton, Prince of Kaunitz-Rietberg, was proud of wresting as large a share as he did, with the rich salt mines of Bochnia and Wieliczka. To Austria fell Zator and Auschwitz (Oświęcim), part of Lesser Poland embracing parts of the counties of Kraków and Sandomir and the whole of Galicia, less the city of Kraków. Catherine of Russia was also very satisfied. By this "diplomatic document" Russia came into possession of that section of Livonia that had remained in Commonwealth control, and of Belarus embracing the counties of Vitebsk, Polotsk and Mstislavl.[1]

Rejtan at Sejm 1773, oil on canvas by Jan Matejko, 1866, 282 cm × 487 cm (111 in × 192 in), Royal Castle in Warsaw.
By this partition, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth lost about 30% of its territory and half of its population[1] (four million people), of which a large portion had not been ethnically Polish. By seizing northwestern Poland, Prussia instantly gained control over 80% of the Commonwealth's total foreign trade. Through levying enormous customs duties, Prussia accelerated the collapse of the Commonwealth.[10]
After having occupied their respective territories, the three partitioning powers demanded that King Stanisław and the Sejm approve their action. When no help was forthcoming and the armies of the combined nations occupied Warsaw to compel by force of arms the calling of the assembly, no alternative could be chosen save passive submission to their will. The so-called Partition Sejm, with Russian military forces threatening the opposition, on September 18, 1773, signed the treaty of cession, renouncing all claims of the Commonwealth to the occupied territories.
Second Partition

After the Second Partition (1793)
By 1790 the First Polish Republic had been weakened to such a degree that it was forced into an unnatural and terminal alliance with its enemy, Prussia. The Polish–Prussian Pact of 1790 was signed. The conditions of the Pact contributed to the subsequent final two partitions of Poland–Lithuania.
The May Constitution of 1791 enfranchised the bourgeoisie, established the separation of the three branches of government, and eliminated the abuses of the Repnin Sejm. Those reforms prompted aggressive actions on the part of its neighbours, wary of the potential renaissance of the Commonwealth. Arguing that Poland had fallen prey to the radical Jacobinism then at high tide in France, Russian forces invaded the Commonwealth in 1792.
In the War in Defense of the Constitution, pro-Russian conservative Polish magnates, the Confederation of Targowica, fought against Polish forces supporting the constitution, believing that Russians would help them restore the Golden Liberty. Abandoned by their Prussian allies, Polish pro-constitution forces, faced with Targowica units and the regular Russian army, were defeated. Prussia signed a treaty with Russia, agreeing that Polish reforms would be revoked and both countries would receive chunks of Commonwealth territory. In 1793, deputies to the Grodno Sejm, last Sejm of the Commonwealth, in the presence of the Russian forces, agreed to Russian territorial demands. In the Second Partition, Russia and Prussia helped themselves to enough land so that only one-third of the 1772 population remained in Poland. Prussia named its newly gained province South Prussia, with Posen (and later Warsaw) as the capital of the new province.
Targowica confederates, who did not expect another partition, and the king, Stanisław August Poniatowski, who joined them near the end, both lost much prestige and support. The reformers, on the other hand, were attracting increasing support, and in 1794 the Kościuszko Uprising began.
Third Partition
Kosciuszko's ragtag insurgent armies won some initial successes, but they eventually fell before the superior forces of the Russian Empire. The partitioning powers, seeing the increasing unrest in the remaining Commonwealth, decided to solve the problem by erasing any independent Polish state from the map. On 24 October 1795 their representatives signed a treaty, dividing the remaining territories of the Commonwealth among their three countries.
The Russian part included 120,000 km2 (46,332 sq mi) and 1.2 million people with Vilnius, the Prussian part (new provinces of New East Prussia and New Silesia) 55,000 km2 (21,236 sq mi) and 1 million people with Warsaw, and the Austrian 47,000 km2 (18,147 sq mi) with 1.2 million and Lublin and Kraków.
Summary
With regard to population, in the First Partition, Poland lost over four to five million citizens (about a third of its population of 14 million before the partitions).[11] Only about 4 million people remained in Poland after the Second Partition which makes for a loss of another third of its original population, about a half of the remaining population.[12] By the Third Partition, Prussia ended up with about 23% of the Commonwealth's population, Austria with 32%, and Russia with 45%.[13]
| Partition | To Austria | To Prussia | To Russia | Total annexed | Total remaining | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area | % | Area | % | Area | % | Area | % | Area | % | |
| 1772 | 81,900 km2 (31,600 sq mi) | 11.17% | 36,300 km2 (14,000 sq mi) | 4.95% | 93,000 km2 (36,000 sq mi) | 12.68% | 211,200 km2 (81,500 sq mi) | 28.79% | 522,300 km2 (201,700 sq mi) | 71.21% |
| 1793 | — | — | 57,100 km2 (22,000 sq mi) | 7.78% | 250,200 km2 (96,600 sq mi) | 34.11% | 307,300 km2 (118,600 sq mi) | 41.90% | 215,000 km2 (83,000 sq mi) | 29.31% |
| 1795 | 47,000 km2 (18,000 sq mi) | 6.41% | 48,000 km2 (19,000 sq mi) | 6.54% | 120,000 km2 (46,000 sq mi) | 16.36% | 215,000 km2 (83,000 sq mi) | 29.31% | None | 0% |
| Total | 128,900 km2 (49,800 sq mi) | 17.57% | 141,400 km2 (54,600 sq mi) | 19.28% | 463,200 km2 (178,800 sq mi) | 63.15% | 733,500 km2 (283,200 sq mi) | 100% | ||
(Wandycz also offers slightly different total annexed territory estimates, with 18% for Austria, 20% for Prussia and 62% for Russia.)[13]
During the Napoleonic Wars and in their immediate aftermath the borders between partitioning powers shifted several times, changing the numbers seen in the preceding table. Ultimately, Russia ended up with most of the Polish core at the expense of Prussia and Austria. Following the Congress of Vienna, Russia controlled 82% of the pre-1772 Commonwealth's territory (this includes its puppet state of Congress Poland), Austria 11%, and Prussia 7%.[15]
Aftermath

"A map of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania including Samogitia and Curland divided according to their dismemberments with the Kingdom of Prussia" from 1799.
The King of Poland, Stanisław August Poniatowski, under Russian military escort left for Grodno where he abdicated on November 25, 1795; next he left for Saint Petersburg, Russia, where he would spend his remaining days. This act ensured that Russia would be seen as the most important of the partitioning powers.
As a result of the Partitions, Poles were forced to seek a change of status quo in Europe.[16][17] Polish poets, politicians, noblemen, writers, artists, many of whom were forced to emigrate (thus the term Great Emigration), became the revolutionaries of the 19th century, as desire for freedom became one of the defining parts of Polish romanticism.[18][19] Polish revolutionaries participated in uprisings in Prussia, the Austrian Empire and Imperial Russia.[20]Polish legions fought alongside Napoleon[21][22] and, under the slogan of For our freedom and yours, participated widely in the Spring of Nations (particularly the Hungarian Revolution of 1848).[20][23]
Poland would be briefly resurrected—if in a smaller frame—in 1807, when Napoleon set up the Duchy of Warsaw. After his defeat and the implementation of the Congress of Vienna treaty in 1815, the Russian-dominated Congress Kingdom of Poland was created in its place. After the Congress, Russia gained a larger share of Poland (with Warsaw) and, after crushing an insurrection in 1831, the Congress Kingdom's autonomy was abolished and Poles faced confiscation of property, deportation, forced military service, and the closure of their own universities. After the uprising of 1863, Russification of Polish secondary schools was imposed and the literacy rate dropped dramatically. In the Austrian portion, Poles fared better, and were allowed to have representation in Parliament and to form their own universities, and Kraków and Lemberg (Lwów/Lviv) became centers of Polish culture and education. Meanwhile, Prussia Germanized the entire school system of its Polish subjects, and had no more respect for Polish culture and institutions than the Russian Empire. In 1915 a client state of the German Empire and Austria-Hungary was proposed and accepted by the Central Powers of World War I: the Regency Kingdom of Poland. After the end of World War I, the Central Powers' surrender to the Western Allies, the chaos of the Russian Revolution and the Treaty of Versailles finally allowed and helped the restoration of Poland's full independence after 123 years.
"Fourth Partition"
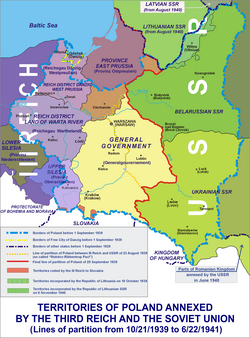
Partition of Poland according to the German–Soviet Pact; division of Polish territories in the years 1939–1941
The terminology describing the partitions of Poland can be somewhat confusing, as the first three partitions are sometimes used to refer to the three dates on which Poland was divided (1772, 1793, and 1795) and sometimes to the three geographic divisions (the German or Prussian partition, Austrian partition, and Russian partition). The term "Fourth Partition" has also been used in both a temporal and a spatial sense.
The term "Fourth Partition of Poland" may refer to any subsequent division of Polish lands, specifically:
- after the Napoleonic era, the 1815 division of the Duchy of Warsaw at the Congress of Vienna;
- the 1832 incorporation of the "Congress Kingdom" into Russia, the 1846 incorporation of the Republic of Kraków into Austria, and the 1848 incorporation of the Grand Duchy of Posen into Prussia; and
- the 1939 division of Poland between Germany and the Soviet Union pursuant to the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact.[24]
If one accepts more than one of those events as partitions, fifth and sixth partitions can be counted, but these terms are very rare.
The term "Fourth Partition" was also used in the 19th and 20th centuries to refer to diaspora communities who maintained a close interest in the project of regaining Polish independence.[25] Sometimes termed Polonia, these expatriate communities often contributed funding and military support to the project of regaining the Polish nation-state. Diaspora politics were deeply affected by developments in and around the homeland, and vice versa, for many decades.[26]
Historiography
More recent studies claim that partitions happened when the Commonwealth had been showing the beginning signs of a slow recovery and see the last two partitions as an answer to strengthening reforms in the Commonwealth and the potential threat they represented to its power-hungry neighbours.[17][27][28][29][30][31][32]
As historian Norman Davies stated, because the balance of power equilibrium was observed, many contemporary observers accepted explanations of the "enlightened apologists" of the partitioning state.[33][27] 19th-century historians from countries that carried out the partitions, such as 19th-century Russian scholar Sergey Solovyov, and their 20th century followers, argued that partitions were justified, as the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth had degenerated to the point of being partitioned because the counterproductive principle of liberum veto made decision-making on divisive issues, such as a wide-scale social reform, virtually impossible. Solovyov specified the cultural, language and religious break between the supreme and lowest layers of the society in the east regions of the Commonwealth, where the Belarusian and Ukrainian serf peasantry was Orthodox. Russian authors emphasized the historical connections between Belarus, Ukraine and Russia, as former parts of the medieval old Russian state where dynasty of Rurikids reigned (Kievan Rus').[34] Thus, Nikolay Karamzin wrote: "Let the foreigners denounce the partition of Poland: we took what was ours."[35] Russian historians often stressed that Russia annexed primarily Ukrainian and Belorussian provinces with Eastern Slavic inhabitants,[36] although many Ruthenians were no more enthusiastic about Russia than about Poland, and ignoring ethnically Polish and Lithuanian territories also being annexed later. A new justification for partitions arose with the Russian Enlightenment, as Russian writers such as Gavrila Derzhavin, Denis Fonvizin, and Alexander Pushkin stressed degeneration of Catholic Poland and the need to "civilize" it by its neighbors.[28]
Nonetheless other 19th century contemporaries were much more skeptical; for example, British jurist Sir Robert Phillimore discussed the partition as a violation of international law;[37] German jurist Heinrich Bernhard Oppenheim presented similar views.[38] Other older historians who challenged such justifications for the Partitions included French historian Jules Michelet, British historian and politician Thomas Babington Macaulay, and Edmund Burke.[27] Edmund Burke was alone in criticizing the immorality of this act.[39]
Several scholars focused on the economic motivations of the partitioning powers. Jerzy Czajewski wrote that the Russian peasants were escaping from Russia to the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth in significant enough numbers to become a major concern for the Russian Government sufficient to play a role in its decision to partition the Commonwealth.[40] Increasingly in the 18th century until the partitions solved this problem, Russian armies raided territories of the Commonwealth, officially to recover the escapees, but in fact kidnapping many locals.[40]Hajo Holborn noted that Prussia aimed to take control of the lucrative Baltic grain trade through Danzig (Gdańsk).[41]
Some scholars use the term 'sector' in reference to Commonwealth territories consisting of Polish (not Polish-Lithuanian) cultural heritage as well as historical monuments dating as far back as the first days of Poland's statehood.[42]
Other countries
The Ottoman Empire was one of only two countries in the world that refused to accept the partitions[43] and reserved a place in its diplomatic corps for an Ambassador of Lehistan (Poland).
Il Canto degli Italiani, the Italian National Anthem, contains a reference to the partition.[44]
The ongoing partitions of Poland were a major topic of discourse in The Federalist Papers, where the structure of the government of Poland, and of foreign influence over it, is used in several papers (Federalist No. 14, Federalist No. 19, Federalist No. 22, Federalist No. 39 for examples) as a cautionary tale for the writers of the U.S. Constitution.
See also
Administrative division of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth in the course of partitions- Administrative division of Polish–Lithuanian territories after partitions
Three Emperors' Corner at the border of the Russian, Austrian and the German Empire- Ambassadors and envoys from Russia to Poland (1763–1794)
Notes
^ Although the full name of the partitioned state was the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, while referring to the partitions, virtually all sources use the term Partitions of Poland, not Partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, as Poland is the common short name for the state in question. The term Partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth is effectively not used in literature on this subject.
References
^ abcdefghi "Partitions of Poland". Encyclopædia Britannica Online. 2008. Retrieved 8 June 2011..mw-parser-output cite.citationfont-style:inherit.mw-parser-output qquotes:"""""""'""'".mw-parser-output code.cs1-codecolor:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registrationcolor:#555.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration spanborder-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-errordisplay:none;font-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-errorfont-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-formatfont-size:95%.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-leftpadding-left:0.2em.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-rightpadding-right:0.2em
^ Bideleux, Robert; Jeffries, Ian (1998). A History of Eastern Europe: Crisis and Change. Routledge. p. 156.
^ Batt, Judy; Wolczuk, Kataryna (2002). Region, State and Identity in Central and Eastern Europe. Routledge. p. 153.
^ Sinkoff, Nancy (2004). Out of the Shtetl: Making Jews Modern in the Polish Borderlands. Society of Biblical Literature. p. 271.
^ abc Scott, Hamish M. (2001). The Emergence of the Eastern Powers, 1756–1775. Cambridge University Press. pp. 181–182. ISBN 0-521-79269-X.
^ H. Wickham Steed, A Short History of Austria-Hungary and Poland Archived 2007-09-24 at the Wayback Machine., 1914, Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. Retrieved on 3 August 2007.
^ abc Seton-Watson, Hugh (1967). The Russian Empire, 1801–1917. Oxford University Press. p. 44. ISBN 0-19-822152-5.
^ Various, The Story of My Life, Penguin Classics, 2001,
ISBN 0-14-043915-3, Google Print, p. 528
^ Butterwick, Richard (1998). Poland-Lithuania's Last King and English Culture: Stanisław August Poniatowski, 1732–1798. Oxford University Press. p. 169. ISBN 0-19-820701-8.
^ von Guttner, Darius (2015). The French Revolution. Nelson Cengage. p. 139.
^ Jerzy Lukowski; W. H. Zawadzki (2001). A Concise History of Poland: Jerzy Lukowski and Hubert Zawadzki. Cambridge University Press. pp. 96–98. ISBN 978-0-521-55917-1. Retrieved 8 January 2013.
^ Jerzy Lukowski; W. H. Zawadzki (2001). A Concise History of Poland: Jerzy Lukowski and Hubert Zawadzki. Cambridge University Press. pp. 101–103. ISBN 978-0-521-55917-1. Retrieved 8 January 2013.
^ ab Piotr Stefan Wandycz (2001). The Price of Freedom: A History of East Central Europe from the Middle Ages to the Present. Taylor & Francis Group. pp. 133–. ISBN 978-0-415-25490-8. Retrieved 8 January 2013.
^ Davies, Norman (2005). God's Playground. A History of Poland. The Origins to 1795. I (revised ed.). Oxford University Press. p. 394. ISBN 978-0-19-925339-5.
^ "Po przyłączeniu do obwodu białostockiego w 1807 roku do cesartwa i utworzeniu osiem lat później Królestwa Polskiego wnuk Katarzyny zjednoczył pod swoim berłem około 82% przedrozbiorowego terytorium Rzeczypospolitej (dla porównania – Austria 11%, Prusy 7%). "[in:] Basil Kerski, Andrzej Stanisław Kowalczyk. Realiści z wyobraźnią. Uniwersytet Marii Curie-Skłodowskiej. 2007 page. 318
ISBN 978-83-227-2620-4
^ Johnson, Lonnie R. (1996). Central Europe: Enemies, Neighbors, Friends. Oxford University Press. pp. 127–128. ISBN 0-19-510071-9.
^ ab Piotr Stefan Wandycz (2001). The Price of Freedom: A History of East Central Europe from the Middle Ages to the Present. Routledge. p. 133. ISBN 0-415-25491-4.
^ Zawadzki, W. H. (1993). A Man of Honour: Adam Czartoryski as a Statesman of Russia and Poland, 1795–1831. Oxford University Press. p. 330. ISBN 0-19-820303-9.
^ Auer, Stefan (2004). Liberal Nationalism in Central Europe. Routledge. p. 60. ISBN 0-415-31479-8.
^ ab Dowe, Dieter (2001). Europe in 1848: Revolution and Reform. Berghahn. p. 180. ISBN 1-57181-164-8.While it is often and quite justifiably remarked that there was hardly a barricade or battlefield in Europe between 1830 and 1870 where no Poles were fighting, this is especially true for the revolution of 1848/1849.
^ Pachonski, Jan; Wilson, Reuel K. (1986). Poland's Caribbean Tragedy: A Study of Polish Legions in the Haitian War of Independence 1802–1803. East European Monographs/Columbia University Press. ISBN 0-88033-093-7.
^ Fedosova, Elena I. (1998). "Polish Projects of Napoleon Bonaparte". Journal of the International Napoleonic Society.
^ Gods, Heroes, & Legends
^ Brecher, Michael; Wilkenfeld, Jonathan (1997). A Study of Crisis. University of Michigan Press. p. 255. ISBN 0-472-10806-9.
^ Cygan, Mary (1998). "Inventing Polonia: Notions of Polish American Identity, 1870–1990". Prospects. 23: 209–246.
^ Lopata, Helena Znaniecka (1994). Polish Americans. Transaction.
^ abc Norman Davies, Europe: A History, Oxford University Press, 1996,
ISBN 0-19-820171-0, Google Print, p.661
^ ab Nowak, Andrzej (1997). "The Russo-Polish Historical Confrontation". Sarmatian Review. XVII (1).
^ The Army of Grand Duchy of Warsaw Archived 2005-12-14 at the Wayback Machine.
^ Hon. Carl L. Bucki, University of Buffalo's History of Poland series, The Constitution of May 3, 1791 Archived December 5, 2008, at the Wayback Machine.
^ Paul W. Schroeder, The Transformation of European Politics 1763–1848, Oxford University Press, 1996,
ISBN 0-19-820654-2, Google print p.84
^ Geoffrey Russell, The Making of Modern Europe, 1648–1780, Routledge, 2003,
ISBN 0-415-30155-6, Google Print, p.548
^ Norman Davies, God's Playground: A History of Poland in Two Volumes, Oxford University Press, 2005,
ISBN 0-19-925339-0, Google Print, p.283
^ E.g., Sergey Solovyov's History of the Downfall of Poland (Moscow, 1863).
^ Н.М. Карамзин. Записка о древней и новой России в ее политическом и гражданском отношениях
^ Riasanovsky, Nicholas V. (1952). "Old Russia, the Soviet Union and Eastern Europe". American Slavic and East European Review. 11 (3): 171–188.
^ Sir Robert Phillimore, Commentaries Upon International Law, 1854, T. & J. W. Johnson, Google Print, p.819
^ Sharon Korman, The Right of Conquest: The Acquisition of Territory by Force in International Law and Practice, Oxford University Press, 1996,
ISBN 0-19-828007-6, Google Print, p.101
^ Poland The First Partition
^ ab Jerzy Czajewski, "Zbiegostwo ludności Rosji w granice Rzeczypospolitej" (Russian population exodus into the Rzeczpospolita), Promemoria journal, October 2004 nr. (5/15), ISSN 1509-9091, Table of Content online, Polish language
^ Hajo Holborn (1 December 1982). A History of Modern Germany: 1648–1840. Princeton University Press. p. 256. ISBN 978-0-691-00796-0. Retrieved 16 February 2012.
^ Nuria Sanz, Dominik Maczynski (2002). "The Prussian Sector In: Guidelines for a Common Inventory". Living Wooden Culture Throughout Europe. Council of Europe. p. 99. ISBN 9287148821. Retrieved 25 March 2013.
^ Prazmowska, Anita (2010). Poland: A Modern History. I. B. Tauris. p. 25.
^ "L'Inno nazionale". Quirinale.it. Retrieved 2013-11-17.
Further reading
- Lord, Robert. The second partition of Poland; a study in diplomatic history (1915) online
- Lukowski, Jerzy. The Partitions of Poland 1772, 1793, 1795 (1998); online review
- Lewitter, Lucjan R. "The Partitions of Poland" in A. Goodwyn, ed. The New Cambridge Modern History: vol 8 1763–93 (1965) pp 333–59
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Partitions of Poland. |
- Krzysztof Wroński, Rozbiory Polski w XVIII w. " ich uwarunkowania i skutki (in Polish)